Generic name: meloxicam [ mel-OKS-i-kam ]
Brand names: Anjeso, Mobic, Vivlodex
Drug class: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
What is Mobic?
Mobic is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It works by reducing hormones that cause pain, fever, and inflammation in the body.
Mobic is used to relieve pain, tenderness, swelling, and stiffness caused by osteoarthritis (arthritis caused by a breakdown of the lining of the joints) and rheumatoid arthritis (arthritis caused by swelling of the lining of the joints).
Mobic is also used to relieve the pain, tenderness, swelling, and stiffness caused by juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (a type of arthritis that affects children) in children 2 years of age and older.
Warnings
Mobic can increase your risk of fatal heart attack or stroke, especially if you use it long term or take high doses, or if you have heart disease. Even people without heart disease or risk factors could have a stroke or heart attack while taking this medicine.
Do not use this medicine just before or after heart bypass surgery (coronary artery bypass graft, or CABG).
Get emergency medical help if you have chest pain, weakness, shortness of breath, slurred speech, or problems with vision or balance.
Mobic may also cause stomach or intestinal bleeding, which can be fatal. These conditions can occur without warning while you are using this medicine, especially in older adults.
Call your doctor at once if you have symptoms of stomach bleeding such as black, bloody, or tarry stools, or coughing up blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds.
Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol as they also increase your risk of stomach bleeding.
Before taking this medicine
Mobic can increase your risk of fatal heart attack or stroke. Do not use this medicine just before or after heart bypass surgery (coronary artery bypass graft, or CABG).
Mobic may also cause stomach or intestinal bleeding, which can be fatal. These conditions can occur without warning while you are using meloxicam, especially in older adults.
You should not use Mobic if you are allergic to meloxicam, or if you ever had an asthma attack or severe allergic reaction after taking aspirin or an NSAID.
To make sure Mobic is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have ever had:
-
heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or if you smoke;
-
a heart attack, stroke, or blood clot;
-
ulcers or stomach bleeding;
-
asthma;
-
kidney disease (or if you are on dialysis);
-
liver disease; or
-
fluid retention.
If you are pregnant, you should not take Mobic unless your doctor tells you to. Taking an NSAID during the last 20 weeks of pregnancy can cause serious heart or kidney problems in the unborn baby and possible complications with your pregnancy.
Mobic may cause a delay in ovulation (the release of an egg from an ovary). You should not take Mobic if you are undergoing fertility treatment, or are otherwise trying to get pregnant.
Ask a doctor if it is safe to breastfeed while using this medicine.
Mobic tablets are not approved for use in children weighing less than 132 lb (60 kg).
How is Mobic given?
Take Mobic exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow all directions on your prescription label and read all medication guides or instruction sheets. Use the lowest effective dose for your condition.
If you use Mobic long-term, you may need frequent medical tests.
Store Mobic tablets at room temperature, away from moisture and heat. Keep the bottle tightly closed when not in use.
Dosing Information
Usual Adult Dose for Osteoarthritis:
Oral Tablets:
-Initial dose: 7.5 mg orally once a day
-Maintenance dose: 15 mg orally once a day in patients requiring additional analgesia
-Maximum dose: 15 mg orally once a day.
Usual Adult Dose for Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Oral Tablets:
-Initial dose: 7.5 mg orally once a day
-Maintenance dose: 15 mg orally once a day in patients requiring additional analgesia
-Maximum dose: 15 mg orally once a day.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis:
2 years or older:
Oral Tablets:
Weight: 60 kg or greater: 7.5 mg orally once a day
-No additional benefit has been demonstrated with doses above 7.5 mg/day.
Comments:
-Oral formulations have not shown equivalent systemic exposure and are not considered interchangeable
-The oral tablets should not be used in children who weigh less than 60 kg.
What happens if I miss a dose?
Use the medicine as soon as you can, but skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next dose. Do not use two doses at one time.
What happens if I overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
What should I avoid while receiving Mobic?
Drinking alcohol may increase your risk of stomach bleeding.
Avoid taking aspirin while you are taking Mobic, unless your doctor tells you to.
Ask a doctor or pharmacist before using other medicines for pain, fever, swelling, or cold/flu symptoms. They may contain ingredients similar to Mobic (such as aspirin, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, or naproxen).
Mobic side effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction to Mobic (hives, difficult breathing, swelling in your face or throat) or a severe skin reaction (fever, sore throat, burning eyes, skin pain, red or purple skin rash with blistering and peeling).
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of a heart attack or stroke: chest pain spreading to your jaw or shoulder, sudden numbness or weakness on one side of the body, slurred speech, leg swelling, feeling short of breath.
Meloxicam may cause serious side effects. Stop using Mobic and call your doctor at once if you have:
-
the first sign of any skin rash, no matter how mild;
-
shortness of breath (even with mild exertion);
-
swelling or rapid weight gain;
-
signs of stomach bleeding — bloody or tarry stools, coughing up blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds;
-
liver problems — nausea, upper stomach pain, itching, tired feeling, flu-like symptoms, loss of appetite, dark urine, clay-colored stools, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes);
-
low red blood cells (anemia) — pale skin, unusual tiredness, feeling light-headed, cold hands and feet; or
-
kidney problems — little or no urination, swelling in your feet or ankles, feeling tired or short of breath.
Common Mobic side effects may include:
-
stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, heartburn;
-
diarrhea, constipation, gas;
-
dizziness; or
-
cold symptoms, flu symptoms.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What other drugs will affect Mobic?
Ask your doctor before using Mobic if you take an antidepressant. Taking certain antidepressants with an NSAID may cause you to bruise or bleed easily.
