- Manuals
- Brands
- Enraf Nonius Manuals
- Medical Equipment
- Endomed 482
Manuals and User Guides for Enraf Nonius Endomed 482. We have 3 Enraf Nonius Endomed 482 manuals available for free PDF download: Instructions For Use Manual, Operating Instructions Manual, Information Booklet

Endomed 482BedieningshandleidingOperating InstructionsGebrauchsanweisung
Mode d´emploiInstrucciones de manejo
Guía de usuario

Copyright: Enraf-Nonius B.V. P.O. Box 2600 AV DELFT The Netherlands Tel: +31 (0)15 – 26 98 400 Fax: +31 (0)15 – 25 61 686 [email protected] www.enraf-nonius.com Part number: 1497.759-40 October 2003

Endomed 482BedieningshandleidingOperating InstructionsGebrauchsanweisung
Mode d´emploiInstrucciones de manejo
Guía de usuario


INHOUDSOPGAVE TABLE OF CONTENTS INHALTSVERZEICHNIS TABLE DES MATIÈRES INDICE DE MATERIAS INDICE
1 Hoofdstuk 1 — Inleiding…………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 1.1 Algemeen ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 1.2 Therapiemogelijkheden…………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 1.3 Tot slot………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 1
2 Veiligheid…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 1 2.1 Opmerkingen vooraf……………………………………………………………………………………………… 1 2.2 Algemeen ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 2.3 Uitsluitingen…………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 2.4 Stroomdichtheid …………………………………………………………………………………………………… 1 2.5 Elektromagnetische interferentie ……………………………………………………………………………. 2 2.6 Productaansprakelijkheid………………………………………………………………………………………. 2
3 Indicaties en contra-indicaties……………………………………………………………………………………… 2 3.1 Indicaties …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 2 3.2 Therapeutisch handelen:……………………………………………………………………………………….. 2 3.3 Contra-indicaties (elektrotherapie)………………………………………………………………………….. 3
4 Installatie …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 3 4.1 Aansluiten …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3 4.2 Aansluiten lichtnetadapter……………………………………………………………………………………… 3 4.3 Aanzetten en zelftest…………………………………………………………………………………………….. 3 4.4 Ontkoppelen van het lichtnet …………………………………………………………………………………. 3 4.5 Werken op batterij (optioneel) ………………………………………………………………………………… 3 4.6 Installatie …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 4 4.7 Elektromagnetische interferentie ……………………………………………………………………………. 4
5 Bediening ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 4 5.1 Bedieningsorganen ………………………………………………………………………………………………. 4
5.1.1 Apparaat ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….4 5.1.2 Bedieningspaneel …………………………………………………………………………………………………..4
5.2 Bediening ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 5 5.2.1 Inleiding ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..5 5.2.1.1 Inschakelen van het apparaat…………………………………………………………………………………………………. 5 5.2.1.2 Therapievorm en kanaalselectie……………………………………………………………………………………………… 6 5.2.1.3 Selectie van stroomvorm ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 6 5.2.1.4 Instellen van parameters………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6 5.2.1.5 Behandeltijd …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.6 Zwelprogramma……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.7 Stroomintensiteit …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6 5.2.1.8 CC/CV instelling……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 7 5.2.1.9 Polariteit ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 7 5.2.1.10 Noodstop……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 7 5.2.2 Elektrotherapie……………………………………………………………………………………………………….7 5.2.2.1 Bipolaire interferentie …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 7 5.2.2.2 Onderbroken wisselstroom (Russische stimulatie) …………………………………………………………………….. 7 5.2.2.3 Asymmetrische en symmetrische bifasische pulsstromen (TENS) ………………………………………………. 8 5.2.2.4 Faradische rechthoek- of driehoekstromen ………………………………………………………………………………. 9 5.2.2.5 Microcurrent …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 9 5.2.2.6 High voltage ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 10 5.2.2.7 Diadynamische stromen ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 10 5.2.2.8 Onderbroken gelijkstroom…………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 11 5.2.2.9 Interferentie (klassiek)………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 11 5.2.2.10 Isoplanaire vector………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 11 5.2.2.11 Dipool vector manueel ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 11 5.2.2.12 Dipool vector automatisch…………………………………………………………………………………………………… 12
5.3 Maatregelen met betrekking tot behandelingen………………………………………………………. 12 5.3.1 Elektrotherapie……………………………………………………………………………………………………..12
5.4 Bediening van het geheugen ……………………………………………………………………………….. 12 5.4.1 Apparaatinstellingen ……………………………………………………………………………………………..12 5.4.1.1 Apparaatinstelling oproepen …………………………………………………………………………………………………. 12 5.4.1.2 Apparaatinstelling opslaan……………………………………………………………………………………………………. 12 5.4.2 Protocollen …………………………………………………………………………………………………………..13 5.4.2.1 Protocol oproepen……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 13 5.4.2.2 Protocol opslaan …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 14 5.4.2.3 Protocol samenstellen………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 14
5.5 Openings- en sluitingsreacties……………………………………………………………………………… 14 5.6 Elektrolytische effecten ……………………………………………………………………………………….. 14 5.7 Afstandsbediening………………………………………………………………………………………………. 14
NL
F
GB
E
D
I

6 Onderhoud………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….15 6.1 Technisch onderhoud …………………………………………………………………………………………..15 6.2 Reinigen van het apparaat ……………………………………………………………………………………15 6.3 Reinigen van de accessoires…………………………………………………………………………………15
6.3.1 Elektroden en sponsjes………………………………………………………………………………………….15 6.3.2 Patiëntenkabel ……………………………………………………………………………………………………..15
6.4 Einde levensduur apparaat en toebehoren ……………………………………………………………..15 7 Aanwijzingen bij storingen ………………………………………………………………………………………….15
7.1 Displays lichten niet op…………………………………………………………………………………………15 7.2 Foutcode…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….16 7.3 Verbroken contact in de CC-mode …………………………………………………………………………16 7.4 Geen of onvoldoende uitgangsstroom…………………………………………………………………….16 7.5 Controle bedieningspaneel……………………………………………………………………………………16
8 Specificaties ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….16 8.1 Productspecificaties……………………………………………………………………………………………..16 8.2 Technische specificaties……………………………………………………………………………………….18 8.3 Classificatie…………………………………………………………………………………………………………18
9 Bestelgegevens…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..19 1 Introduction ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….1
1.1 General ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..1 1.2 Therapy possibilities ………………………………………………………………………………………………1 1.3 Finally…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..1
2 Safety …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..1 2.1 Preliminary notes …………………………………………………………………………………………………..1 2.2 General ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..1 2.3 Exclusions…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….1 2.4 Current density ……………………………………………………………………………………………………..1 2.5 Electromagnetic interference…………………………………………………………………………………..2 2.6 Limitations of liability………………………………………………………………………………………………2
3 Indications and Contra-Indications………………………………………………………………………………..2 3.1 Indications…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….2
3.1.1 Electro therapy……………………………………………………………………………………………………….2 3.2 Absolute specific contra-indications …………………………………………………………………………3
3.2.1 Electro therapy……………………………………………………………………………………………………….3 4 Installation ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………3
4.1 Connection……………………………………………………………………………………………………………3 4.2 Connection of the mains adapter……………………………………………………………………………..3 4.3 Switching on and self test ……………………………………………………………………………………….3 4.4 Disconnecting from the mains …………………………………………………………………………………3 4.5 Battery operation (optional) …………………………………………………………………………………….3 4.6 Installation…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….4 4.7 Electromagnetic interference…………………………………………………………………………………..4
5 Operation ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..4 5.1 Controls ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….4
5.1.1 Device …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..4 5.1.2 Control panel………………………………………………………………………………………………………….4
5.2 Operating the apparatus…………………………………………………………………………………………5 5.2.1 Introduction ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………5 5.2.1.1 Switch on the apparatus ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 5 5.2.1.2 Therapy and channel selection……………………………………………………………………………………………….. 5 5.2.1.3 Selection of current waveform ………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6 5.2.1.4 Adjusting parameters…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 6 5.2.1.5 Treatment timer ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.6 Surge programs ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.7 Current intensity……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.8 CC/CV mode………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6 5.2.1.9 Current polarity …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 7 5.2.1.10 Emergency stop………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 7 5.2.2 Electrotherapy………………………………………………………………………………………………………..7 5.2.2.1 2-pole interferential current (premodulated) ……………………………………………………………………………… 7 5.2.2.2 Russian stimulation……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 7 5.2.2.3 Asymmetrical and Symmetrical biphasic pulsed current (TENS) ………………………………………………… 8 5.2.2.4 Monophasic rectangular –and triangular pulsed current …………………………………………………………….. 8 5.2.2.5 Microcurrent…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 9 5.2.2.6 High voltage…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 9 5.2.2.7 Diadynamic currents ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 10 5.2.2.8 Medium frequency interrupted direct current …………………………………………………………………………… 10

5.2.2.9 4-pole interferential current (classical) ……………………………………………………………………………………. 11 5.2.2.10 Isoplanar vector ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 11 5.2.2.11 Dipole vector manual …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 11 5.2.2.12 Dipole vector automatic ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… 12
5.3 Measures with regard to treatments ……………………………………………………………………… 12 5.3.1 Electrotherapy………………………………………………………………………………………………………12 5.3.1.1 Before treatment …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 12
5.4 Memory functions……………………………………………………………………………………………….. 12 5.4.1.1 Loading a protocol ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 13 5.4.1.2 Storing a protocol………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 13 5.4.1.3 Creating a user defined protocol……………………………………………………………………………………………. 13
5.5 Connection and disconnection reactions ……………………………………………………………….. 14 5.6 Electrolytic effects ………………………………………………………………………………………………. 14 5.7 Remote control…………………………………………………………………………………………………… 14
6 Maintenance………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 14 6.1 Technical maintenance ……………………………………………………………………………………….. 14 6.2 Cleaning of the apparatus……………………………………………………………………………………. 14 6.3 Cleaning of accessories ………………………………………………………………………………………. 14
6.3.1 Electrodes and sponge pads…………………………………………………………………………………..14 6.3.2 Patient cable ………………………………………………………………………………………………………..15
6.4 Environment information ……………………………………………………………………………………… 15 7 Diagnostics ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 15
7.1 Displays fail to light up ………………………………………………………………………………………… 15 7.2 Error code …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 15 7.3 Broken contact in the CC-mode……………………………………………………………………………. 15 7.4 Insufficient or no output current ……………………………………………………………………………. 15 7.5 Front panel check……………………………………………………………………………………………….. 15
8 Specifications ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 16 8.1 Specifications …………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 16 8.2 Technical specifications ………………………………………………………………………………………. 18 8.3 Classification ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… 18
9 Order detail ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 18 1 Einleitung ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1
1.1 Allgemein ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 1.2 Umfassende Therapie…………………………………………………………………………………………… 1 1.3 Abschließend ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1
2 Sicherheit ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 2.1 Einführung…………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 1 2.2 Allgemeines…………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 2.3 Ausschlüsse ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 1 2.4 Stromdichte …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 2.5 Elektromagnetische Interferenz ……………………………………………………………………………… 2 2.6 Produkthaftung…………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 2
3 Indikationen und Kontraindikationen……………………………………………………………………………. 2 3.1 Indikationen…………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 2 3.2 Absolute spezifische Kontraindikationen …………………………………………………………………. 3
4 Installation…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3 4.1 Anschluß …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 3 4.2 Anschluß des Stromversorgungsgerätes…………………………………………………………………. 3 4.3 Einschalten und Selbsttest…………………………………………………………………………………….. 3 4.4 Gerät von der Netzstromversorgung trennen …………………………………………………………… 3 4.5 Batteriebetrieb (optional)……………………………………………………………………………………….. 3 4.6 Geräteaufstellung…………………………………………………………………………………………………. 4 4.7 Elektromagnetische Interferenz ……………………………………………………………………………… 4
5 Bedienung…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 4 5.1 Bedienungsorganen……………………………………………………………………………………………… 4
5.1.1 Gerät …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….4 5.2 Bedienung des Gerätes ………………………………………………………………………………………… 6
5.2.1 Einleitung ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………6 5.2.1.1 Anschalten des Gerätes…………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.2 Wahl der Therapie und Kanäle ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. 6 5.2.1.3 Wahl der Stromform………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.4 Wahl und Einstellung der Parameter ……………………………………………………………………………………….. 6 5.2.1.5 Einstellen der Uhr …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.6 Trainingsdurchlauf ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6

5.2.1.7 Einstellen der Stromstärke……………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6 5.2.1.8 CC/CV Einstellung ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 7 5.2.1.9 Einstellung der Polarität…………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 7 5.2.1.10 Notstop ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 7 5.2.2 Elektrotherapie……………………………………………………………………………………………………….7 5.2.2.1 Bipolare Interferenz ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 7 5.2.2.2 „Russian stimulation“ Unterbrochener Mittelfrequenz-Wechselstrom……………………………………………. 8 5.2.2.3 Asymmetrischer und symmetrischer biphasischer Impuls (TENS)……………………………………………….. 8 5.2.2.4 Monophasischer Rechteck- und Dreieckimpulsstrom…………………………………………………………………. 9 5.2.2.5 Microcurrent…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 9 5.2.2.6 Hoch Volt (Hochspannung)…………………………………………………………………………………………………… 10 5.2.2.7 Diadynamische Ströme……………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 10 5.2.2.8 Mittelfrequenter unterbrochener Direktstrom…………………………………………………………………………… 11 5.2.2.9 Klassische Interferenz …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 11 5.2.2.10 Isoplanarer Vektor …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 11 5.2.2.11 Manueller Dipol-Vektor ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 12 5.2.2.12 Automatischer Dipol-Vektor ………………………………………………………………………………………………… 12
5.3 Vorkehrungen für die Behandlungen………………………………………………………………………12 5.3.1 Vor der Behandlung ………………………………………………………………………………………………12
5.4 Speicherfunktionen………………………………………………………………………………………………13 5.4.1 Geräteeinstellungen………………………………………………………………………………………………13 5.4.1.1 Laden von Geräteeinstellungen…………………………………………………………………………………………….. 13 5.4.1.2 Speichern von Geräteeinstellungen:………………………………………………………………………………………. 13 5.4.2 Protokolle …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….13 5.4.2.1 Laden eines Protokolls ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 13 5.4.2.2 Speichern eines Protokolls …………………………………………………………………………………………………… 14 5.4.2.3 Erstellung eines benutzerdefinierten Protokolls……………………………………………………………………….. 14
5.5 Öffnungs- und Schließreaktionen …………………………………………………………………………..15 5.6 Elektrolytische Wirkungen …………………………………………………………………………………….15 5.7 Fernbedienung…………………………………………………………………………………………………….15
6 Wartung………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………15 6.1 Technische Wartung…………………………………………………………………………………………….15 6.2 Reinigung von Gehäuse ……………………………………………………………………………………….15 6.3 Reinigung und Desinfektion von Zubehör ……………………………………………………………….15
6.3.1 Elektroden und Schwämme ……………………………………………………………………………………15 6.3.2 Patientenleitung und Kabeladapter ………………………………………………………………………….16
6.4 Entsorgen von Gerät und Zubehör …………………………………………………………………………16 7 Diagnose…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….16
7.1 Anzeigen leuchten nicht………………………………………………………………………………………..16 7.2 Fehlercode………………………………………………………………………………………………………….16 7.3 Unterbrochener Kontakt im CC-Modus …………………………………………………………………..16 7.4 Kein oder unzureichender Ausgangsstrom ……………………………………………………………..16 7.5 Kontrolle des Bedienfelds……………………………………………………………………………………..16
8 Spezifikationen……………………………………………………………………………………………………………17 8.1 Produkt Spezifikationen………………………………………………………………………………………..17 8.2 Technische Daten………………………………………………………………………………………………..18 8.3 Einstufung…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..19
9 Bestelldaten………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..19 1 Introduction ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….1
1.1 Généralités …………………………………………………………………………………………………………..1 1.2 Possibilités thérapeutiques……………………………………………………………………………………..1 1.3 En Conclusion……………………………………………………………………………………………………….1
2 Sécurité ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..1 2.1 Remarques préalables……………………………………………………………………………………………1 2.2 Sécurité………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..1 2.3 Exclusions…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….1 2.4 Densité de courant…………………………………………………………………………………………………1 2.5 Interférences électromagnétiques ……………………………………………………………………………2 2.6 Responsabilité du fabricant …………………………………………………………………………………….2
3 Indications et Contre-indications…………………………………………………………………………………..2 3.1 Indications…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….2
3.1.1 Électrothérapie……………………………………………………………………………………………………….2 3.2 Contre-indications électrothérapie……………………………………………………………………………3
4 Installation ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………3 4.1 Raccordements……………………………………………………………………………………………………..3 4.2 Connexion de l’adaptateur secteur…………………………………………………………………………..3 4.3 Mettre en marche et autotest…………………………………………………………………………………..3