Tell your doctor about all your other medicines, especially:
-
cyclosporine;
-
lithium;
-
methotrexate;
-
pemetrexed;
-
sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate);
-
a blood thinner (warfarin, Coumadin, Jantoven);
-
heart or blood pressure medication, including a diuretic or «water pill»; or
-
steroid medicine (such as prednisone).
This list is not complete. Other drugs may interact with meloxicam, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Not all possible drug interactions are listed here.
Popular FAQ
Meloxicam is a once-daily non-steroid antiinflammatory drug (NSAID) that you can take by mouth at any time of the day. Try to take your medicine at the same time each day with food or a meal to help prevent an upset stomach. The manufacturer states you can take it with or without meals, but if it causes you stomach upset, you should take it with a meal. Take this medicine exactly as prescribed, at the lowest dose possible for your treatment, and for the shortest time period needed.
Continue reading
Common antidepressants used for orthopedic pain relief may include SSRIs like fluoxetine (Prozac), paroxetine (Paxil), and sertraline (Zoloft), SNRIs such as duloxetine (Cymbalta), or tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) like amitriptyline (Elavil) or nortriptyline (Pamelor). Continue reading
At lower doses, meloxicam is more similar to Celebrex (celecoxib) than it is to other NSAIDs, like ibuprofen or naproxen, because it is relatively selective for the COX-2 enzyme. But at higher doses, even within the prescribed range, meloxicam can inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, which may lead to side effects like stomach ulcers or bleeding. COX-2 selectivity is a dose-related effect. Continue reading
More FAQ
- Meloxicam vs Ibuprofen, what’s the difference?
- Can I take Meloxicam and Aleve or Tylenol together?
- Which painkiller should you use?
- How long do I wait after taking ibuprofen to take meloxicam?
- Can meloxicam cause drowsiness and headache?
- Is meloxicam a narcotic?
View more FAQ
Further information
Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use Mobic only for the for the indication prescribed.
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Medical Disclaimer
Copyright 1996-2023 Cerner Multum, Inc. Version: 16.01.
Мелоксикам (Meloxicam) инструкция по применению
📜 Инструкция по применению Мелоксикам
💊 Состав препарата Мелоксикам
✅ Применение препарата Мелоксикам
📅 Условия хранения Мелоксикам
⏳ Срок годности Мелоксикам
Описание лекарственного препарата
Мелоксикам
(Meloxicam)
Основано на официально утвержденной инструкции по применению препарата и подготовлено для электронного издания справочника Видаль 2011 года, дата обновления: 2019.11.26
Владелец регистрационного удостоверения:
Код ATX:
M01AC06
(Мелоксикам)
Лекарственные формы
| Мелоксикам |
Таб. 7.5 мг: 10, 20 или 30шт. рег. №: ЛС-001708 |
|
|
Таб. 15 мг: 10, 20 или 30 шт. рег. №: ЛС-001708 |
Форма выпуска, упаковка и состав
препарата Мелоксикам
Таблетки светло-желтого с зеленоватым оттенком цвета, плоскоцилиндрические, с фаской.
Вспомогательные вещества: крахмал картофельный 33.4 мг, кремния диоксид коллоидный (аэросил) 4.4 мг, лактозы моногидрат 165 мг, магния стеарат 2.2 мг.
10 шт. — упаковки ячейковые контурные (2) — пачки картонные.
10 шт. — упаковки ячейковые контурные (1) — пачки картонные.
10 шт. — упаковки ячейковые контурные (3) — пачки картонные.
Таблетки светло-желтого с зеленоватым оттенком цвета, плоскоцилиндрические, с фаской.
Вспомогательные вещества: крахмал картофельный 16.7 мг, кремния диоксид коллоидный 2.2 мг, лактозы моногидрат 82.5 мг, магния стеарат 1.1 мг.
10 шт. — упаковки ячейковые контурные (2) — пачки картонные.
10 шт. — упаковки ячейковые контурные (1) — пачки картонные.
10 шт. — упаковки ячейковые контурные (3) — пачки картонные.
Клинико-фармакологическая группа:
НПВС
Фармако-терапевтическая группа:
НПВП
Фармакологическое действие
Мелоксикам — нестероидный противовоспалительный препарат, обладающий обезболивающим, противовоспалительным и жаропонижающим действием. Механизм действия связан с ингибированием синтеза простагландинов в результате избирательного подавления ферментативной активности циклооксигеназы-2 (ЦОГ-2), участвующей в биосинтезе простагландинов в области воспаления. При применении в высоких дозах, длительном применении и индивидуальных особенностях организма ЦОГ-2 селективность снижается. Подавляет синтез простагландинов в области воспаления в большей степени, чем в слизистой оболочке желудка или почках, что связано с относительно избирательным ингибированием ЦОГ-2. Реже вызывает эрозивно-язвенные изменения ЖКТ. В меньшей степени мелоксикам действует на циклооксигеназу-1 (ЦОГ-1), участвующую в синтезе простагландинов, защищающих слизистую оболочку ЖКТ и принимающих участие в регуляции кровотока в почках.
Фармакокинетика
Хорошо всасывается из желудочно-кишечного тракта, абсолютная биодоступность мелоксикама — 89%. Одновременный прием пищи не изменяет всасывание. При использовании препарата внутрь в дозах 7.5 и 15 мг его концентрации пропорциональны дозам. Равновесная концентрация достигается в течение 3-5 дней. При длительном применении препарата (более 1 года), концентрации сходны с таковыми, которые отмечаются после первого достижения устойчивого состояния фармакокинетики. Связывание с белками плазмы составляет более 99%. Диапазон различий между максимальными и базальными концентрациями препарата после его приема один раз в день относительно невелик и составляет при использовании дозы 7.5 мг 0.4-1.0 мкг/мл, а при использовании дозы 15 мг – 0.8-2.0 мкг/мл, (приведены, соответственно, значения Cmin и Cmax). Мелоксикам проникает через гистогематические барьеры, концентрация в синовиальной жидкости достигает 50% Cmax препарата в плазме. Почти полностью метаболизируется в печени с образованием четырех неактивных в фармакологическом отношении производных. Основной метаболит, 5′-карбокси-мелоксикам (60% от величины дозы), образуется путем окисления промежуточного метаболита, 5′-гидроксиметилмелоксикама, который также экскретируется, но в меньшей степени (9% от величины дозы). Исследования in vitro показали, что в данном метаболическом превращении важную роль играет CYP2C9, дополнительное значение имеет изофермент CYP3A4. В образовании двух других метаболитов (составляющих, соответственно, 16% и 4% от величины дозы препарата) принимает участие пероксидаза, активность которой, вероятно, индивидуально варьирует.
Выводится в равной степени через кишечник и почки, преимущественно в виде метаболитов.
Через кишечник в неизмененном виде выводится менее 5% от величины суточной дозы, в моче в неизмененном виде препарат обнаруживается только в следовых количествах. T1/2 мелоксикама составляет 15-20 ч. Плазменный клиренс составляет в среднем 8 мл/мин. У лиц пожилого возраста клиренс препарата снижается. Vd низкий, и составляет в среднем 11 л.
Печеночная или почечная недостаточность средней степени тяжести не оказывает существенного влияния на фармакокинетику мелоксикама.
Показания препарата
Мелоксикам
- симптоматическое лечение остеоартроза;
- симптоматическое лечение ревматоидного артрита;
- симптоматическое лечение анкилозирующего спондилита (болезнь Бехтерева), других дегенеративных заболеваний суставов, сопровождающихся болевым синдромом.
Режим дозирования
Препарат принимают внутрь во время еды в суточной дозе 7.5-15 мг.
Рекомендуемый режим дозирования:
Ревматоидный артрит: 15 мг в сут. В зависимости от лечебного эффекта доза может быть снижена до 7.5 мг в сут.
Остеоартроз: 7.5 мг в сут. При неэффективности доза может быть увеличена до 15 мг в сут.
Анкилозирующий спондилит: 15 мг в сут. Максимальная суточная доза не должна превышать 15 мг.
У пациентов с повышенным риском развития побочных эффектов, а также у пациентов с тяжелой почечной недостаточностью, находящихся на гемодиализе, доза не должна превышать 7.5 мг в сут.
Побочное действие
Частота побочных реакций, приведенных ниже, определялась соответственно следующему: очень часто (≥1/10); часто (≥1/100, <1/10); нечасто (≥1/1000, <1/100); редко (≥1/10000, <1/1000); очень редко (<1/10000, включая отдельные сообщения).
Со стороны пищеварительной системы: часто — диспепсия, в т.ч. тошнота, рвота, абдоминальные боли, запор, метеоризм, диарея; нечасто — преходящее повышение активности «печеночных» трансаминаз, гипербилирубинемия, отрыжка, эзофагит, гастродуоденальная язва, кровотечение из ЖКТ (в т.ч. скрытое), стоматит; редко — перфорация ЖКТ, колит, гепатит, гастрит.
Со стороны органов кроветворения: часто — анемия; нечасто — изменение формулы крови, в т.ч. лейкопения, тромбоцитопения.
Со стороны кожных покровов: часто — зуд, кожная сыпь; нечасто — крапивница; редко — фотосенсибилизация, буллезные высыпания, многоформная эритема, в т.ч. синдром Стивенса-Джонсона, токсический эпидермальный некролиз.
Со стороны дыхательной системы: редко — бронхоспазм.
Со стороны нервной системы: часто — головокружение, головная боль; нечасто — вертиго, шум в ушах, сонливость; редко — спутанность сознания, дезориентация, эмоциональная лабильность.
Со стороны сердечно-сосудистой системы: часто — периферические отеки; нечасто — повышение артериального давления, ощущение сердцебиения, «приливы» крови к коже лица.
Со стороны мочевыделительной системы: нечасто — гиперкреатининемия и/или повышение концентрации мочевины в сыворотке крови; редко — острая почечная недостаточность; связь с приемом мелоксикама не установлена — интерстициальный нефрит, альбуминурия, гематурия.
Со стороны органов чувств: редко — конъюнктивит, нарушение зрения, в т.ч. нечеткость зрительного восприятия.
Аллергические реакции: редко — ангионевротический отек, анафилактоидные/анафилактические реакции.
Противопоказания к применению
- гиперчувствительность к мелоксикаму или вспомогательным компонентам препарата; в состав входит лактоза, поэтому пациенты с редкими наследственными заболеваниями, такими как непереносимость лактозы, дефицит лактазы или глюкозо-галактозной мальабсорбцией не должны принимать препарат;
- состояние после проведения аортокоронарного шунтирования;
- декомпенсированная сердечная недостаточность;
- анамнестические данные о приступе бронхообструкции, ринита, крапивницы после приема ацетилсалициловой кислоты или иного НПВП (полное или неполное сочетание бронхиальной астмы, рецидивирующего полипоза носа и околоносовых пазух и непереносимости ацетилсалициловой кислоты или других нестероидных противовоспалительных препаратов (в т.ч. в анамнезе);
- эрозивно-язвенные изменения слизистой оболочки желудка или 12-перстной кишки, активное желудочно-кишечное кровотечение;
- воспалительные заболевания кишечника (язвенный колит, болезнь Крона);
- цереброваскулярное кровотечение или иные кровотечения;
- выраженная печеночная недостаточность или активное заболевание печени;
- хроническая почечная недостаточность у больных, не подвергающихся диализу (клиренс креатинина менее 30 мл/мин), прогрессирующие заболевания почек в т.ч. подтвержденная гиперкалиемия;
- беременность, период грудного вскармливания;
- детский возраст до 12 лет.