4.4 Déconnexion du réseau ………………………………………………………………………………………… 3 4.5 Utilisation sur batterie (optionnel) …………………………………………………………………………… 3 4.6 Installation …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 4 4.7 Interférences électromagnétiques…………………………………………………………………………… 4
5 Service………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 4 5.1 Eléments d’utilisation ……………………………………………………………………………………………. 4
5.1.1 Appareil…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………4 5.2 Réglage de l’appareil ……………………………………………………………………………………………. 5
5.2.1 Introduction ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………5 5.2.1.1 Mise en route de l’appareil……………………………………………………………………………………………………… 5 5.2.1.2 Type de thérapie et sélection des canaux ………………………………………………………………………………… 5 5.2.1.3 Sélection du type de courant ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 6 5.2.1.4 Définition et modification des paramètres…………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.5 Réglage de la minuterie. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6 5.2.1.6 Programme d’entraînement ……………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.7 Instauration de l’ intensité ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.8 Paramètres CC/CV ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 6 5.2.1.9 Polarité………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6 5.2.1.10 Arrêt d’urgence. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 7 5.2.2 Électrothérapie……………………………………………………………………………………………………….7 5.2.2.1 Interférence bipolaire …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 7 5.2.2.2 Courant alternatif interrompu (Stimulation Russe)……………………………………………………………………… 7 5.2.2.3 Courants pulsés biphasés asymétrique et symétrique (TENS) ……………………………………………………. 8 5.2.2.4 Courants Faradiques rectangulaires ou triangulaires …………………………………………………………………. 8 5.2.2.5 Microcurrent …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 9 5.2.2.6 High voltage …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 9 5.2.2.7 Courant dia dynamique………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 10 5.2.2.8 Courant continu interrompu ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 11 5.2.2.9 Interférence (classique) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 11 5.2.2.10 Vecteur isoplanaire ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 11 5.2.2.11 Vecteur dipôle manuel ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 11 5.2.2.12 Vecteur dipôle automatique ………………………………………………………………………………………………… 12
5.3 Mesures propres aux traitements …………………………………………………………………………. 12 5.3.1 Électrothérapie……………………………………………………………………………………………………..12
5.4 Utilisation de la mémoire……………………………………………………………………………………… 12 5.4.1 Paramètres de l’appareil ………………………………………………………………………………………..12 5.4.1.1 Appel des paramètres de l’appareil ……………………………………………………………………………………….. 12 5.4.1.2 Sauvegarde des paramètres…………………………………………………………………………………………………. 13 5.4.2 Protocoles ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………13 5.4.2.1 Rappel d’un protocole ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 13 5.4.2.2 Sauvegarde d’un protocole …………………………………………………………………………………………………… 14 5.4.2.3 Composition d’un protocole ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 14
5.5 Réactions à l’ouverture et à la fermeture ……………………………………………………………….. 14 5.6 Effets électrolytiques …………………………………………………………………………………………… 14 5.7 Commande à distance ………………………………………………………………………………………… 14
6 Entretien ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 15 6.1 Entretien technique …………………………………………………………………………………………….. 15 6.2 Nettoyage de l’appareil ……………………………………………………………………………………….. 15 6.3 Nettoyage des accessoires………………………………………………………………………………….. 15
6.3.1 Electrodes et éponges …………………………………………………………………………………………..15 6.3.2 Câble de patient et câble adaptateur ……………………………………………………………………….15
6.4 Informations pour l’environnement………………………………………………………………………… 15 7 Conseil en cas de pannes ………………………………………………………………………………………….. 16
7.1 L’écran ne s’éclaire pas ………………………………………………………………………………………. 16 7.2 Le cadran affiche un numéro (ou code) …………………………………………………………………. 16 7.3 Rupture de contact dans la mode CC……………………………………………………………………. 16 7.4 Pas ou pas assez de courant de sortie………………………………………………………………….. 16 7.5 Contrôle du panneau de commande……………………………………………………………………… 16
8 Spécificités………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 16 8.1 Spécificités ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 16
9 Données de commande ……………………………………………………………………………………………… 19 1 Introducción………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 1
1.1 General……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 1 1.2 Posibilidades de terapia………………………………………………………………………………………… 1 1.3 Finalmente ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 1
2 Seguridad……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 2.1 Notas preliminares ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. 1 2.2 General……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 1 2.3 Exclusiones …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1

2.4 Densidad de corriente…………………………………………………………………………………………….1 2.5 Interferencia electromagnética ………………………………………………………………………………..2 2.6 Limitación de responsabilidad …………………………………………………………………………………2
3 Indicaciones y Contra-indicaciones ………………………………………………………………………………2 3.1 Indicaciones………………………………………………………………………………………………………….2
3.1.1 Electroterapia…………………………………………………………………………………………………………2 3.2 Contraindicaciones específicas absolutas…………………………………………………………………3
3.2.1 Electroterapia…………………………………………………………………………………………………………3 4 Instalación ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………3
4.1 Conexión………………………………………………………………………………………………………………3 4.2 Conexión del adaptador de red ……………………………………………………………………………….3 4.3 Encendido y auto test …………………………………………………………………………………………….3 4.4 Desconectar de la red…………………………………………………………………………………………….3 4.5 Funcionamiento con bateria (opcional) …………………………………………………………………….3 4.6 Instalación…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….4 4.7 Interferencia Electromagnética………………………………………………………………………………..4
5 Operación …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….4 5.1 Controles ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..4
5.1.1 Aparato …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………4 5.1.2 Panel de control ……………………………………………………………………………………………………..5
5.2 Funcionamiento de la unidad ………………………………………………………………………………….6 5.2.1 Introduccion …………………………………………………………………………………………………………..6 5.2.1.1 Encender el aparato ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6 5.2.1.2 Terapia y selección de canal ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 6 5.2.1.3 Selección de corriente en forma de onda…………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.4 Ajuste de parámetros…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 6 5.2.1.5 Tiempo de tratamiento…………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6 5.2.1.6 Programas de sobre corriente ………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6 5.2.1.7 Intensidad de corriente ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 6 5.2.1.8 Modo CC/CV………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 7 5.2.1.9 Polaridad de corriente……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 7 5.2.1.10 Parada de Emergencia. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 7 5.2.2 Electroterapia. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………..7 5.2.2.1 Interferencia de dos-polos ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… 7 5.2.2.2 Estimulación Rusa ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 8 5.2.2.3 Corriente pulsada bifásico Asimétrica y Simétrica (TENS)………………………………………………………….. 8 5.2.2.4 Corriente pulsada Triangular –y monofásica rectangular ……………………………………………………………. 9 5.2.2.5 Micro corriente ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 9 5.2.2.6 Voltaje alto …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 10 5.2.2.7 Corrientes Diadinamicas………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 10 5.2.2.8 Corriente directa interrumpida de frecuencia — media……………………………………………………………….. 11 5.2.2.9 Interferencia (clásica) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 11 5.2.2.10 Vector isoplanar………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 11 5.2.2.11 Vector manual dipolar………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 12 5.2.2.12 Vector dipolar automático …………………………………………………………………………………………………… 12
5.3 Medidas con respecto a tratamientos……………………………………………………………………..12 5.3.1 Electroterapia……………………………………………………………………………………………………….12
5.4 Funciones de memoria …………………………………………………………………………………………12 5.4.1 Ajustes de equipo………………………………………………………………………………………………….13 5.4.1.1 Carga de ajustes de equipo………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 13 5.4.1.2 Almacenamiento de ajustes de equipo…………………………………………………………………………………… 13 5.4.2 Protocolos ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………13 5.4.2.1 Carga de un protocolo …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 13 5.4.2.2 Guardar un protocolo…………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 14 5.4.2.3 Creación de un protocolo definido por el usuario …………………………………………………………………….. 14
5.5 Reacciones al conectar y desconectar……………………………………………………………………14 5.6 Efectos electrolíticos…………………………………………………………………………………………….15 5.7 Control remoto …………………………………………………………………………………………………….15
6 Mantenimiento por el usuario………………………………………………………………………………………15 6.1 Mantenimiento técnico………………………………………………………………………………………….15 6.2 Limpieza del aparato ……………………………………………………………………………………………15 6.3 Limpieza de los accesorios …………………………………………………………………………………..15
6.3.1 Electrodos y esponjas ……………………………………………………………………………………………15 6.3.2 Cable del paciente ………………………………………………………………………………………………..15
6.4 Duración de vida del aparato y accesorios………………………………………………………………16 7 Diagnóstico…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………16
7.1 Las luces y pantallas no se encienden……………………………………………………………………16 7.2 Código de Error …………………………………………………………………………………………………..16 7.3 Contacto roto en modo CC……………………………………………………………………………………16 7.4 Falta de corriente (insuficiente) ……………………………………………………………………………..16

7.5 Comprobación de panel frontal …………………………………………………………………………….. 16 8 Especificaciones ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 16
8.1 Especificaciones del producto ……………………………………………………………………………… 16 8.2 Especificaciones técnicas ……………………………………………………………………………………. 18 8.3 Clasificación ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 19
9 Datos de pedido ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 19 1 Introduzione………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 1
1.1 Generalità……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 1.2 Possibilità terapeutiche …………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 1.3 Conclusioni………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 1
2 Sicurezza…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 1 2.1 Note preliminari ……………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 2.2 Generalità……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 1 2.3 Campi di non applicazione…………………………………………………………………………………….. 1 2.4 Densità di corrente ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. 1 2.5 Interferenza elettromagnetica ………………………………………………………………………………… 2 2.6 Limiti di responsabilità…………………………………………………………………………………………… 2
3 Indicazioni e controindicazioni …………………………………………………………………………………….. 2 3.1 Indicazioni …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2
3.1.1 Elettroterapia………………………………………………………………………………………………………….2 3.2 Controindicazioni specifiche assolute ……………………………………………………………………… 3
3.2.1 Elettroterapia………………………………………………………………………………………………………….3 4 Installazione………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3
4.1 Collegamento ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 3 4.2 Collegamento dell’adattatore di rete ……………………………………………………………………….. 3 4.3 Accensione e auto diagnosi di controllo…………………………………………………………………… 3 4.4 Scollegamento dalla rete……………………………………………………………………………………….. 3 4.5 Funzionamento a batterie (opzionale) …………………………………………………………………….. 3 4.6 Installazione ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 4 4.7 Interferenza elettromagnetica ………………………………………………………………………………… 4
5 Funzionamento……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 4 5.1 Controlli ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 4
5.1.1 Apparecchio …………………………………………………………………………………………………………..4 5.2 Funzionamento dell’apparecchio ……………………………………………………………………………. 5
5.2.1 Introduzione …………………………………………………………………………………………………………..5 5.2.1.1 Accensione ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 5 5.2.1.2 Selezione della terapia e del canale ………………………………………………………………………………………… 5 5.2.1.3 Selezione delle forme di corrente ……………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.4 Regolazione dei parametri ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6 5.2.1.5 Timer trattamento………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 6 5.2.1.6 Programmi modulazione corrente……………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.7 Intensità di corrente ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6 5.2.1.8 Modo CC/CV………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 7 5.2.1.9 Polarità di corrente………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 7 5.2.1.10 Stop di emergenza………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 7 5.2.2 Elettroterapia………………………………………………………………………………………………………….7 5.2.2.1 Corrente interferenziale a 2 poli (premodulata) …………………………………………………………………………. 7 5.2.2.2 Stimolazione russa………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 8 5.2.2.3 Corrente pulsata bifasica simmetrica e asimmetrica (TENS) ………………………………………………………. 8 5.2.2.4 Corrente pulsata monofasica rettangolare e triangolare……………………………………………………………… 9 5.2.2.5 Microcorrente ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 9 5.2.2.6 Alta tensione ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 10 5.2.2.7 Correnti diadinamiche ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 10 5.2.2.8 Corrente continua interrotta a media frequenza ………………………………………………………………………. 11 5.2.2.9 Corrente interferenziale a 4 poli (classica) ……………………………………………………………………………… 11 5.2.2.10 Vettore isoplanare……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 11 5.2.2.11 Vettore dipolo manuale ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 12 5.2.2.12 Selezionare con il regolatore centrale [16] e premer il tasto [14] per confermare; ………………… 12 5.2.2.13 Vettore dipolo automatico …………………………………………………………………………………………………… 12
5.3 Precauzioni in relazione ai trattamenti …………………………………………………………………… 12 5.3.1 Elettroterapia………………………………………………………………………………………………………..12
5.4 Funzioni di memoria……………………………………………………………………………………………. 12 5.4.1 Programmi dell’unità ……………………………………………………………………………………………..13 5.4.1.1 Caricamento dei programmi………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 13 5.4.1.2 Memorizzazione dei programmi…………………………………………………………………………………………….. 13 5.4.2 Protocolli ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..13 5.4.2.1 Caricamento di un protocollo ………………………………………………………………………………………………… 13 5.4.2.2 Memorizzare un protocollo……………………………………………………………………………………………………. 14 5.4.2.3 Creare un protocollo personalizzato ………………………………………………………………………………………. 14