С осторожностью. ИБС, цереброваскулярные заболевания, застойная сердечная недостаточность, дислипидемия/гиперлипидемия, сахарный диабет, заболевания периферических артерий, курение, анамнестические данные о развитии язвенного поражения ЖКТ, наличие инфекции Helicobacter pylori, ХПН с клиренсом креатинина 30-60 мл/мин, пожилой возраст, длительное использование НПВП, частое употребление алкоголя, тяжелые соматические заболевания, сопутствующая терапия следующими препаратами:
- антикоагулянты (например, варфарин);
- антиагреганты (например, ацетилсалициловая кислота, клопидогрел);
- пероральные глюкокортикостероиды (например, преднизолон);
- селективные ингибиторы обратного захвата серотонина (например, циталопрам, флуоксетин, пароксетин, сертралин).
Для снижения риска развития нежелательных явлений со стороны ЖКТ следует использовать минимальную эффективную дозу максимально возможным коротким курсом.
Применение при беременности и кормлении грудью
Препарат не рекомендуется применять в период беременности и лактации.
Применение при нарушениях функции печени
Противопоказан при выраженной печеночной недостаточности или активном заболевании печени.
Следует соблюдать осторожность и контролировать показатели функции почек при применении препарата у пациентов с циррозом печени
Применение при нарушениях функции почек
Противопоказан при хронической почечной недостаточности у больных, не подвергающихся диализу (клиренс креатинина менее 30 мл/мин), при прогрессирующих заболеваниях почек в т.ч. подтвержденной гиперкалиемии.
С осторожностью: ХПН с клиренсом креатинина 30-60 мл/мин.
У пациентов с незначительным или умеренным снижением функции почек (клиренс креатинина более 30 мл/мин) не требуется коррекции режима дозирования.
Применение у детей
Противопоказан детям до 12 лет.
Применение у пожилых пациентов
Следует соблюдать осторожность и контролировать показатели функции почек при применении препарата у пациентов пожилого возраста.
Особые указания
Следует соблюдать осторожность при применении препарата у пациентов, в анамнезе у которых язвенная болезнь желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки, а также у пациентов, находящихся на антикоагулянтной терапии. У таких пациентов повышен риск возникновения эрозивно-язвенных поражений ЖКТ. Следует соблюдать осторожность и контролировать показатели функции почек при применении препарата у пациентов пожилого возраста, пациентов с хронической сердечной недостаточностью с явлениями недостаточности кровообращения, у пациентов с циррозом печени, а также у пациентов с гиповолемией в результате хирургических вмешательств.
У пациентов с незначительным или умеренным снижением функции почек (клиренс креатинина более 30 мл/мин) не требуется коррекции режима дозирования. Пациенты, принимающие одновременно мочегонные средства и мелоксикам, должны принимать достаточное количество жидкости.
Мелоксикам, также как и другие НПВП, может маскировать симптомы инфекционных заболеваний.
Применение мелоксикама, как и других препаратов, блокирующих синтез простагландинов может влиять на фертильность, поэтому не рекомендуется женщинам, планирующим беременность.
Если в процессе лечения возникли аллергические реакции (зуд, кожная сыпь, крапивница, фотосенсибилизация), а также пациентам, отмечающим на фоне приема препарата нарушения зрения, необходимо обратиться к врачу с целью решения вопроса о прекращении приема препарата.
В период лечения необходимо соблюдать осторожность при вождении автотранспорта и занятии другими потенциально опасными видами деятельности, требующими повышенной концентрации внимания и быстроты психомоторных реакций.
Передозировка
Симптомы: нарушение сознания, тошнота, рвота, боли в эпигастрии, ЖКТ- кровотечение, острая почечная недостаточность, печеночная недостаточность, остановка дыхания, асистолия.
Лечение: специфического антидота нет; при передозировке препарата следует провести промывание желудка, прием активированного угля (в течение ближайшего часа), симптоматическая терапия. Форсированный диурез, защелачивание мочи, гемодиализ — малоэффективны из-за высокой связи препарата с белками крови.
Лекарственное взаимодействие
При одновременном применении с другими нестероидными противовоспалительными препаратами (а также с ацетилсалициловой кислотой) увеличивается риск возникновения эрозивно-язвенных поражений и кровотечений ЖКТ.
При одновременном применении с гипотензивными препаратами, возможно снижение эффективности действия последних.
При одновременном применении с препаратами лития возможно развитие кумуляции лития и увеличения его токсического действия (рекомендуется контроль концентрации лития в крови).
При одновременном применении с метотрексатом усиливается побочное действие последнего на кроветворную систему (опасность возникновения анемии и лейкопении, показано периодическое проведение общего анализа крови).
При одновременном применении с диуретиками и с циклоспорином возрастает риск развития почечной недостаточности.
При одновременном применении с внутриматочными контрацептивными средствами возможно снижение эффективности действия последних.
При одновременном применении с антикоагулянтами (гепарин, тиклопидин, варфарин), а также с тромболитическими препаратами (стрептокиназа, фибринолизин) увеличивается риск развития кровотечений (необходим периодический контроль показателей свертываемости крови).
При одновременном применении с колестирамином, ускоряется выведение препарата из организма.
При одновременном применении с селективными ингибиторами обратного захвата серотонина возрастает риск развития желудочно-кишечных кровотечений.
Условия хранения препарата Мелоксикам
Препарат хранят в сухом защищенном от света месте при температуре не выше 25°С. Хранить в недоступном для детей месте.
Срок годности препарата Мелоксикам
Срок годности — 3 года. Не применять по истечении срока годности.
Условия реализации
Препарат отпускается по рецепту.