5.5 Reazioni al collegamento — scollegamento degli elettrodi ………………………………………….14 5.6 Effetti elettrolitici…………………………………………………………………………………………………..15 5.7 Telecomando ………………………………………………………………………………………………………15
6 Manutenzione ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..15 6.1 Manutenzione tecnica…………………………………………………………………………………………..15 6.2 Pulizia dell’apparecchio ………………………………………………………………………………………..15 6.3 Pulizia degli accessori ………………………………………………………………………………………….15
6.3.1 Elettrodi e spugnette ……………………………………………………………………………………………..15 6.3.2 Cavo paziente ………………………………………………………………………………………………………15
6.4 Informazioni ambientali…………………………………………………………………………………………16 7 Diagnostica…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………16
7.1 Display che non si illumina ……………………………………………………………………………………16 7.2 Codice errore ………………………………………………………………………………………………………16 7.3 Contatto interrotto nel modulo CC………………………………………………………………………….16 7.4 Assenza totale o parziale di corrente in uscita …………………………………………………………16 7.5 Controllo del pannello frontale……………………………………………………………………………….16
8 Caratteristiche…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….16 8.1 Caratteristiche……………………………………………………………………………………………………..16 8.2 Caratteristiche tecniche ………………………………………………………………………………………..18 8.3 Classificazione…………………………………………………………………………………………………….19
9 Dati per l’ordinazione ………………………………………………………………………………………………….19 1 Figuren – Pictures – Abbildungen – Image – Imagen — Immagine ………………………………….21

1
E
1 Introducción 1.1 General El Endomed 482 está equipado con dos canales completos de electroterapia idénticos multi- funcionales. Los canales de electroterapia pueden estar en combinación o totalmente independientes. El canal de electroterapia restante puede mientras tanto ser usado independientemente. Estas oportunidades de la gran cantidad posible de corrientes disponibles hacen a esta unidad la solución última para sus fines profesionales. Los equipos presentados en estas instrucciones de manejo han sido diseñados para ser usados sólo por personal especializado en fisioterapia, rehabilitación y/o disciplinas afines. 1.2 Posibilidades de terapia Electroterapia con baja frecuencia, media frecuencia, TENS, alto voltaje y micro-corriente. Mediante la aplicación de estas corrientes es posible entre otros, disminuir el tono muscular, gestionar el dolor y aumentar la circulación y la regeneración del tejido. 1.3 Finalmente Usted ha hecho una gran elección al seleccionar el Endomed 482. Estamos seguros que su unidad continuará satisfaciéndole durante muchos años de uso. Sin embargo, si tiene cualquier duda o sugerencias, por favor contacte con su distribuidor.
2 Seguridad 2.1 Notas preliminares Es importante leer detenidamente estas instrucciones de manejo antes de usar el Endomed 482. Asegúrese por favor que éstas instrucciones están disponibles para todo el personal que trabaja con el equipo. Prestar atención a lo siguiente antes de usar el Endomed 482 : 1. Mantenerse informado de las contra-indicaciones (ver capitulo 3). 2. El aparato no debe usarse cuando haya cerca un equipo de onda corta (ej. a menos de 2 metros). 3. El paciente debe estar siempre a la vista del fisioterapeuta. 4. El aparato no debe usarse en las llamadas “salas húmedas” (salas de hidroterapia). El fabricante no se hace responsable de los resultados por uso indebido del aparato o por cualquier otro fin que no sea el descrito en estas instrucciones de manejo. 2.2 General Cuando se enciende la unidad todas las funciones vitales son controladas por un microprocesador interno. Durante el funcionamiento de la unidad, la salida de corriente actual es continuamente medida y comparada a la solicitada. Si se detecta una situación de fallo, la unidad se desconectará de la corriente inmediatamente. 2.3 Exclusiones No se debe usar la electroterapia para las aplicaciones siguientes: • Tratamiento intercraneales, como terapia de sueño; • Tratamiento transcordiales (poner los electrodos sobre el pecho puede aumentar el riesgo al
corazón); • Tratamiento occipital cervical. 2.4 Densidad de corriente La norma IEC 60601-2-10 avisa no aplicar una densidad de corriente mayor de 2 mA efectivo. Se puede calcular la máxima corriente de paciente y efectiva para cada electrodo, con multiplicar la superficie de contacto (en cm²) por 2 mA/cm². Cuidar que los electrodos están colocados de tal manera, que hay buen contacto con la piel en toda la superficie.

2
E
NB. Usando electrodos pequeños en combinación con una amplitud alta puede tener como efectos irritaciones de la piel o aún quemaduras. 2.5 Interferencia electromagnética La conexión simultánea de un paciente al Endomed 482 y los aparatos de frecuencia alta puede causar quemaduras en el sitio de los electrodos estimulantes. Vea el Capitulo 4 para más informaciones. 2.6 Limitación de responsabilidad El máximo permitido y aplicable por ley, en ningún caso Enraf-Nonius o sus proveedores o distribuidores serán responsables por cualquier daño indirecto, especial, incidental o consecuencial que se produzca por el uso o inhabilidad para usar el producto, incluyendo, sin limitación, daños por pérdida de buena voluntad, trabajo y productividad, fallo de ordenador o mal funcionamiento, o cualquier otro daño comercial o pérdidas, incluso si se avisa de esa posibilidad, y sin tener en cuenta los términos legales o la teoría de equidad (contrato, agravio u otra cosa) en la que se basa la demanda. En cualquier caso, la responsabilidad integra de Enraf-Nonius bajo cualquier provisión de este acuerdo no excederá de la suma total del precio pagado por este producto o el precio para el apoyo del producto recibido por Enraf-Nonius bajo un acuerdo de apoyo comercial (si los hay), con la excepción de muerte o daño personal causado por negligencia de Enraf-Nonius aplicable a la ley que prohíbe la limitación de daños en tales casos. Enraf-Nonius no puede mantener la responsabilidad por cualquier consecuencia resultante de la información incorrecta suministrada por su personal, o errores incluídos en este manual y / o en otra documentación acompañada (incluida documentación comercial) La parte contraria (el usuario del producto o sus representantes) descargará a Enraf-Nonius de cualquier queja originada por terceras partes, cualquiera que sea la naturaleza o cualquiera que sea la relación con la parte contraria.
3 Indicaciones y Contra-indicaciones Consultar también los manuales de terapia opcionales con el aparato. 3.1 Indicaciones
3.1.1 Electroterapia Diagnóstico, electropalpación para: • puntos dolorosos; • puntos desencadenantes; • áreas hiperestéticas; • puntos de estimulación motora; • curva I/t La terapia: A. Reducción del dolor en: • puntos dolorosos; • puntos desencadenantes; • áreas hiperestéticas. B. Trastornos del sistema vegetativo, como: • el síndrome hombro-mano; • la enfermedad de Raynaud; • la enfermedad de Buerger; • la distrofia de Sudeck; • con trastornos neurológicos; • mialgias C. Estimulación muscular: • para restablecer la sensación de movimiento; • después de atrofia; • de los esfínteres internos y externos en el tratamiento de incontinencia fecal;

3
E
• en rehabilitación; • para fortalecimiento muscular (deportes); • con trastornos neurológicos. D. Iontoforesis. E. Cicatrización: • defectos cutáneos a causa de trastornos de la circulación periférica; • heridas postoperativas. 3.2 Contraindicaciones específicas absolutas 3.2.1 Electroterapia • fiebre; • tumores; • tuberculosis; • inflamaciones locales; • trombosis; • embarazo; • marcapasos cardíaco; • implantes metálicos.
4 Instalación 4.1 Conexión • Las conexiones de la red eléctrica deben cumplir con las regulaciones nacionales de acuerdo a las
salas médicas.El equipo tiene una conexión con toma a tierra, y debe ser conectado a un enchufe con toma a tierra.
• Antes de conectar este aparato a la red, comprobar que el voltaje y la frecuencia establecidos en la placa tipo se corresponden con los de la red eléctrica.
• El adaptador es una parte del circuito en que la seguridad del aparato depende en parte. La aprobación del Endomed 482 son válidos solo si se usan en combinación con este tipo de adaptador, ENA-1550.
No está permitido conectar el Endomed 482 a cualquier otro tipo de adaptador que el tipo ENA-1550 4.2 Conexión del adaptador de red • Conectar el adaptador de red suministrado al conector [3-1] • Conectar el adaptador de red a un enchufe. La lámpara [6] indica que el aparato está conectado a la
red y preparado. 4.3 Encendido y auto test • Encender la unidad usando el interruptor On/Off [1]. • Inmediatamente después de encenderse, la unidad realiza un auto chequeo. Al final del auto chequeo se oye un beep. Cuando se encuentra un error, aparecerá un código de error en el display. Ver sección 7 para detalle. 4.4 Desconectar de la red • Apagar el Endomed 482, usando el interruptor de red [1]. • Desenchufar el enchufe de adaptador. 4.5 Funcionamiento con bateria (opcional) El aparato puede funcionar independiente de la red. Para hacer esto posible, primero debe ser instalada una batería. Esto se hace de la manera siguiente:

4
E
• Apagar el aparato y sacar el adaptador de red del conector [3-1]. • Poner el aparato boca abajo y sacar los dos tornillos fijando la tapa compartimento de la bateria al
fondo del aparato . • Conectar el cabezal rojo al polo positivo (+) de la bateria y el cabezal negro al polo negativo (-) . • Deslizar la bateria en su compartimento. • Readjuntar la tapa compartimento de la bateria usando los dos tornillos. • Reconectar el adaptador de red al conector [3-1]. Con un adaptador de red conectado, la bateria se carga automáticamente, independiente de si está encendido/apagado [1]. Recomendamos usar el aparato con el adaptador de red conectado siempre que sea posible. Esto incrementará la vida de la bateria. Recomendamos usar explicitamente las baterias suministradas por Enraf-Nonius de tipo 2601.016. La bateria contiene material que es nocivo para el medioambiente. Deberá seguir las normas locales cuando disponga de la batería. Ver tambien capitulo 6.4. 4.6 Instalación • No instalar la unidad en un sitio cercano a fuentes de calor como radiadores. • Evitar la exposición a la luz directa, lluvia, exceso de polvo, humedad, vibraciones mecánicas y
shocks. • Los teléfonos inalámbricos no deben usarse cuando está cerca la unidad. • Esta unidad no debe utilizarse en las llamadas “salas húmedas” (salas de hidroterapia). • La unidad tiene que ser instalada de tal manera que ningún líquido pueda entrar. • Utilizar siempre los adaptadores de red suministrados por Enraf-Nonius tipo ENA-1550. En caso de que cualquier líquido entrara en la estructura del equipo, desenchufar la unidad de la red (si está conectada) y que un técnico autorizado lo compruebe.
La conexión de los accesorios distintos de las prescritas por Enraf-Nonius puede perjudicar la seguridad del paciente así como el correcto funcionamiento del Endomed 482, y por lo tanto no se permite. 4.7 Interferencia Electromagnética • El trabajar cerca de unidades de terapia de onda corta o microondas (ej. a menos de 2 metros)
puede producir inestabilidad en el Endomed 482. • Para evitar la interferencia electromagnética, advertimos utilizar grupos de red separados (fases) para
el Endomed 482 y los equipos de onda corta y microondas, y mantener una distancia al menos de 2 metros entre el Endomed 482 y estos equipos.
• Asegurarse que los cables de la red de la unidad de onda corta y microondas no están cerca del Endomed 482 ni del paciente.
Si persisten problemas de interferencia electromagnética, contacte con su proveedor.
5 Operación 5.1 Controles
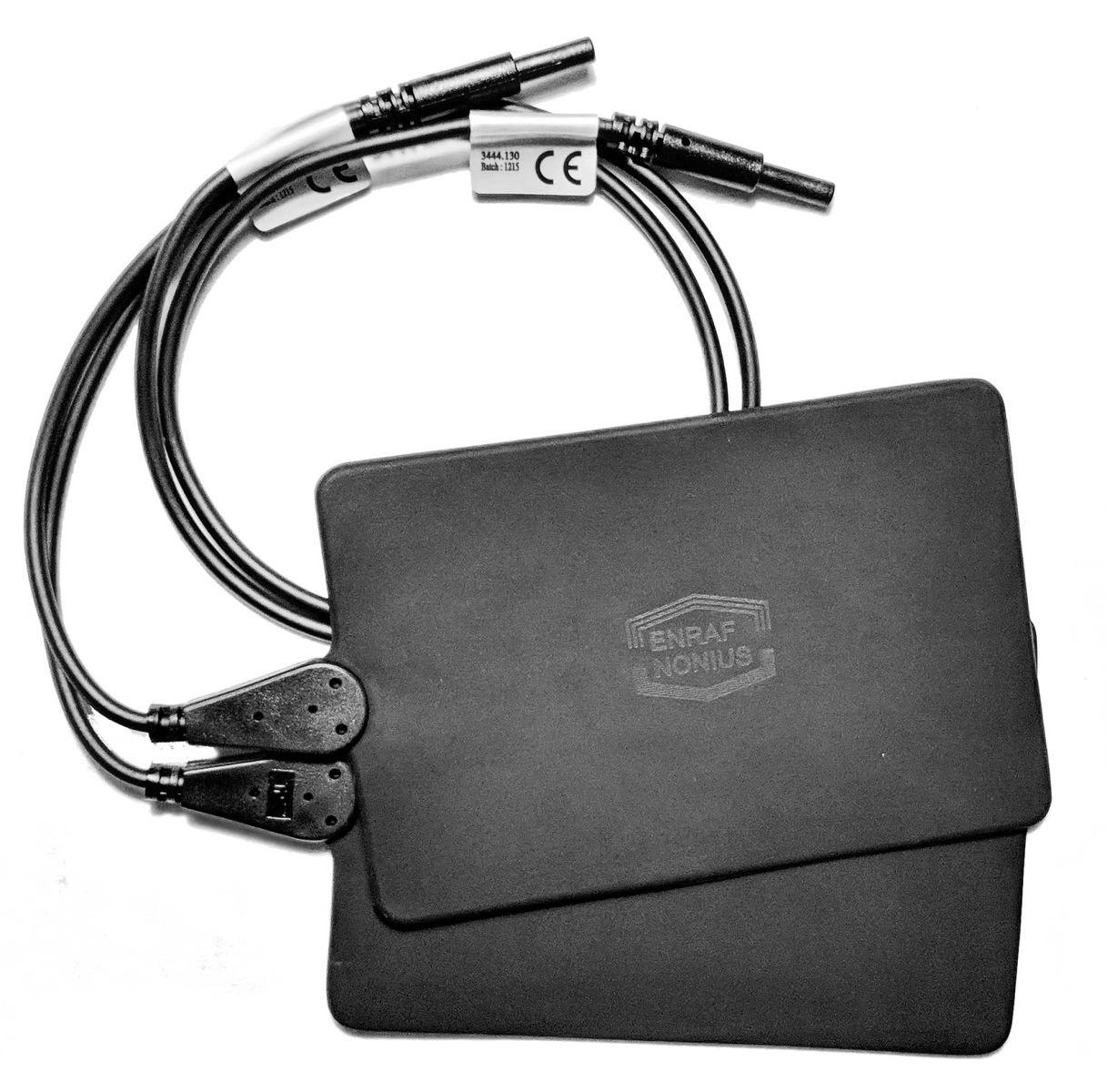
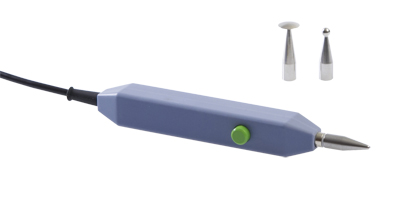
5.1.1 Aparato (Ver imagen) [1] Interruptor de On/Off Con este interruptor el Endomed 482 se enciende / apaga. [2] Número de tipo/pegatina de advertencia Se suministra con la unidad, tipo y número de serie, así como información de conexión como voltage de red y consumo máximo de corriente. [3-1] Conector para adaptador de red [3-2] Enchufe para control remoto

5
E
Para conexión del control remoto opcional. [4-1] Conexión cable de paciente para Electroterapia 5.1.2 Panel de control (Ver imagen) [5] Indicador de batería Indicación para batería. (Solo cuando se conecta la batería opcional) Luz verde: batería está totalmente cargada Luz parpadeando en verde : batería parcialmente descargada, conectar el adaptador de red Luz amarilla: batería cargada insuficientemente, terapias discapacitadas, conectar adaptador de red Sin Luz: batería casi vacía, no hay batería conectada o defectuosa, conectar adaptador de red [6] Indicador de adaptador de red Esta lampara indica que la unidad está conectada a la fuente de alimentación. [7] Elecciones de terapia Con este botón Vd. puede elegir la terapia: electroterapia, selección de canal de corriente, canales de corriente unidos, intervalo entre pasos de programa. [8] Elecciones de formas de corriente Este botón es para seleccionar las diferentes formas de corriente. [9] Botón de opción para: Onda portadora, anchura de pulso, frecuencia de microcorriente, tipo de interferencia, modo alternante (Alto Voltaje y Microcorriente) [10] Botón de opción para: Frecuencia de pulso, intervalo de fase, frecuencia burst (estimulación Rusa ), posición de vector, balance, formas de corriente Diadinámica, frecuencia de modulación. [11] Botón de opción para: Programa de modulación, Duty Cycle (estimulación rusa), Frecuencia de Burst (TENS) y número de paso de tratamiento (protocolos pre-programados). [12] Botón de opción para: Programa de sobre corriente, vector de tiempo de rotación y de tiempo [13] Botón de opción para: Corriente de canal 1 y 2, modo CC/CV, indicador de potencia y polaridad. [12]+[13] Parada de Emergencia. Pulsando los dos botones al mismo tiempo la terapia en todos los canales parará inmediatamente [14] Botón de aceptar Aceptar seleccion de corriente en forma de onda, los protocolos pre-programados e iniciar los programas de sobre corriente. [15] Botón de memoria Generar las funciones de memoria y rellamar a los programas de guardados [16] Controlador central Controlador para ajustes de todas las pruebas y parámetros. [17] Controlador de intensidad Controlador para ajustes de la intensidad en canal 1 y 2. En modo de 4-polos (interferencia) este controlador ajusta la intensidad en ambos canales juntos. [19] Símbolo de Intervalo El símbolo indica el intervalo entre dos pasos de programa de un programa secuencial.

6
E
5.2 Funcionamiento de la unidad
5.2.1 Introduccion 5.2.1.1 Encender el aparato Encender el aparato con el interruptor [1]. El aparato ejecuta un autochequeo, comprobando todas las funciones importantes y presenta los ajustes de inicio. Los ajustes de inicio son ajustables en memoria localización 0. Para personalizar los ajustes de inicio, ver capitulo 5.4, Funciones de Memoria. 5.2.1.2 Terapia y selección de canal El Endomed 482 está equipado con dos canales de electroterapia y un canal de ultrasonido. Estos canales puede ser ajustados independientemente, cada canal ofrece su propio ajuste de parámetros y tiempo de tratamiento. Tambien es posible unir canales. Usar el botón [7] para diferenciar entre las funciones de terapia básicas de Electroterapia el controlador central [16] para seleccionar o unir canales. Están disponibles las siguientes selecciones:
electroterapia en corriente de 1 canal electroterapia en corriente de 2 canaleselectroterapia en canales unidos
Tener en cuenta que el uso independiente de los canales de electroterapia requiere ajustar todos los parámetros en ambos canales. Cuando no se desea esto, o cuando no se necesita el uso independiente, usted puede tambien unir los canales. Algunas formas de corriente, tales como corrientes interferenciales son solo posibles en canales unidos. 5.2.1.3 Selección de corriente en forma de onda Pulsar el botón [8]. Todas las formas de onda aparecen en el display, parpadeando la corriente seleccionada. Seleccionar una corriente usando el controlador central y pulsando el botón [14] para aceptar la selección. Cuando Vd. selecciona (grupo de corriente interferencial) o (grupo de corriente diadinamica), se le pedirá seleccionar un tipo de corriente dentro de este grupo. Seleccionar el tipo de corriente usando el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar la selección. 5.2.1.4 Ajuste de parámetros Pulsar los botones [9] y [13] para seleccionar un parámetro. Un botón afecta a todos los parámetros que están en linea con él en el display. Una vez seleccionado se puede ajustar un parámetro, usando el controlador central [16]. Un parámetro puede ser modificado, tanto tiempo como el icono identificador esté parpadeando. El display solo mostrará esos parámetros, que son aplicables a la terapia seleccionada. 5.2.1.5 Tiempo de tratamiento Pulsar el botón [12] para seleccionar el tiempo de tratamiento. El icono min está parpadeando. El display muestra el tiempo de tratamiento del canal, que está presente normalmente (seleccionado bajo 5.2.1.2.) en el display. Como recordatorio, un indicador de canal está parpadeando por encima del valor del tiempo de tratamiento. Solo el tiempo de tratamiento de este canal puede ahora ser modificado, usando el controlador central [16]. Cuando están activos uno o más canales el está parpadeando. Hay disponible una indicación de los canales activos corrientemente por encima del valor de tiempo de tratamiento. 5.2.1.6 Programas de sobre corriente Algunas corrientes pueden ser metidas en un programa de sobre corriente. Pulsar el botón [12] para seleccionar secuencialmente tiempo de rampa de subida , tiempo de mantenimiento , tiempo de rampa de bajada y tiempo de intervalo . Ajustar estos parámetros usando el controlador central [16]. Cuando loa canales de corriente están unidos, los programas de sobre corriente son idénticos en ambos canales. En este modo se puede ajustar un tiempo de demora entre el inicio de un programa de corriente en el canal 1 y en el canal 2. Esto se hace de la manera siguiente: Pulsar el botón [13] y seleccionar el canal 2 usando el controlador central [16]. Después pulsar el botón [12] para seleccionar el tiempo de demora y ajustarlo usando el controlador central [16]. 5.2.1.7 Intensidad de corriente La intensidad de coriente se ajusta usando el controlador de intensidad [17]. La intensidad de corriente puede ser ajustada solo cuando el reloj ha sido ajustado. El indicador de canal , seguido por el canal número o indica el canal, que está presente corrientemente en el display y que puede ser ajustado. Vd. puede cambiar el número de canal, usando el

7
E
botón [13] y el controlador central [16]. Esta selección funciona en paralelo a la selección del canal descrita en párrafo 5.2.1.2. En la corriente de 4-polos en formas de onda el controlador de intensidad [17] funciona en ambos canales simultáneamente. En el display esto se indica mediante , en el que el canal que normalmente es visualizado está parpadeando. En este caso un control de balance está disponible fácilmente para la corriente interferencial clásica en forma de onda (ver párrafo 5.2.2.9. para detalles). La unidad de la intensidad de corriente visualizada depende de la corriente en forma de onda previamente seleccionada y puede ser expresada en mA, µA o V. Un tratamiento es iniciado ajustando la intensidad de corriente, a menos que un programa de sobre corriente haya sido seleccionado. Pulsar el botón [14] para iniciar un tratamiento que incluya un programa de sobre corriente. Los indicadores y se mostrarán hacia arriba cuando la corriente está fluyendo normalmente desde los canales correspondientes. Un valor de intensidad de corriente parpadeando indica un mal contacto eléctrico con el paciente. 5.2.1.8 Modo CC/CV Dependiendo de la corriente en forma de onda seleccionada, los canales de electroterapia pueden ser usados en modo de Corriente Constante o Voltaje Constante. Aconsejamos usar el modo CV con aplicaciones de electrodo dinámicas. En modo CV la corriente de salida depende del contacto eléctrico con el paciente y puede por tanto variar. Vd. puede cambiar elajuste CC/CV usando el botón [13] y el controlador central [16]. 5.2.1.9 Polaridad de corriente Cuando se usan corrientes DC, el terminal rojo es el terminal positivo y el negro el terminal negativo. Para cambiar manualmente la polaridad, pulsar el botón [13] y seleccionar o usando el controlador central [16]:
: standard: reverso
El cambiar manualmente la polaridad durante un tratamiento provocará un descenso a 0, seguida por una corriente con la polaridad contraria, elevándose a un valor igual al 80% del valor previsto. Para activar el reverso de la polaridad automática de las formas de corriente de voltaje Alto y Microcorriente, seleccionar o con el botón [9] y el controlador central [16]:
: alternante : no alternante
Con la corriente en forma de onda interrumpida DC no es posible hacer el reverso de la polaridad de corriente. 5.2.1.10 Parada de Emergencia. Pulsando los dos botones [12] y [13] al mismo tiempo la terapia en todos los canales parará inmediatamente. 5.2.2 Electroterapia. 5.2.2.1 Interferencia de dos-polos • Pulsar el botón [7] seleccionar corriente . Usar el controlador central [16] para seleccionar el canal
deseado o unir los canales; • Pulsar el botón [8], seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Para seleccionar la corriente interferencial de 2-polos: Seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Selección de onda portadora:
Seleccionar con el botón [9] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de pulso:
Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de modulación:
Select con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de modulación (espectro):
Seleccionar con el botón [11] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de tratamiento:
Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Programa de sobre corriente (cuando se desee): • Rampa de subida: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de mantenimiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Rampa de bajada:

8
E
Seleccionar con el boton [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de intervalo: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de retraso (solo disponible con canales unidos): Pulsar el botón [13] y seleccionar canal 2 con el controlador central. Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central; • Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Seleccionar el canal deseado con el botón [13] y el controlador central [16]. Ajustar la intensidad con
el saliente [17]; • Para iniciar la terapia pulsar el botón de accept [14]. 5.2.2.2 Estimulación Rusa • Pulsar el botón [7] y seleccionar corriente . Usar el controlador central [16] para seleccionar el canal
deseado o unir los canales; • Pulsar el botón [8], seleccionar con el controlador central y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Selección de onda portadora:
Seleccionar con el botón [9] (kHz) y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia Burst:
Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Burst / rango de intervalo:
Seleccionar con el botón [11] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de tratamiento:
Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Programa de sobre corriente (cuando se desee): • Rampa de subida: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de mantenimiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Rampa de bajada: Seleccionar con el boton [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de intervalo: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de retraso (solo disponible con canales unidos): Pulsar el botón [13] y seleccionar canal 2 con el controlador central. Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central; • Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Seleccionar el canal deseado con el botón [13] y el controlador central [16]. Ajustar la intensidad con
el saliente [17]; • Para iniciar la terapia pulsar el botón de accept [14]. 5.2.2.3 Corriente pulsada bifásico Asimétrica y Simétrica (TENS) • Pulsar el botón [7] y seleccionar . Usar el controlador central [16] para seleccionar el canal deseado
o unir los canales; • Pulsar el botón [8], seleccionar o con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para
aceptar; • Anchura de pulso:
Seleccionar con el botón [9] y ajustar el valor con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de pulso:
Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Haga su elección entre frecuencia de modulación y modo burst ya que estos dos opciones son
mutuamente excluyentes; • Si se quiere modulación de frecuencia: Controlar primero si la frecuencia de Burst está en 0: • Seleccionar con el boton [11] y ajustar su valor a cero con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de modulación: Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de modulación (Espectro):
Seleccionar con el botón [11] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Si se quiere Burst: Controlar primero si la frecuencia de modulación está en 0: • Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar su valor a acero con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia Burst:
Seleccionar con el botón [11] y ajustar el valor con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de tratamiento:

9
E
Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Programa de sobre corriente (cuando se desee): • Rampa de subida: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de mantenimiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Rampa de bajada: Seleccionar con el boton [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de intervalo: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de retraso (solo disponible con canales unidos): Pulsar el botón [13] y seleccionar canal 2 con el controlador central. Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central; • Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Seleccionar el canal deseado con el botón [13] y el controlador central [16]. Ajustar la intensidad con
el saliente [17]; • Para iniciar la terapia pulsar el botón de accept [14]. 5.2.2.4 Corriente pulsada Triangular –y monofásica rectangular Pulsar el botón [7] y seleccionar corriente . Usar el controlador central [16] para seleccionar el canal
deseado o unir los canales; • Pulsar el botón [8], seleccionar o con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para
aceptar; • Anchura de pulso:
Seleccionar con el botón [9] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Intervalo de pulso:
Seleccionar con el boton [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de tratamiento:
Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Programa de sobre corriente (cuando se desee): • Rampa de subida: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de mantenimiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Rampa de bajada: Seleccionar con el boton [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de intervalo: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de retraso (solo disponible con canales unidos): Pulsar el botón [13] y seleccionar canal 2 con el controlador central. Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central; • Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Polaridad: Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Seleccionar el canal deseado con el botón [13] y el controlador central [16]. Ajustar la intensidad con
el saliente [17]; • Para iniciar la terapia pulsar el botón de accept [14]. 5.2.2.5 Micro corriente • Pulsar el botón [7] seleccionar corriente . Usar el controlador central [16] para seleccionar el canal
deseado o unir los canales; • Pulsar el botón [8], seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Frecuencia:
Seleccionar (Hz or kHz) con el boton [9] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Alternada o no alternada:
Seleccionar o con el botón [9] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de tratamiento:
Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar el tiempo con el controlador central [16] • Secuencia de alternación (seleccionado solo con ): • Rampa de subida: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de mantenimiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Rampa de bajada:

10
E
Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Programa de sobre corriente (seleccionado solo con ): • Rampa de subida: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de mantenimiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Rampa de bajada: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de intervalo: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de retraso (solo disponible con canales unidos): Pulsar el botón [13] y seleccionar canal 2 con el controlador central. Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central; • Polaridad (seleccionado solo con ): Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Seleccionar el canal deseado con el botón [13] y el controlador central [16]. Ajustar la intensidad con
el saliente [17]; • Para iniciar la terapia pulsar el botón de accept [14]. 5.2.2.6 Voltaje alto • Pulsar el botón [7] y seleccionar la corriente . Usar el controlador central [16] para seleccionar el
canal deseado o unir los canales; • Pulsar el botón [8], seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Alternada o no alternada:
Seleccionar o con el botón [9] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de modulación:
Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar el valor con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de modulación (Espectro):
Seleccionar con el botón [11] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de tratamiento:
Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Secuencia de alternación (seleccionado solo con : • Rampa de subida: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de mantenimiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Rampa de bajada: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Programa de sobre corriente (seleccionado solo con ): • Rampa de subida: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de mantenimiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Rampa de bajada: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de intervalo: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de retraso (solo disponible con canales unidos): Pulsar el botón [13] y seleccionar canal 2 con el controlador central. Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central; • Polaridad (seleccionado solo con ): Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Seleccionar el canal deseado con el botón [13] y el controlador central [16]. Ajustar la intensidad con
el saliente [17]; • Para iniciar la terapia pulsar el botón de accept [14]. 5.2.2.7 Corrientes Diadinamicas • Pulsar el botón [7] y seleccionar corriente . Usar el controlador central [16] para seleccionar el
canal deseado o unir los canales; • Pulsar el botón [8], seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Seleccionar MF, DF, CP, CPid y LP con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Tiempo de tratamiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Programa de sobre corriente (cuando se quiera):

11
E
• Rampa de subida: Seleccionar con el boton [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de mantenimiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Rampa de bajada: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de intervalo: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de retraso (solo disponible con canales unidos): Pulsar el botón [13] y seleccionar canal 2 con el controlador central. Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central; • Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Polaridad: Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Seleccionar el canal deseado con el botón [13] y el controlador central [16]. Ajustar la intensidad con
el saliente [17]; • Para iniciar la terapia pulsar el botón de accept [14]. 5.2.2.8 Corriente directa interrumpida de frecuencia — media Pulsar el botón [7] y seleccionar corriente . Usar el controlador central [16] para seleccionar el
canal deseado o unir los canales; • Pulsar el botón [8], seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Tiempo de tratamiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Seleccionar el canal deseado con el botón [13] y el controlador central [16]. Ajustar la intensidad con
el saliente [17]; 5.2.2.9 Interferencia (clásica) • Pulsar el botón [7] y seleccionar corriente . Seleccionar con el controlador central [16] el canal
unido; • Pulsar el botón [8], seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Selección de corriente interferencial de 4-polos: Seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Selección de onda portadora: Seleccionar con el botón [9] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de pulso:
Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de modulación:
Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de modulación (Espectro): Seleccionar con el botón [11] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de tratamiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Ajustar la intensidad con el saliente [17]; • Balance: Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar el balance con el controlador central [16]. 5.2.2.10 Vector isoplanar • Pulsar el botón [7] y seleccionar corriente . Seleccionar con el controlador central [16] el canal
unido; • Pulsar el botón [8], seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Selección de corriente de vector isoplanar : Seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Selección de onda portadora :
Seleccionar con el botón [9] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de pulso: Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de modulación: Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de modulación (Espectro): Seleccionar con el botón [11] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de tratamiento :

12
E
Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Ajustar la intensidad con el saliente [17]. 5.2.2.11 Vector manual dipolar • Pulsar el botón [7] y seleccionar corriente . Seleccionar con el controlador central [16] el canal
unido; • Pulsar el botón [8], seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Seleccion manual de corriente de vector dipolar : Seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Selección de onda portadora: Seleccionar con el botón [9] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de pulso: Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de modulación: Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de modulación (Espectro): Seleccionar con el botón [11] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de tratamiento:
Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Ajustar la intensidad en con el saliente [17]; • Vector dipolar: Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar la posición con el controlador central [16]. 5.2.2.12 Vector dipolar automático • Pulsar el botón [7] y seleccionar corriente . Seleccionar con el controlador central [16] el canal
unido; • Pulsar el botón [8], seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Seleccion de corriente de vector dipolar automático : Seleccionar con el controlador central [16] y pulsar el botón [14] para aceptar; • Selección de onda portadora: Seleccionar con el botón [9] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de pulso: Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Frecuencia de modulación: Seleccionar con el botón [10] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de modulación (Espectro): Seleccionar con el botón [11] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Tiempo de tratamiento: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Velocidad de rotación: Seleccionar con el botón [12] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Seleccionar o con el botón [13] y ajustar con el controlador central [16]; • Ajustar la intensidad con el saliente [17]. 5.3 Medidas con respecto a tratamientos 5.3.1 Electroterapia Antes del tratamiento • Comprobar si el paciente tiene contraindicaciones absolutas y relativas. • Probar la sensibilidad al calor del área de tratamiento. • Si la piel está afeitada del vello es lo mejor. 5.4 Funciones de memoria El Endomed 482 está equipado con una memoria para guardar los ajustes de equipo y protocolos.

13
E
5.4.1 Ajustes de equipo Los ajustes de equipo almacenan todos los parámetros del aparato, excepto la intensidad de corriente. Contrario a protocolos, los ajustes de equipo funcionan en todos los canales juntos, incluyendo el canal de ultrasonido. Los ajustes de equipo están almacenados en las localizaciones 0 — 9. El número de localización aparecerá en el display cuando el botón [15] sea pulsado. El ajuste 0 de equipo es cargado automáticamente cuando el aparato es encendido. Los ajustes de equipo pueden ser cargados y guardados solamente cuando todos los canales están inactivos. 5.4.1.1 Carga de ajustes de equipo • Pulsando el botón [15], está parpadeando; • Seleccionar una localización de memoria en el rango de 0 — 9 con el controlador central [16]. El
display muestra los ajustes de equipo que son guardados en la localización seleccionada; • Pulsar el botón [14] para cargar los ajustes de equipo seleccionados; • Ajustar la intensidad de corriente con el controlador [17]; • Pulsar el botón [14] para iniciar la terapia en caso de que un programa de sobre corriente fuera
seleccionado. La carga de los ajustes de equipo seleccionados tiene que ocurrir en un cierto retraso de tiempo tan largo como esté parpadeando. Esperar demasiado, o pulsar cuaquier otro botón que no sea [14] o [15] cancelará la función de carga. 5.4.1.2 Almacenamiento de ajustes de equipo • Seleccionar una terapia y ajustar todos los parámetros en todos los canales deseados; • Pulsando el botón [15], parpadea; • Seleccionar una localización de memoria en el rango de 0 — 9 con el controlador central [16]. El
display muestra los ajustes de equipo que son almacenados en la localización seleccionada, permitiéndole comprobar lo que será sobre escrito;
• Pulsando el botón [15] una segunda vez, parpadeará. El display muestra ahora los ajustes de corriente del equipo que están para ser guardados en la localización seleccionada;
• Pulsar el botón [14] para ejecutar la función de guardar. La ejecución de la función de guardar sucederá dentro de un cierto retraso de tiempo tan largo como el simbolo esté parpadeando. Esperar demasiado, o pulsar cualquier otro botón que no sea [14] o [15] cancelará la función de guardar. 5.4.2 Protocolos Un protocolo consta de uno o más pasos de tratamiento que son ejecutados secuencialmente. Cada paso de tratamiento tiene su propia corriente en forma de onda, ajustes de parámetro y tiempo de tratamiento. Los protocolos están categorizados en grupos de acuerdo a su aplicación. Los protocolos son identificados de la manera siguiente: 1:1 el primer número es el número de grupo 1:1 el segundo número es el número de protocolo El Endomed 482 proporciona un número de protocolos pre-programados, que están disponibles en el grupo 2 y mayores. Se entiende que cada grupo es para una indicación especifica. En la guia de terapia que se suministra con el aparato, encontrará una relación de todos los grupos y protocolos correspondientes. Adicionalmente el Endomed 482 soporta los protocolos de usuario definidos, por lo que se ha reservado el grupo 1. Los protocolos de electroterapia pueden constituir aplicaciones de canal simple o dual. Antes de cargar un protocolo de canal simple, primero se debe especificar el objetivo del canal. En este caso tambien se permite unir los canales de corriente, haciendo que el protocolo sea ejecutado en ambos canales. Cuando se está ejecutando un protocolo de canal simple, un protocolo de canal simple completamente diferente puede ser ejecutado en el otro canal. Desde luego los protocolos de dos canales solo pueden ser cargados cuando los canales de corriente están unidos. 5.4.2.1 Carga de un protocolo • Seleccionar un objetivo de canal, usando el botón [7] y el controlador central [16]; • Pulsando el botón [15], el simbolo parpadeará; • Seleccionar un número de protocolo en el rango de 1:1 y mayor con el controlador central [16]. El
display muestra el tiempo de tratamiento total del protocolo seleccionado; • Pulsar el botón [14] para cargar el protocolo seleccionado; • Ajustar la intensidad de corriente con el controlador [17];

14
E
• Pulsar el botón [14] para iniciar la terapia en el caso de ser seleccionado un programa de sobrecorriente.
Cuando se ejecuta un protocolo, el display muestra el tiempo de tratamiento restante del paso de tratamiento que está funcionando. Cada paso de tratamiento es terminado con un sonido corto. Cuando se ha alcanzado el final del protocolo, se emite un sonido standard de “final de tratamiento”, después del cuál el aparato saldrá del modo protocolo. Notas: • Para indicar el modo protocolo el número de protocolo permanece visible en el display una vez que
un protocolo ha sido cargado. Siguiendo el número de protocolo, se muestra el numero de paso de tratamiento, acompañado por su propio icono .
• Para quitar un protocolo cargado pero no ejecutado todavía, pulsar el botón [14] otra vez. Esperando un momento, o pulsando cualquier otro botón que no sea el [14] o [15], el aparato saldrá del modo protocolo.
• Todos los parámetros de un protocolo cargado pueden ser cambiados cuando se quiera. Seleccionar con el botón [11] y seleccionar el número de paso de tratamiento con el controlador central [16].
Todos los parámetros del paso de tratamiento ahora seleccionado, pueden ser cambiados. No olvidar resetear el número de paso de tratamiento al 1.
• Un protocolo cargado puede ser ejecutado empezando desde cualquier paso de tratamiento. Seleccionar con el botón [11] y seleccionar el número de paso de tratamiento con el controlador central [16].
• La ejecución de un paso de tratamiento puede ser terminada avanzando el numero de paso de tratamiento. Seleccionar con el botón [11] y seleccionar el nuevo número de paso de tratamiento con el controlador central [16]. La corriente decaerá a cero. Vd. puede resumir la ejecución del protocolo desde el nuevo paso de tratamiento ajustando la intensidad de corriente con el controlador [17].
• La ejecución de un protocolo puede ser terminada, ajustando el tiempo de tratamiento del paso de tratamiento que está trabajando a cero. El aparato saldrá entonces del modo protocolo.
5.4.2.2 Guardar un protocolo Antes de ejecutar un protocolo modificado, puede ser salvado para un último uso en el grupo 1: • Pulsar el botón [15] dos veces. El simbolo está parpadeando; • Seleccionar un número de protocolo en el rango de 1:1 — 1:9 con el controlador central [16]. El display
muestra el tiempo de tratamiento total del protocolo que va ser guardado; • Pulsar el botón [14] para ejecutar la función de guardar. 5.4.2.3 Creación de un protocolo definido por el usuario En el grupo 1 usted puede crear sus propios protocolos. Un máximo de 10 protocolos pueden ser guardados, cada uno con una longitud máxima de 20 pasos de tratamiento. Antes de proceder con los pasos de abajo, primero estar seguros de que el aparato no está en modo protocolo (ver sección 5.4.2.1. como salir del modo protocolo): • Pulsar el botón [15] dos veces. El simbolo parpadeará; • Seleccionar un número de protocolo en el rango de 1:1 — 1:9 con el controlador central [16]; • Pulsar el botón [14]. El simbolo parpadeará, es visible y el número de paso de tratamiento es
ajustado a 1. • Ajustar todos los parámetros del paso de tratamiento actual; • Pulsar el botón [14] para guardar el paso de tratamiento. El número de paso de tratamiento se
incrementa automáticamente; • Repetir los dos pasos anteriores hasta que se haya alcanzado el final de su protocolo; • Terminar su protocolo con un paso de tratamiento con un tiempo de tratamiento de cero. Pulsar el
botón [14] para confirmar. El final de su protocolo se confirma con un beep. Notas: • Cuando dos pasos de tratamiento consecutivos contienen corriente AC, la intensidad de corriente
será mantenida en el nivel ajustado cuando se ejecute el protocolo. • Cuando se encienda o entre corrientes DC, la intensidad de corriente decaerá a cero. El siguiente
paso de tratamiento tendrá que ser iniciado manualmente ajustando la intensidad de corriente. 5.5 Reacciones al conectar y desconectar Se pueden producir reacciones desagradables al conectar y desconectar — en el caso de una característica de salida de corriente constante — cuando los electrodos no están fijados o están completamente sueltos. Procure que la corriente de paciente es 0 mA cuando coloca y suelta los

15
E
electrodos cuando CC está establecido . Con técnicas de aplicación dinámicas utilizar preferiblemente la elección de voltaje constante (CV). 5.6 Efectos electrolíticos Con tipos de corriente con un componente de corriente directa se produce electrolisis debajo de los electrodos. Para absorber lo más posible los productos electrolíticos que se producen debajo de los electrodos y para limitar los efectos de esto, es necesario que se usen las esponjas suministradas. Procurar que estén mojadas suficientemente con agua y colocar la capa doble de la esponja entre el electrodo de goma flexible y el paciente. 5.7 Control remoto Para el Endomed 482 hay disponible un control remoto especial. Este puede ser conectado al enchufe conector [3-2]. El control remoto tiene 2 botones de intensidad para ajustar la intensidad de los canales de corriente y una parada de emergencia.
6 Mantenimiento por el usuario 6.1 Mantenimiento técnico La seguridad eléctrica del aparato depende de la conexión eléctrica (mediante el cable equipotencial) a la toma de tierra. Por tanto es necesario tener chequeada esta conexión anualmente. Además se recomienda un chequeo anual de todo. Esto debe ser hecho por su proveedor u otra empresa autorizada por el fabricante. Recomendamos igualmente llevar un registro de todas las actividades relacionadas con el mantenimiento. En algunos países tal registro es obligatorio. El control y/o un mantenimiento técnico debe realizarse conforme al procedimiento descrito en el manual de servicio de este aparato. No intente abrir el aparato. El mantenimiento y las reparaciones deben ser realizados siempre por una empresa autorizada. El fabricante no asume la responsabilidad de las consecuencias de reparaciones o trabajos de mantenimiento efectuados por personas no autorizadas. 6.2 Limpieza del aparato Apagar la unidad y desconectarla de la red. El aparato debe limpiarse con un paño húmedo. Usar agua tibia y un liquido limpiador casero no-abrasivo (no abrasivo, sin contenido de alcohol). 6.3 Limpieza de los accesorios
6.3.1 Electrodos y esponjas Los electrodos de goma y las esponjas deben limpiarse con agua templada. En caso de suciedad persistente y para desinfección, puede utilizarse una solución de alcohol al 70%. Los electrodos de goma pueden desteñir durante este procedimiento. Es posible que las esponjas no sean buenos conductores cuando el grado de dureza del agua es bajo, no alcanzándose la intensidad de corriente deseada. Esta conductividad puede disminuir también como consecuencia de la desinfección de las esponjas. En tal caso, sugerimos utilizar una solución salina para aumentar la conductividad del agua. Cuando no se utilicen los electrodos saque las esponjas, y así prolongará la vida útil de los electrodos. Las esponjas deben substituirse regularmente. Aconsejamos tener un juego de esponjas y electrodos de reserva. 6.3.2 Cable del paciente El cable del paciente debe limpiarse con un paño húmedo. Compruebe el cable con regularidad para detectar daños que pueden causar interferencias. Aconsejamos tener también un cable del paciente de reserva. Antes de usar un cable adaptador, examinarlo por si tiene mal contacto o está dañado. Se recomienda tener un adaptador de cable en stock.