Если вы хотите разместить ссылку на описание этого препарата — используйте данный код
Аналоги препарата
Амелотекс®
(ФармФирма Сотекс, Россия)
Артрозан®
(ФАРМСТАНДАРТ-ЛЕКСРЕДСТВА, Россия)
Генитрон®
(ВЕЛФАРМ, Россия)
Мелбек
(NOBEL ILAC SANAYII AND TICARET, Турция)
Мелбек Форте
(NOBEL ILAC SANAYII AND TICARET, Турция)
Мелокс
(MEDOCHEMIE, Кипр)
Мелоксикам
(ОЗОН, Россия)
Мелоксикам
(БОРИСОВСКИЙ ЗАВОД МЕДИЦИНСКИХ ПРЕПАРАТОВ, Республика Беларусь)
Мелоксикам
(АЛТАЙВИТАМИНЫ, Россия)
Мелоксикам
(МЕДИСОРБ, Россия)
Все аналоги
Торговое название:
Мобик
Mobic
Состав:
Каждая таблетка содержит: Мелоксикам – 7,5 мг.
Свойства:
Мелоксикам — нестероидный противовоспалительный препарат (НПВП), обладающий противовоспалительными, анальгетическими и жаропонижающими свойствами.
Показания:
Кратковременное симптоматическое лечение обострения остеоартроза. Длительное симптоматическое лечение ревматоидного артрита или анкилозирующего спондилита.
Способ применения и дозы:
Внутрь, таблетки принимают с водой 1 раз в день, во время еды. Препарат следует назначать максимально короткими курсами и в наименьших эффективных дозах. При остеоартрозе — 7,5 мг/сут. При неэффективности доза может быть увеличена до 15 мг/сут. При ревматоидном артрите, анкилозирующем спондилите — 15 мг/сут. После достижения терапевтического эффекта доза может быть снижена до 7,5 мг/сут. Максимальная суточная доза не должна превышать 15 мг. Рекомендуемая доза пожилым пациентам – 7,5мг в день.
У пациентов с повышенным риском развития побочных эффектов, а также у пациентов с выраженной почечной недостаточностью, находящихся на гемодиализе, доза не должна превышать 7,5 мг/сут.
Противопоказания:
Дети до 16 лет; повышенная чувствительность к мелоксикаму, аспирину, другим НПВП или какому-либо компоненту препарата; обострение язвенной болезни желудка и 12-перстной кишки, желудочные кровотечения; состояние после проведения аорто-коронарного шунтирования; тяжелая почечная недостаточность; беременность и лактация.
Меры предосторожности:
Может вызвать тяжелую аллергическую реакцию: отек лица, астма, шок, покраснение кожи, сыпь, волдыри; особенно у людей, страдающих аллергией на аспирин. В этом случае стоит прекратить прием препарата. Использовать с осторожностью пациентам с фенилкетонурией, с сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями, с заболеваниями ЖКТ (риск возникновения воспаления, кровотечения, изъязвления и перфорации желудка или кишечника). Перед применением проконсультируйтесь со специалистом. Не используйте до или после операции на сердце.
Побочные эффекты:
Тошнота, рвота, боль в животе, диарея, запор, метеоризм, кровотечения желудочно-кишечного тракта (скрытое или явное), гепатит, колит, стоматит, сухость во рту, отрыжка; тахикардия, повышение АД; обострение течения бронхиальной астмы, кашель; головная боль, головокружение, шум в ушах нарушение сна, вертиго; отеки, инфекция мочевыводящих путей, почечная недостаточность; конъюнктивит, нечеткость зрения; зуд, кожная сыпь, крапивница; анемия; аллергические реакции; лихорадка.
Способ хранения:
Хранить при температуре не выше 30С в защищенном от света и недоступном для детей месте.
Упаковка:
Картонная пачка содержит блистер по 10 таблеток, бумажную инструкцию.
Произношение
Общее название: meloxicam (mel OKS i kam)
Именамарок:Mobic.Vivlodex

Mobic (meloxicam) — нестероидный противовоспалительный препарат (NSAID). Meloxicam работает, уменьшая гормоны, которые вызывают воспаление и боль в организме.
Mobic используется для лечения боли или воспаления, вызванных ревматоидным артритом и остеоартритом у взрослых. Mobic также используется для лечения ювенильного ревматоидного артрита у детей, которым не менее 2 лет.
Mobic также может использоваться для целей, не указанных в данном руководстве.
Mobic может увеличить риск смертельного сердечного приступа или инсульта, особенно если вы используете его на длительный срок или принимаете высокие дозы, или если у вас есть сердечные заболевания. Не используйте это лекарство непосредственно перед или после операции шунтирования сердца (шунтирование коронарной артерии или АКШ).
Получите экстренную медицинскую помощь, если у вас есть боль в груди, слабость, одышка, невнятная речь или проблемы со зрением или равновесием.
Mobic может также вызвать желудочное или кишечное кровотечение, которое может быть фатальным. Эти условия могут возникать без предупреждения, когда вы используете Mobic, особенно у пожилых людей.
Немедленно позвоните своему врачу, если у вас есть симптомы кровотечения в желудке, такие как черный, кровавый или смолистый стул, или кашель крови или рвоты, которая похожа на кофейную гущу.
Слайд-шоу Преднизон: 12 вещей, которые вы должны знать
Избегайте употребления алкоголя. Это может увеличить риск кровотечения в желудке.
Попросите врача или фармацевта, прежде чем использовать любые другие лекарства от простуды, аллергии или боли. Лекарства, подобные мелоксикам, содержатся во многих комбинированных лекарствах. Проверьте этикетку, чтобы узнать, содержит ли лекарство NSAID (нестероидный противовоспалительный препарат), такой как аспирин, ибупрофен, кетопрофен или напроксен.