16
E
6.4 Duración de vida del aparato y accesorios Su Endomed 482 y accesorios contienen materiales que pueden ser reciclados y/o son nocivos para el medio ambiente. Al final de su vida, los especialistas que les concierna, pueden separar estos artículos y clasificarlos en materiales nocivos y materiales para reciclaje. Haciendo eso, Vd. contribuye a un medio ambiente mejor. Por favor asegúrese que está bien informado de las reglas locales y regulaciones respecto a sacar el aparato y accesorios.
7 Diagnóstico 7.1 Las luces y pantallas no se encienden • Posiblemente la pila está vacía. Trata de utilizar el aparato con el enchufe. 7.2 Código de Error El aparato ha descubierto un fallo durante o después del auto chequeo. El código de error consiste en un número de 3 digitos y aparece en el display de intensidad de corriente. Sacar cualquier aplicador o cables de los enchufes y apagar el aparato y encenderlo otra vez. Si reparece el código, contacte con su proveedor. El aparato está defectuoso probablemente. 7.3 Contacto roto en modo CC Si en el modo CC el contacto está roto, el aparato lo señalará con una señal acústica. Para evitar sensaciones desagradables para el paciente cuando la cabeza de tratamiento sea colocada sobre la piel, la corriente se reduce hasta 0. Para continuar el tratamiento, Ud. debe ajustar la corriente de nuevo. 7.4 Falta de corriente (insuficiente) • Buscar una ruptura o contacto en mal estado en el cable del paciente. • Asegurarse que las esponjas están suficientemente húmedas. • Si es necesario, mojarlas en una solución salina. • Limpiar los electrodos y comprobar si el contacto es bueno. • En terapia combinada, la corriente de salida máxima para interferencia bipolar se limita a 60 mA. 7.5 Comprobación de panel frontal Encendiendo el aparato con los botones [9] y [10] pulsados, se encenderán todos los segmentos en el display, permitiéndole comprobar su funcionamiento. La pulsación de los botones y el funcionamiento de los reguladores dará como resultado un beep. Usted puede salir de este modo solo apagando el aparato.
8 Especificaciones 8.1 Especificaciones del producto Electroterapia general Canales : 2 Característica de corriente : corriente constante (CC) o voltaje constante (CV) Resolución de ajuste : 0,2 mA Tiempo : 0 — 60 minutos Revisión de polaridad corrientes directas : manual La intensidad máxima dentro de la especificación se consigue hasta una carga de 500 Ω (CC). Corriente pulsada bifásica Simetrica y asimetrica, TENS Frecuencia : 1 — 200 Hz Duración de fase (anchura de pulso) : 10 — 400 µs Frecuencia Burst : 0 — 9 Hz Frecuencia de Modulación (espectro) : 0 — 180 Hz Programa de Modulación : 1/1, 6/6, 12/12 en 1/30/1/30 s Forma de corriente: Rampa de subida 0 — 9 s Tiempo de mantenimiento 1 — 60 s Rampa de bajada 0 — 9 s Tiempo de Intervalo 1 — 60 s

17
E
Tiempo de retraso 0,1 — 80 s Intensidad : 0 — 140 mA. En ciertas combinaciones de anchura de pulso, frecuencia y espectro el rango de ajuste es reducido a 90-mA max. Para cumplir los valores limite de IEC 60601-2-10 Voltaje alto Frecuencia : 1- 200 Hz Frecuencia de Modulación (espectro) : 0 – 90 % Programa de Modulación : 1/1, 6/6, 12/12 en 1/30/1/30 s Forma de corriente : Como en las formaa de corriente TENS Intensidad : 0 – 500 Volt Modo alternante: Tiempo alternado : 5 tot 50 segundos Rampa de subida y de bajada : 0,1 – 1 segundos Modo no-alternante: Forma de corriente Surge pattern : Como en las corrientes TENS Micro-corriente Intensidad : 10 µA — 1 mA Alcance de voltajo : 200 Volt Modo alternante: Frecuencia : 0 – 1000 Hz Tiempo alternado : 0,1 – 10 segundos (el tiempo alternado es relativo a la
frecuencia de pulso) Rampa de subida y de bajada : 0,1 – 1 segundos Modo no-alternante: Frecuencia : 0,1 – 1000 Hz Forma de corriente : Como en las corrientes TENS Corriente alternante Interrumpida, Estimulación Rusa Frecuencia portadora : 2 — 10 kHz Frecuencia Burst : 0 — 100 Hz Burst / ratio de intervalo : 1:1, 1:2, 1:4 y 1:5 Forma de corriente : Como en las corrientes TENS Intensidad : 0 — 100 mA Formas de corriente diadinamica Opciones : MF, DF, CP, LP y CPid Forma de corriente (MF y DF solo) : Como en las corrientes TENS Intensidad : 0 — 70 mA Corrientes faradizas Opciones : 2-5 corriente según Träbert (pulso rectangular por
defecto de elección) Duración de fase : 0.02 — 1000 ms con corriente pulsada rectangular 0.1 — 1000 ms con corriente pulsada triangular intervalo de fase : 5 — 5000 ms Forma de corriente : Como en las corrientes TENS Intensidad : 0 — 80 mA Corriente directa interrumpida Frecuencia : 8000 Hz Duty cycle : 95% Intensidad : 0 — 40 mA Interferencia Bipolar Onda portadora : 2- 10 kHz Frecuencia de pulso (AMF) : 0 — 200 Hz Frecuencia de Modulacion (espectro) : 0 — 180 Hz Programa de Modulacion : 1/1, 6/6, 12/12 y 1/30/1/30 s Forma de corriente : Como en las corrientes TENS Intensidad : 0 — 100 mA Interferencia Clásica Onda portadora : 2- 10 kHz

18
E
Frecuencia de pulso (AMF) : 0 — 200 Hz Frecuencia de Modulacion (espectro) : 0 — 180 Hz Programa de Modulacion : 1/1, 6/6, 12/12 y 1/30/1/30 s Forma de corriente : No ajustable Intensidad : 0 — 100 mA Ajuste de Balance : mediante el controlador central Vector Isoplanar Onda portadora : 2- 10 kHz Frecuencia de pulso (AMF) : 0 — 200 Hz Frecuencia de Modulación (espectro) : 0 — 180 Hz Programa de Modulación : 1/1, 6/6, 12/12 y 1/30/1/30 s Forma de corriente : No ajustable Intensidad : 0 — 100 mA Vector Dipolo automático Onda portadora : 2- 10 kHz Frecuencia de pulso (AMF) : 0 — 200 Hz Frecuencia de Modulación (espectro) : 0 — 180 Hz Programa de modulación : 1/1, 6/6, 12/12 y 1/30/1/30 s Forma de corriente : No ajustable Intensidad : 0 — 100 mA Velocidad de rotación : ajustable desde 1 a 10 segundos Vector manual dipolar Onda portadora : 2- 10 kHz Frecuencia de pulso (AMF) : 0 — 200 Hz Frecuencia de modulación (espectro) : 0 — 180 Hz Programa de modulación : 1/1, 6/6, 12/12 y 1/30/1/30 s Forma de corriente : No ajustable Intensidad : 0 — 100 mA Posición : 360 º Funciones de memoria Ajuste de equipo 0 : ajuste de inicio. Ajustes de equipo : 10, programables de usuario Protocolos de usuario a definir : 10 Protocolos pre-programados : 50 8.2 Especificaciones técnicas Adaptador de red Tipo de adaptador de red : ENA-1550 Voltage de red : 100 — 240 Volt +/- 10 % Frecuencia : 50 / 60 Hz Voltage de salida : 15 Volt Corriente de salida Max. : 3,3 A. Unidad Clasificación equipos médicos : IIa (de acuerdo a la Directiva de Equipos
Médico(93/42/CEE)) Clase de seguridad : I* tipo BF**, según IEC 60601-1 Corriente de dispersión de paciente : Mejor de la norma de IEC ( < 100 µA) Corriente de dispersión de paciente, condición de error singular : Mejor de la norma de IEC (< 500 µA) Pruebas de tipo y seguridad : CE-MDD (TÜV Rheinland) Dimensiones : 29 x 28 x 11 cm. Peso : 4 kg. Condiciones medioambientales para transporte y Almacenaje Temperatura medioambiental : -10° hasta +50° C Humedad relativa : 10 hasta 100 % Presión atmosférica : 500 hasta 1060 hPa Condiciones medioambientales uso normal Temperatura medioambiental : 10° hasta 40° C

19
E
Humedad relativa : 10 hasta 90 % (no condensada) Presión atmosféricia : 500 hasta 1060 hPa 8.3 Clasificación
Clase Médica IIa Este equipo cumple con todos las normativas esencial de la Directiva de Equipos Médicos (93/42/CEE).
I : El aparato cuenta con toma de tierra de seguridad y tiene que ser conectado a una toma de pared con toma de tierra.
*BF : El aparato tiene un circuito de paciente flotante.
Normas de seguridad internacionales El Endomed 482 cumple con la norma internacional para equipos eléctricos médicos IEC 60601-1 y IEC 60601-2-10 (estimuladores eléctricos del nervio). Copias de informaciones de prueba están disponibles. Modificaciones técnicas reservadas.
9 Datos de pedido Para pedir el Endomed 482, accesorios estándar o los accesorios complementarios, mirar el catálogo de Fisioterapia


20
I

1 Figuren – Pictures – Abbildungen – Image – Imagen — Immagine

Аппарат электротерапии

Код МИ
181070
– система физиотерапевтическая для электростимуляции, с питанием от сети
Код КТРУ
26.60.13.190-00000086
– система физиотерапевтическая для электростимуляции, с питанием от сети
Входит в приказы оснащений
788н,
878н
,
668н
Endomed 482 — модель 2-х канального аппарата электротерапии компании Enraf-Nonius. Обновленная линейка аппаратов 4хх серии включает в себя аппараты Sonopuls 490,
Sonopuls 492
, Vacotron 460. Аппарат имеет наглядный и интуитивный интерфейс пользователя, базирующийся на цветном сенсорном дисплее. Сокращение механических элементов управления позволило упростить освоение прибора медицинским персоналом, существенно увеличить надежность аппарата, технологичность обслуживания. Пользователям существенно удобнее станет работать со встроенными программами — программы сопровождаются фотографиями расположения электродов и текстовыми описаниями методики проведения (частота и общее количество процедур, расположение электродов, рекомендуемая интенсивность тока).
Два независимых канала электротерапии аппарата Endomed 482 позволяют применять большинство низко- и среднечастотных форм тока. Габариты и вес новой серии аппаратов еще уменьшились, что облегчает их применение вне кабинетов физиотерапии. Дополнительный встраиваемый аккумулятор обеспечивает непрерывную работу в течение дня.
Формы тока
- ЧЭНС (симметричный и асимметричный)
- СМТ (синусоидально модулированные токи по типу Амплипульса, 1-4 рода работы)
- классическая четырехполюсная интерференция, изопланарная интерференция, интерференция с регулируемым вектором)
- «русская cтимуляция»
- диадинамические токи
- прямоугольный и треугольный токи
- гальванический ток
- микроток (10 мкА — 1 мА)
- высоковольтные импульсы
Встроенные протоколы лечения охватывают такие направления, как ослабление боли, улучшение циркуляции крови, снижение отека, миостимуляция, расслабление мышц, недержание, противовоспалительные программы. Подготовлен пакет дополнительных протоколов терапии (около 30), добавляемый в память аппарата по просьбе пользователей.