Mobic может увеличить риск смертельного сердечного приступа или инсульта, особенно если вы используете его на длительный срок или принимаете высокие дозы, или если у вас есть сердечные заболевания. Даже люди без сердечной болезни или факторы риска могут иметь инсульт или сердечный приступ при приеме этого лекарства.
Не используйте это лекарство непосредственно перед или после операции шунтирования сердца (шунтирование коронарной артерии или АКШ).
Mobic может также вызвать желудочное или кишечное кровотечение, которое может быть фатальным. Эти условия могут возникать без предупреждения, когда вы используете Mobic, особенно у пожилых людей.
Вы не должны использовать Mobic, если у вас аллергия на мелоксикам, или если у вас когда-либо был приступ астмы или серьезная аллергическая реакция после приема аспирина или НПВС.
Чтобы убедиться, что Mobic безопасен для вас, сообщите своему врачу, если у вас есть:
-
Сердечные заболевания, высокое кровяное давление, высокий уровень холестерина, диабет, или если вы курите;
-
История сердечного приступа, инсульта или сгустка крови;
-
История язв желудка или кровотечение;
-
астма;
-
Заболевания почек (или если вы находитесь на диализе);
-
болезнь печени; или
-
задержка жидкости.
Взятие Mobic в течение последних 3 месяцев беременности может нанести вред нерожденному ребенку. Расскажите своему врачу, если вы беременны или планируете забеременеть.
Mobic может вызвать задержку в овуляции (высвобождение яйца из яичника). Вы не должны принимать Mobic, если вы проходите лечение бесплодия, или иначе пытаетесь забеременеть.
Мелоксикам может проникать в грудное молоко и может нанести вред грудному ребенку. Вы не должны кормить грудью при использовании этого лекарства.
Mobic не одобрен для использования кем-либо моложе 2 лет.
Возьмите Mobic точно так, как предписано вашим доктором. Следуйте всем указаниям на этикетке рецепта. Ваш врач может иногда изменять вашу дозу, чтобы убедиться, что вы получите наилучшие результаты. Не принимайте это лекарство в больших количествах или дольше, чем рекомендуется. Используйте самую низкую дозу, которая эффективна при лечении вашего состояния.
Вы можете взять Mobic с пищей или без нее.
Встряхните пероральную суспензию (жидкость) хорошо перед измерением дозы. Измерьте жидкое лекарство с помощью дозирующего шприца или специальной дозирующей ложкой или чашкой для лекарств. Если у вас нет устройства для измерения дозы, спросите своего фармацевта за один.
Если ребенок принимает этот препарат, сообщите своему врачу, если у ребенка есть какие-либо изменения в весе. Мобные дозы основаны на весе у детей.
Если вы используете это лекарство в долгосрочной перспективе, вам могут потребоваться частые медицинские тесты.
Храните Mobic при комнатной температуре, вдали от влаги и тепла. Держите бутылку плотно закрытой, если она не используется.
Прочтите всю информацию о пациентах, руководства по лекарствам и инструкции, предоставленные вам. Если у вас есть какие-либо вопросы, спросите своего врача или фармацевта.
См. Также: Информация дозирования (более подробно)
Примите пропущенную дозу, как только вспомните. Пропустите пропущенную дозу, если это почти время для вашей следующей запланированной дозы. Не принимайте дополнительное лекарство, чтобы восполнить пропущенную дозу.

Обратитесь за неотложной медицинской помощью или позвоните в справочную строку Poison по телефону 1-800-222-1222.
Читайте так же про препарат Symproic.
Избегайте употребления алкоголя. Это может увеличить риск кровотечения в желудке.
Избегайте приема аспирина во время приема Mobic.
Попросите врача или фармацевта перед использованием любых препаратов для лечения простуды, аллергии или обезболивания. Многие лекарства, доступные за прилавком, содержат аспирин или другие лекарства, подобные Mobic. Взятие некоторых продуктов вместе может привести к тому, что вы получите слишком много этого типа лекарств. Проверьте этикетку, чтобы узнать, содержит ли лекарство аспирин, ибупрофен, кетопрофен или напроксен.
Получите неотложную медицинскую помощь, если у вас есть признаки аллергической реакции на Mobic: чихание, жидкий или душный нос; Свистящее дыхание или затрудненное дыхание; крапивница; Отек лица, губ, языка или горла.
Получите неотложную медицинскую помощь, если у вас есть признаки сердечного приступа или инсульта: боль в груди распространяется на вашу челюсть или плечо, внезапное онемение или слабость на одной стороне тела, невнятная речь, ощущение дыхания.
Прекратите использование Mobic и сразу же обратитесь к врачу, если у вас есть:
-
Первый признак любой кожной сыпи, какой бы мягкой она ни была;
-
Одышка (даже при мягком напряжении);
-
Отек или быстрое увеличение веса;
-
Признаки желудочного кровотечения — кровавые или смолистые стула, кашель крови или рвота, которая похожа на кофейную гущу;
-
Проблемы с печенью — тошнота, боль в верхнем желудке, зуд, усталость, симптомы гриппа, потеря аппетита, темная моча, стул из глинистого цвета, желтуха (пожелтение кожи или глаз);
-
Проблемы с почками — мало или совсем не мочеиспускание, болезненное или затрудненное мочеиспускание, отек в ногах или лодыжках, чувство усталости или нехватки дыхания;
-
Низкие эритроциты (анемия) — бледная кожа, ощущение легкого голова или нехватка дыхания, быстрый сердечный ритм, концентрация внимания; или
-
Сильная реакция на кожу — лихорадка, боль в горле, отек в вашем лице или языке, жжение в глазах, боль в коже, сопровождаемая красной или фиолетовой сыпью на коже, которая распространяется (особенно на лице или верхней части тела) и вызывает образование пузырей и шелушение.
Общие побочные эффекты Mobic могут включать:
-
Расстройство желудка, тошнота, рвота, изжога;
-
Диарея, запор, газ;
-
головокружение; или
-
Симптомы простуды, симптомы гриппа.
Это не полный список побочных эффектов, и другие могут возникнуть. Спросите у своего доктора о побочных эффектах. Вы можете сообщить о побочных эффектах FDA на уровне 1-800-FDA-1088.
См. Также: Побочные эффекты (более подробно)
Читайте так же про препарат ацидофил.
Обычная доза для взрослых от Mobic для остеоартрита:
Начальная доза: 7,5 мг перорально один раз в день
Поддерживающая доза: 7,5 мг перорально один раз в день
Максимальная доза: 15 мг устно ежедневно
Обычная доза для взрослых для ревматоидного артрита:
Начальная доза: 7,5 мг перорально один раз в день
Поддерживающая доза: 7,5 мг перорально один раз в день
Максимальная доза: 15 мг устно ежедневно
Обычная детская доза для ювенильного ревматоидного артрита:
Больше или равно 2 годам: 0,125 мг / кг перорально один раз в день
Максимальная доза: 7,5 мг устно ежедневно
Не было никакой дополнительной пользы, продемонстрированной увеличением дозы выше 0,125 мг / кг один раз в день в клинических испытаниях.
Попросите вашего врача, прежде чем использовать Mobic, если вы принимаете антидепрессант, такой как циталопрам, эсциталопрам, флуоксетин (прозак), флувоксамин, пароксетин, сертралин (Золофт), тразодон или вилазодон. Взятие любого из этих лекарств с НПВС может привести к сильному кровотечению или кровотечению.
Расскажите своему врачу обо всех ваших текущих лекарствах и о том, что вы начинаете или прекращаете использовать, особенно:
-
циклоспорин;
-
лития;
-
метотрексат;
-
Натрийполистиролсульфонат (Kayexalate);
-
Разбавитель крови (варфарин, кумадин, джентенов);
-
Сердца или артериального давления, включая мочегонное средство или «таблетку для воды»; или
-
Стероидная медицина (например, преднизон).
Этот список не является полным. Другие препараты могут взаимодействовать с мелоксикамом, включая рецептурные и внебиржевые лекарства, витамины и растительные продукты. Не все возможные взаимодействия перечислены в данном руководстве по лекарствам.
- Ваш фармацевт может предоставить дополнительную информацию о Mobic.
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information
needed to use MOBIC safely and effectively. See full prescribing
information for MOBIC. Mobic® (meloxicam) tablets Mobic® (meloxicam) oral suspensionInitial U.S. Approval:
2000BOXED WARNING
WARNING: CARDIOVASCULAR and
GASTROINTESTINAL RISKS
See full prescribing
information for complete boxed warning.
Cardiovascular Risk
NSAIDs may cause an increased risk of serious
cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke,
which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients
with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease
may be at greater risk. (5.1)
MOBIC is contraindicated for the treatment
of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft
(CABG) surgery (4.2, 5.1)
Gastrointestinal Risk
NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious
gastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and
perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These
events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms.
Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal
events. (5.2)
INDICATIONS AND USAGEMOBIC is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drug indicated for:
Osteoarthritis (OA) (1.1)
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (1.2)
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) in patients 2 years
of age or older (1.3)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONUse the lowest effective dose for the shortest
duration consistent with individual treatment goals for the individual
patient.
OA (2.2) and RA (2.3):
Starting dose: 7.5 mg once daily
Dose may be increased to 15 mg once daily
JRA (2.4):
0.125 mg/kg once daily up to a maximum of 7.5 mg. JRA dosing
using the oral suspension should be individualized based on the weight
of the child. (2.4)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 7.5 mg, 15 mg (3)
Oral Suspension: 7.5 mg/5 mL (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactoid reactions and
serious skin reactions) to meloxicam (4.1)
History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions
after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs (4.1)
Use during the peri-operative period in the setting of coronary
artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (4.2)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Serious and potentially fatal cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic
events, myocardial infarction, and stroke. Patients with known CV
disease/risk factors may be at greater risk. (5.1)
Serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events which can be
fatal. The risk is greater in patients with a prior history of ulcer
disease or GI bleeding, and in patients at higher risk for GI events,
especially the elderly. (5.2)
Elevated liver enzymes, and rarely, severe hepatic reactions.