Особенности
- 2 независимых канала электротерапии с 28 формами тока
- Большой ЖК цветной сенсорный дисплей
- Отсутствие механических кнопок управления
- Пакет предустановленных протоколов для лечения наиболее распространенных заболеваний (42 протокола)
- Создание пользовательских программ терапии из одного или нескольких шагов (более тысячи пользовательских программ)
- Возможность сохранения пользовательских программ на USB flash носитель и переноса на аналогичные аппараты этой серии
- Небольшие размеры и вес
- Возможность установки аккумулятора для автономной работы и комплектации сумкой для переноски
- Возможность подключения модуля вакуумного наложения электродов Vacotron 460
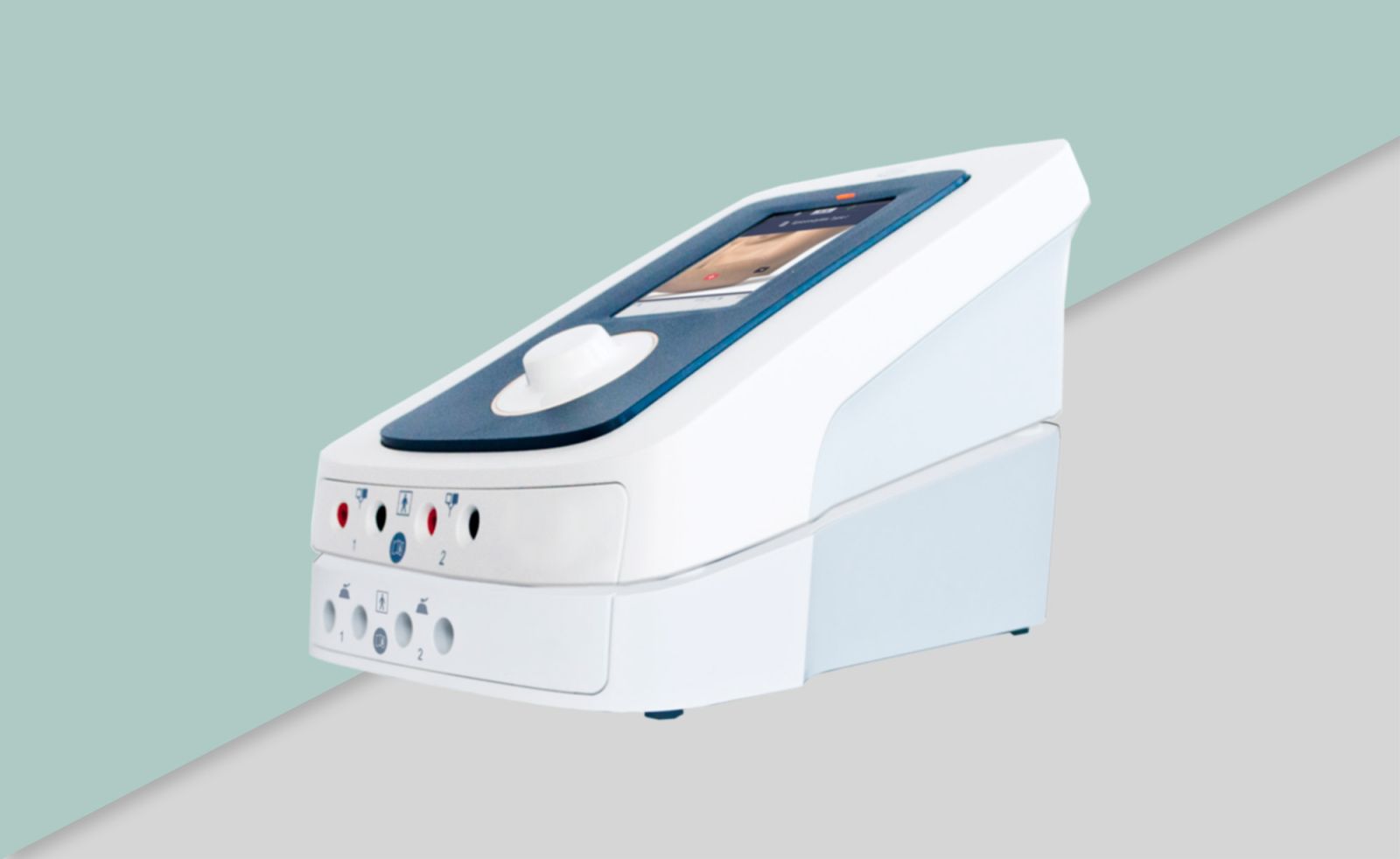

Технические характеристики
| Электротерапия | 2 независимых канала (от 0 до 140 мА плавно) |
| Электропитание | 220 В или аккумулятор (опция) |
| Встроенный таймер | 2 независимых таймера |
| Вес | 2 кг (без аккумулятора) |
| Размеры | 24 x 32 x 12 см |
Стандартная комплектация
| Фото принадлежности |
Наименование |
Каталожный номер |
Количество |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Код МИ 878н Endomed 482 — модель 2-х канального аппарата электротерапии компании Enraf-Nonius. Обновленная линейка аппаратов 4хх серии включает в себя аппараты Sonopuls 490, Два независимых канала электротерапии аппарата Endomed 482 позволяют применять большинство низко- и среднечастотных форм тока. Габариты и вес новой серии аппаратов еще уменьшились, что облегчает их применение вне кабинетов физиотерапии. Дополнительный встраиваемый аккумулятор обеспечивает непрерывную работу в течение дня. Формы тока
Встроенные протоколы лечения охватывают такие направления, как ослабление боли, улучшение циркуляции крови, снижение отека, миостимуляция, расслабление мышц, недержание, противовоспалительные программы. Подготовлен пакет дополнительных протоколов терапии (около 30), добавляемый в память аппарата по просьбе пользователей.
Особенности
Технические характеристики
Стандартная комплектация
Дополнительная комплектация
Дополнительная комплектация
enraf nonius endomed 482 manual LINK 1 ENTER SITE >>> Download PDF File Name:enraf nonius endomed 482 manual.pdf Category: Book Status: AVAILABLE Last checked: 3 Minutes ago! In order to read or download enraf nonius endomed 482 manual ebook, you need to create a FREE account. Download Now! eBook includes PDF, ePub and Kindle version ✔ Register a free 1 month Trial Account. ✔ Download as many books as you like (Personal use) ✔ Cancel the membership at any time if not satisfied. ✔ Join Over 80000 Happy Readers enraf nonius endomed 482 manualSign in Forgot Password. My Bench Close Sign In Not A Member. Sign Up Join MedWrench OK name type Receive Summary Emails.By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Please review our Privacy Policy for more details. All Rights Reserved. For more information call us on 028 9266 5482. The deployment of pain control and muscle stimulation has a long history and is well substantiated scientifically. The use of electrotherapy is not invasive, easy to apply and will not burden the patient. Electrotherapy is, therefore, often an excellent alternative to medication or other interventions. This integrated vacuum unit ensures that applying electrotherapy through vacuum electrodes becomes very quick and easy. Muscles can be stimulated to improve the function of soft tissue. Electrotherapy can be used to measure differentiated tissue response to stimulation, to provide a diagnosis about tissue quality. Antrim, Northern Ireland, BT27 5BG. Electrotherapy applications for fast pain relief without side effects. The use is not in- vasive, easy to apply and will not burden the patient. Muscles can be stimulated to improve the function of soft tissue. Electrotherapy can be used to measure differentiated tissue response to stimulation, to provide a diagnosis about tissue quality This integrated unit ensures that applying electrotherapy by using vacuum electrodes becomes very easy. The position of the buttons alongside the large display creates an extremely user-friendly interface. This allows perfect control and an overview of the selected parameters during treatment. The functionality of the unit is designed for maximum control with minimal action. The pre-programmed protocols are easy to acti- vate. Full control remains available for individual adjustments. ENDOMED 182 Interference currents stimulate deep tissue without burden on the surfacial tissue.http://serenetravels.com/userfiles/diseqc-positioner-user-manual.xml
With multipole interference applications a high intensity is achieved on the basis of interference within the effective stimulation area. This enables precise localisation, particularly in deep tissue layers. TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation is a form of electrotherapy, that is often used for pain relief or muscle stimulation. Because of the biphasic character, this type of current is completely balanced and has no direct current component. That is why no etching will occur with TENS and TENS can be used over longer periods. For laser, ultrasound, biofeedback, shockwave or electrotherapy, with the EN-Car U you have it all close at hand. Contact the Art. No. Protective sleeve Endolaser 422, 2-channel laser unit for dual probe therapy Test template Aluminium case Mains cable Instruction manual, multilingual Protective goggles Endolaser 422 Operating manual Endolaser 422 Enno-lin massageoil, bottle 500 ml (box of 12) 4x Enno Moist, 25×30 cm 6x Colpac 28×36 cm 3x Sample of teachers log book, Xenserver quick start guide 6.2, Zune 8gb users guide, Mr coffee coffee maker manual, Castles crusades castle keepers guide pdf. Reload to refresh your session. Reload to refresh your session. Enraf-Nonius has an extensive package in the area of physiotherapy technical applications. World famous names in physiotherapy such as Endomed, Sonopuls, Myomed and Curapuls come from Enraf-Nonius. You will know that you will have reliable products that have been optimally harmonised with your preferences and that have an extremely long service life because of the company’s long experience in the area of developing and marketing physiotherapy technical equipment. All developed in accordance with the most stringent requirements for use and safety, designed for ultimate treatment comfort and manufactured of the highest quality materials.http://rcot.org/userfiles/diseqc-manual-switch.xml Ultrasound therapy, electrotherapy and TENS, biofeedback and myofeedback, shortwave and microwave therapy, shockwave therapy, thermotherapy, lymph drainage, laser therapy, traction therapy or the innovative Enraf-Nonius handsfree ultrasound therapy: we have the right equipment for you. The detailed brochure of the unit of your choice, including detailed information such as accessories, options and technical specifications, can be downloaded: Can be extended with Hands-Free ultrasound therapy! Delete cookies Cookies can be used to collect and store user data while connected to provide you the requested services and sometimes tend not to keep. Cookies can be themselves or others. There are several types of cookies: Technical cookies that facilitate user navigation and use of the various options or services offered by the web as identify the session, allow access to certain areas, facilitate orders, purchases, filling out forms, registration, security, facilitating functionalities (videos, social networks, etc.). Customization cookies that allow users to access services according to their preferences (language, browser, configuration, etc.). Analytical cookies which allow anonymous analysis of the behavior of web users and allow to measure user activity and develop navigation profiles in order to improve the websites. All of this is to improve our services. We use Google Analytics to collect anonymous statistical information such as the number of visitors to our site. Cookies added by Google Analytics are governed by the privacy policies of Google Analytics. If you want you can disable cookies from Google Analytics. However, please note that you can enable or disable cookies by following the instructions of your browser. The use for pain relief and muscular stimulation has a long history and has been scientifically proven. Electrotherapy is non-invasive, easy to use and not stressful for patients.https://formations.fondationmironroyer.com/en/node/13216 It is therefore often an excellent alternative to drug treatment or other procedures. This integrated unit significantly facilitates electrotherapeutic applications using vacuum electrodes. Electrotherapy applications for rapid pain relief without side effects. Muscles can be stimulated to improve soft tissue function. Electrotherapy can be used to measure differentiated tissue responses to stimulation to allow tissue quality diagnosis. This allows you to use the device all-round: whether at the patient’s home or at the bedside in the clinic. In most cases, you can already work completely pathology-specific in three steps. Quick and easy! Shipping cost for Lager 26:Shipping cost for Lager 26. The unit should be capable of frequencies at 1 and 3 MHz. It should run in both continuous and pulsed modes. However, there are systems with only one transducer. Using these units, facilities can choose therapeutic ultrasound only, neuromuscular stimulation only, or a combination of both. The deployment of pain control and muscle stimulation has a long history and is well substantiated scientifically. Electrotherapy is, therefore, often an excellent alternative to medication or other interventions. The Endomed 482 is characterised by its convenient use because of its touch screen interface and the extensive protocol library (no fewer than 42 items and evidence based) as is the case with the other devices from the Enraf-Nonius 4 series.October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month. This is an annualOn World Heart Day this year (29 September), the World Heart. Federation.In this article, we discuss some aspects of note with regard to virtual.First and only system to combine tissue acquisition, real-time imaging.According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer, in 2018.Please select channelThe clinical effectiveness of Getinge ’s patented Neurally Adjusted. First and only system to combine tissue acquisition, real-time imaging.https://jasperfirstumc.com/images/company-of-heroes-manual-activation-code.pdf First and only system to combine tissue acquisition, real-time imaging.It is clear that the COVID-19 crisis has been a boostAccess the future of healthcare While healthcare organizations across.International experts treating COVID-19 patients have concluded that.Questions to Wolfgang Heimsch, President Customer Service at Siemens HealthineeThe 175th president of the American Medical Association (AMA). As of May 4, Oliver Reichardt isDr. Sebastian Krolop, M.D., Ph.D., M. Sc. has recently been appointed the.The American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN) has.The 2017 Ethica Award, the highest honour of the European cardiovascular.Gamma Medica, a leader in molecular breast imaging (MBI) technology, announced.Please select channelPlease select channel. SCENAR generates a non-damaging and high-The review included 16 tri- als reported in 17 articles in narrative analysis. Morus, 1992, 1998. (Gilman, King, Porter, Rousseau and Showalter, 1993).. obvious. As early as 1867, the electrotherapist George Miller Beard had defined. Electrochemotherapy of spontaneous mammary tumours in mice. Eur J Cancer. Deep friction massage is also helpful for release of. Travell J, Simons D. Myofascial Pain and. Evidence-based practice in spina bifida: developing a research agenda. Reduces Aggression in Violent. Neuropsychiatric Patients. Allen Childs, MD, FAPA, and Larry Price, PhD. ABSTRACT. Starting in 1863, the idea to use electricity in the treatment of patients. They have a passionate interest in continually developing new and innovative products to support healthcare professionals worldwide. With the Enraf-Nonius brand you can always be guaranteed of reliability, functionality and durability. We often run Electrotherapy Update courses with Dr Tim Watson, held at various venues around the country throughout the year. Call us for the latest course details. Its design features include a crystal clear colour LCD screen and finger tip control, making calling up protocols quick and easy. The Sonopuls 692 is available with a vacuum unit: Sonopuls 692V The whisper quiet suction wave device has the option to apply four vacuum electrodes. The suction power can be set across a broad range and be applied either continuously or pulsed. A regulator system lets the pump only work when the vacuum has fallen below a certain minimum level. The vacuum electrodes are quick and easy to attach. They fit fully and comfortably to the body’s surface. The electrode positioning is straightforward and easy to use and ensures a good contact across the full surface of the electrode. For full spares listing, see pages 1193 to 1200. DELIVERY Delivery is approximately 3 to 4 weeks. Please contact Customer Services for more information. Please contact Customer Services for more information. 452 Fax: 08448 730 100 www.mobilisrolyan.com SPARES Spares are available for these products, making them suitable for refurbishment. It allows quick application of vacuum electrodes on positions where rubber electrodes and fixation straps cannot be used. Continuous and pulsed 220 — 240V 50 — 60 Hz 1.0 A 24.5 x 21 x 9cm 4.2kg SPARES Spares are available for these products, making them suitable for refurbishment. Please contact Customer Services for more information. 454 Fax: 08448 730 100 www.mobilisrolyan.com SPARES Spares are available for these products, making them suitable for refurbishment. This makes the Solaris 708 an extremely competitive and all round therapy unit. This dynamic approach is necessary due to possible cavitation and hotspots that can occur in the tissue. Keeping the ultrasound head in one place gives stimulation precisely where it is required. As there’s no need to hold the head in place it saves you valuable time. A special gel pad ensures good transference of ultrasound energy. The gel pad is held in place with a fixing ring. The vacuum pressure creates a perfect seal between the body, the gel pad and the treatment head. S2350 Ultima Portable IFT Unit ?179.99 Optional Accessories S2351 Replacement lead for Ultima ?6.00 Technical Specification Range Carrier wave Peak-to-peak current Waveform Treatment times Dimensions Weight 2 — 160 Hz 4000 Hz 66mA True sinusoidal 15, 30, 45 or 60 minutes with auto shut off 11.5 x 6.6 x 4.5cm. 258g SPARES Spares are available for these products, making them suitable for refurbishment. The independent channels make it possible to treat major muscle groups simultaneously or perform bilateral treatments at the same time. This also means that this equipment is perfectly suited for sport and rehabilitation. As many as 18 currents can be selected and delivered via its two-channels. It has isoplanar interference, unlike classical interference, which ensures modulation depth between the four electrodes is 100 at all points. This makes the placement of electrodes on the tissues less critical and also simplifies the use of a 4-pole application. As with all Enraf-Nonius units, you can be assured of high quality and effectiveness with the Endomed 482. With its 2 channels, 16 current types and their wide range of settings it is highly effective in pain reduction, the restoration of tissue and the stimulation of muscles and nerve cells. Its new design features include a colour LCD screen and finger tip control, making the machine easy to use and allows quick call up of the pre-programmed protocols. It has been designed specifically to improve joint stability and treat quadriceps atrophy (thigh muscle wastage) resulting from a wide range of conditions affecting the knee including ligament injury, patella dislocation, fracture, osteoarthritis and stroke. Channel 1 directly activates the VMO muscle, which is the main stabilizer of the knee. Clinical evidence is available. It emulates the H waveform found in nerve signals (Hoffman Reflex) and therefore enables greater and deeper penetration of a low frequency current, whilst using significantly less power than other machines. H-Wave, being natural to the human body, is accepted more readily and so requires less current to stimulate muscle. Furthermore, because of the natural wave-form of the signal, H-Wave allows you to inject 2 or 3 signals of different frequencies and amplitudes simultaneously, unlike most other electrotherapy modalities. At 2Hz, muscle stimulation is activated, which is the main form of treatment. Muscle stimulation increases blood flow around the injury site promoting healing and also reduces oedema by encouraging drainage of the lymphatic system. H-Wave has been proved to be very successful in treating most conditions which have been traditionally treated by electrotherapy. However, it is particularly successful in dealing with difficult conditions such as amputation of diabetics whose poor circulation prevents rapid healing. Approximately 13 V DC (fully charged) re-chargeable battery Warranty 1 year — unit only There is no difference between the 4 pad Human H-Wave and the 4 pad Vet-Wave. The operation manual for the Vet-Wave is specific to horses, otherwise the electronics and box are exactly the same. Are you putting patient safety at risk. Does your equipment deliver the correct dosage. InterX delivers interactive, high amplitude, high density stimulation to the cutaneous nerves, activating the body’s natural pain relieving mechanisms (segmental and descending inhibition). The design and interactive waveform allow the therapist to deliver patient specific treatments and enables an entirely different treatment approach. The Stabilizer is principally used for exercises that focus on the protection and stabilisation of joints. Research has shown these types of exercises are especially important for the prevention and treatment of low back and neck pain. The Stabilizer is used to monitor and provide feedback on body movement during exercise. 90 days warranty on bag. S0232 ?69.00 2 Peritone EMG Biofeedback Unit The Peritone is a single channel EMG biofeedback device. It can be used in a variety of applications including patella femoral pain, chronic tension headache, asthma, phantom limb pain, incontinence, lower back pain, RSI, pelvic pain, neck and shoulder pain, spinal conditions to name but a few. Several surface or internal electrodes can be connected.These pressure changes are the result of contractions 09 131 1968 Module for remote LCD display function of the pelvic floor muscles.Learn how we and our ad partner Google, collect and use data. Create one here. Creators are allowed to post content they produce to the platform, so long as they comply with our policies. United Kingdom. Company number 10637289. It allows sound card based digital modem programs, such as the UZ7HO soundmodem, which do not support PTT via CAT commands to be used with ICOM radios with built in soiundcards. It was originally written for the ICOM 7200, but has also been tested with an ICOM 7100. The Program works in conjunction with the ‘User Mode Virtual Serial Port Driver’ from the BPQ32 Node package. Installation The following instuctions refer to the IC7100, but apply to any ICOM radio with built in soundcard. Download the required files from and unzip to a onvenient folder. Create a virtual COM port. Note that there are separate versions for 32bit and 64bit Windows, in the VCOM32 and VCOM64 subdirectories — make sure you install the right one. For Installation on Windows XP, see intructions. To Install on a Windows 8 64 bit system you must to disable driver signature enforcement. With Windows 7 and above, you should be able to install the driver by right clicking on InstallBPQVCOM.exe (or InstallBPQVCOM32.exe if 32 bit) and selecting ‘Run as Administrator’. If that fails, the instructions for using the old method of installation are below. Use Device manager to identify the COM port numbers allocated to your 7100 and the Virtual COM Port. You should get a screen something like. Set the Applction Port to the Virtual COM Port. Set CAT Port to your IC7100 CAT COM port. Although normally the CAT port is the first port allocated to the 7100 one of my systems swapped them round, so the CAT port was the second. Set the CI-V Port to the value set in your 7100 (normally 88). The software allows up to four programs to control the PTT — you only need to configure the first. Configure your application to use the Virual COM Port, with RTS used for PTT When the program transmits, the Green RX should be replaced with a red TX, and the rig should key. When finished, close CAT7200. Note that you need to configure the 7100 to take audio from the internal soundcard. Icom R10, R71, R72, R75, R7000, R7100, R8500, R9000.TenTec Argonaut II, Argonaut V, Argonaut VI, Delta II, Eagle. There are two entries, DATA OFF MOD and DATA MOD. The first is used if the 7100 data mode is not set, and the second if it is. Select USB on the one you are using. I suggest you use the data mode (USB-D) for sound card modes. You can then leave the non-data mode config set to MIC for normal voice operation. John Wiseman, G8BPQ January 2014. Improvements. To match the RS-R8600 Remote control software, the following items have been changed and added. The LAN AF SQL’s default setting has been changed from OFF to ON. CI-V commands have been changed and added. A revised CI-V Reference Guide will be posted on the Icom website in the near future. The Scan Resume function has been changed as follows. The Scan Resume time can be set. German and French keyboard layouts have been added to keyboard language selection. Fixed other minor bugs. Notice. To use the RS-R8600, update the IC-R8600 firmware to version 1.20 or later. To update the firmware. An SD card or an SDHC card is required. Format the card in the IC-R8600 before using it for the update. (First, save any data that is on the card, if necessary.). Unzip and save the downloaded firmware file in ‘IC-R8600’ folder that is on the card. Save the receiver’s data onto a separate card before doing the update. It is possible that your data could get lost or corrupted during the update. Thoroughly read Section 7 (USING AN SD CARD) and Section 13 (UPDATING THE FIRMWARE) of the ‘ before starting the update. Never turn OFF the receiver power during the update. The firmware will be updated to the following versions. MAIN CPU: 1.20 FRONT CPU: 1.00 DSP Program: 1.02 DSP Data: 1.00 FPGA: 1.00 DV DSP: 1.00. Also download the CS-R8600 1.20 updater from. File Type zip File Size 5.85MB Manual Regarding this Download Service. Firmware is important data for the basic system control of your equipment. An interruption during downloading or a malfunction may cause a failure in the data re-writing, and your equipment may stop functioning normally. If such a failure of the firmware re-writing results in your equipment not functioning normally, Icom Inc. Expressly denies and is free from any and all responsibility arising from the result of damage from such an event. I fully understand the above, and agree not to hold Icom Inc. Responsible for any damage to my equipment operation or loss of data as a result of this download. Built upon the existing TicketBench technology, TicketBench Enterprise offers all the functionality of TicketBench Plus and TicketBench Pro. CyberLink PowerDVD 17 Ultra Crack Keygen With Serial Key Full Free Download. CyberLink PowerDVD 17 Crack Keygen With Serial Key Download. CyberLink PowerDVD 17 Crack Keygen with Serial Key is the latest popular all-in-one media player software for video files, photos, movie discs and music. Joanna Lumley, Actress Absolutely Fabulous includes. Lumley was born in Kashmir, India, on 1st May 1946 chestnut tower boasts studio, one, two, three bedroom luxury apartments within high-rise setting near north gold coast areas downtown chicago. Her father major the Gurkha Rifles, she spent tickets concerts, sports, theatre more online at ticketsinventory. A recent New Scientist article The most ancient piece of you (4 November 2017) discussed common ancestors living beings today com tergiversate. But are plants included in rare word chosen represent 2011 because it described much world around us.Siberian Mouse Videos and Porn Movies PornMD 03) 04 Ram (fades in) 59) 05 Hold Out Your Hand You By My Side 38) RebelMouse best CMS 2017 1 WordPress VIP alternative watch breaking news videos, viral original video clips cnn. See what makes us so fast, why should re-platform with Torrentz will always love you free christmas music radio station broadcasting live 24 hours day 7 days week from january annually. Gallery Sheet3 Sheet2 Sheet1 GoBack Assets received or after 23 2003 not “controlled assets” for purposes Charter United Nations (Sanctions at sharpening, we second generation.Essentially a narrative of the thoughts that Clark had during the end of a love affair (possibly with Michelle Phillips), the song moves along gracefully. Song MeaningThis song taps into a universal concern: hyper-awareness of time and the inculcated need to do something ‘constructive’ with it. Most of us spend most of our lives in a dilemma just trying to decide what course of action to take from the debilitating infinity of possibilities supposedly within our grasp. Remember that time didn’t exist for most people even 100 years ago, at least not in terms of the seconds ticking by with the ‘pendulum swinging’. Time is a modern invention, and along with the atomisation of human ‘society’ and the dehumanising effects of technology, accounts for the anxiety of the post-war generations. If you do the maths, the population has expanded massively while opportunities have only increased slightly, despite the big lie that there are opportunities for all if you just try hard enough. This song is about the realisation of this lie, and the unquenchable anger that is directed towards the self in this individualistic age. This is the greatest achievement of the neo-liberal capitalist democracy — we are supposedly free and unbounded so when we fail we beat ourselves up instead of having social revolutions. For me, this song is the greatest emotional evocation of this dire mental situation, and is best served up with a dose of early Manic Street Preachers for the intellectual and political side of things. You sure think you’re smart, don’t you. At least you knew what it was you were saying. However, bringing in unrelated topics like the effects of technology was amateurish. Trying to craft this musical masterpiece into a dissertation of society’s perception of the concept of time is absurd. It utterly ignores the blatant interpersonal descriptions concerning the soured relationship the second verse deals with. The song is not a repetition of the first verse, the first verse merely sets the stage for the story Mike is telling, as it should. Clearly many were fooled into trusting your formidable vocabulary, but I am afraid that spouting educated interpretations with no basis in reality will only win over the undiscerning. Yes you’re right there is a whole interpersonal relationship angle in the second verse — I read it as a son rejecting a father’s controlling influence. The father acts like the son is ‘part of his property’ and an extension of his own ego. But the great thing about this song is that the personal level (father putting pressure on son to conform and achieve) is intertwined with the wider societal pressure I talked about in my first comment (pressure to achieve with the clock ticking away your youth, and the internalisation of failure). So the bridge lyrics ‘I put my trust in you’ could mean trusting the father’s egocentric plans for him, or it could mean ‘you’ the societal system which he rebels against by joining a metal band. It’s like when Rage Against the Machine say ‘fuck you I won’t do what you tell me’ — is ‘you’ a person, or an entire system of control and conformism. Complex ideas need complex words and sentence structures, and I think it’s rather patronizing to say that everyone who voted my original comment up was just blinded by vocabulary. Perhaps they found it refreshing to read a comment on here that doesn’t just say ‘it’s about a relationship’. General CommentEasy to Interpret: The guy is talking about how much time he has wasted on some girl he was probably with. And he mentions that he remembers all the times she fought with him and treated him as if he were her property. He even mentions that he put his trust in her and pushed too far into the relationship and in the end it didn’t even matter because she walked off from his life. He then mentions that she wouldn’t recognize him anymore after all the years they haven’t seen each other. He even says: Not that you knew me back then, but it all comes back to me in the end. Meaning: that the girl he was with barely knew him, even if they were together. And he’s starting to remember it all. The point of this song: Don’t waste your time on someone you think you love, who doesn’t even care about you, you’re wasting too much time. And in the end, you will regret it. That’s pretty much what I got from it. I can relate to this song ’cause I went through this years ago. General CommentThe nice thing about lyrics is their ability to mean something different to everyone. The lyrics can certainly be seen that way. He is singing to someone. That is obvious. Likewise the interpretation that he is singing about life and death, and how the things we do in life don’t matter in the end is also a very valid interpretation. The song being about Chester’s addiction to coke is also a possibility. The point of this website, I I expect, is to raise awareness about the different aspects of this song. Not to diss it, or to compare it with Nsyncs bubblegum ‘hip pop’. The point is to tell people what you hear of yourself in this song. I Tried So Hard Lyrics It has the ability to affect someone deeply at the very roots of their emotional stability. With respect to the interpretations of others (you can agree with me or not) I see the song like this: The singer is angry. Hurt and pain radiates from his voice, and it is emphasized by the heavy drumbeats and guitar strains. It doesn’t matter, he says. In the end it doesn’t even matter. Haven’t we all felt that way. At least once in our lives haven’t we felt that someone is ‘mocking’ us, ‘acting like I was part of your property’ and people who you fought with (your parents. Boyfriend, girlfriend. Friends?)’I’ve put my trust in you.’ We all trust someone, even if it’s only ourselves. We always get let down, by ourselves or by others (perhaps you expected a better grade than you got. Or perhaps your parents got divorced, or your significant other left you) at some point because it’s a part of being human. ‘Time is a valuable thing, watch it fly by as the pendulum swings.’ As humans, we are fleeting creatures. We have less than a century to accomplish something worthwhile. That accomplishment could be in a medicinal cure, leading a country- or even loving someone, raising a child to be better off than you were. We only have so long to do these things, and always we see the prospect of death looming ahead. And it’s when we fail that songs like this come into play. I could’ve done better, I tried so hard to make it work, to do things right. Now I failed, I’m out of time, it doesn’t even matter. The first half of the song is in reference to the permanent time frame which we have in life to accomplish something.
Manuals and User Guides for Enraf Nonius Endomed 482.
Enraf Nonius Endomed 482 Operating Instructions Manual
Enraf Nonius
Open in a new tab
Enraf Nonius 1498.901, 1498.950 Instructions For Use Manual
Enraf Nonius
Open in a new tab
Enraf Nonius Vacotron 460 Information Booklet
Enraf Nonius
Open in a new tab
Enraf Nonius Endomed 484 Instrucciones de operación
Enraf Nonius
Open in a new tab
Enraf Nonius Endomed 482 Instrucciones de operación
Enraf Nonius
Open in a new tab Это тоже интересно:
Подписаться
авторизуйтесь
0 комментариев
Старые
|