Discontinue use immediately if abnormal liver enzymes persist or worsen. (5.3)
New onset or worsening of hypertension. Blood pressure should
be monitored closely during treatment. (5.4)
Fluid retention and edema. Should be used with caution in
patients with fluid retention or heart failure. (5.5)
Renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury with long-term
use. Use with caution in the elderly, those with impaired renal function,
heart failure, liver dysfunction, and those taking diuretics, ACE-inhibitors,
or angiotensin II antagonists. The use of MOBIC in patients with severe
renal impairment is not recommended. (5.6)
Serious skin adverse events such as exfoliative dermatitis,
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN),
which can be fatal and can occur without warning. Discontinue MOBIC
at first appearance of rash or skin reactions. (5.8)
Side Effects
Most common (≥5% and greater than placebo) adverse events
in adults are diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infections, dyspepsia,
and influenza-like symptoms (6.1)
Adverse events observed in pediatric studies were similar
in nature to the adult clinical trial experience (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at (800) 542-6257 or (800) 459-9906 TTY or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Concomitant use of MOBIC and warfarin may result in increased
risk of bleeding complications (7.7)
Concomitant use of MOBIC and aspirin is not generally recommended
because of the potential of increased adverse effect including increased
GI bleeding (7.2)
Concomitant use with MOBIC increases lithium plasma levels (7.4)
Concomitant use with NSAIDs may reduce the antihypertensive
effect of ACE-inhibitors (7.1)
Due to the presence of sorbitol in MOBIC oral suspension,
there may be a risk of intestinal necrosis (possibly fatal) when the
oral suspension is administered concomitantly with sodium polystyrene
sulfonate (7.8)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. Starting at
30 weeks gestation, MOBIC should be avoided as premature closure of
the ductus arteriosus in the fetus may occur. (5.9, 8.1)
Nursing Mothers: Use with caution, as meloxicam may be excreted
in human milk (8.3)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS
CARDIOVASCULAR and GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS - 1 MOBIC INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 1.1 Osteoarthritis (OA)
- 1.2 Rheumatoid Arthritis
(RA) - 1.3 Juvenile Rheumatoid
Arthritis (JRA) Pauciarticular and Polyarticular Course
- 2 MOBIC DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 2.1 General Instructions
- 2.2 Osteoarthritis
- 2.3 Rheumatoid Arthritis
- 2.4 Juvenile Rheumatoid
Arthritis (JRA) Pauciarticular and Polyarticular Course
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 MOBIC CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 4.1 Allergic Reactions
- 4.2 Coronary Surgery
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic
Events - 5.2 Gastrointestinal
(GI) Effects – Risk of GI Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation - 5.3 Hepatic Effects
- 5.4 Hypertension
- 5.5 Congestive Heart
Failure and Edema - 5.6 Renal Effects
- 5.7 Anaphylactoid Reactions
- 5.8 Adverse Skin Reactions
- 5.9 Pregnancy
- 5.10 Corticosteroid
Treatment - 5.11 Masking of Inflammation
and Fever - 5.12 Hematological Effects
- 5.13 Use in Patients
with Pre-existing Asthma - 5.14 Monitoring
- 5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic
- 6 MOBIC ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 6.1 Clinical Trials
Experience - 6.2 Post Marketing Experience
- 6.1 Clinical Trials
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 7.1 ACE-inhibitors
- 7.2 Aspirin
- 7.3 Diuretics
- 7.4 Lithium
- 7.5 Methotrexate
- 7.6 Cyclosporine
- 7.7 Warfarin
- 7.8 Kayexalate® (sodium
polystyrene sulfonate)
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 8.1 Pregnancy
- 8.2 Labor and Delivery
- 8.3 Nursing Mothers
- 8.4 Pediatric Use
- 8.5 Geriatric Use
- 8.6 Hepatic Impairment
- 8.7 Renal Impairment
- 8.8 Females of Reproductive Potential
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 MOBIC DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 12.1 Mechanism of Action
- 12.2 Pharmacodynamics
- 12.3 Pharmacokinetics
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 14.1 Osteoarthritis
and Rheumatoid Arthritis - 14.2 Juvenile Rheumatoid
Arthritis (JRA) Pauciarticular and Polyarticular Course
- 14.1 Osteoarthritis
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE
AND HANDLING - 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- 17.1 Medication Guide
- 17.2 Cardiovascular
Effects - 17.3 Gastrointestinal
Effects - 17.4 Hepatotoxicity
- 17.5 Adverse Skin Reactions
- 17.6 Weight Gain and
Edema - 17.7 Anaphylactoid Reactions
- 17.8 Effects During
Pregnancy - 17.9 Effects on Female Fertility
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS
CARDIOVASCULAR and GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
-
Cardiovascular Risk
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic
events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This
risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular
disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be at greater
risk [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)
]. -
MOBIC is contraindicated for the treatment
of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft
(CABG) surgery [see Contraindications (4.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)
].
-
Gastrointestinal Risk
-
NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious
gastrointestinal (GI) adverse reactions including bleeding, ulceration,
and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal.
These events can occur at any time during use and without warning
symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal
events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)
].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Osteoarthritis (OA)
MOBIC is indicated for relief of the signs
and symptoms of osteoarthritis [
see Clinical Studies (14.1)
].
1.2 Rheumatoid Arthritis
(RA)
MOBIC is indicated
for relief of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis [
see Clinical Studies (14.1)
].
1.3 Juvenile Rheumatoid
Arthritis (JRA) Pauciarticular and Polyarticular Course
MOBIC is indicated for relief of the signs
and symptoms of pauciarticular or polyarticular course Juvenile Rheumatoid
Arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older [
see Clinical Studies (14.2)
].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Instructions
Carefully consider the potential benefits
and risks of MOBIC and other treatment options before deciding to
use MOBIC. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration
consistent with individual patient treatment goals [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)
].
After
observing the response to initial therapy with MOBIC, adjust the dose
to suit an individual patient’s needs.
In adults, the maximum recommended daily oral dose of
MOBIC is 15 mg regardless of formulation. In patients with hemodialysis,
a maximum daily dosage of 7.5 mg is recommended [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Use in Specific Populations (8.7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
].
MOBIC
oral suspension 7.5 mg/5 mL or 15 mg/10 mL may be substituted for
MOBIC tablets 7.5 mg or 15 mg, respectively.
Shake the oral suspension gently before
using.
MOBIC
may be taken without regard to timing of meals.
2.2 Osteoarthritis
For the relief of the signs and symptoms
of osteoarthritis the recommended starting and maintenance oral dose
of MOBIC is 7.5 mg once daily. Some patients may receive additional
benefit by increasing the dose to 15 mg once daily.
2.3 Rheumatoid Arthritis
For the relief of the signs and symptoms
of rheumatoid arthritis, the recommended starting and maintenance
oral dose of MOBIC is 7.5 mg once daily. Some patients may receive
additional benefit by increasing the dose to 15 mg once daily.
2.4 Juvenile Rheumatoid
Arthritis (JRA) Pauciarticular and Polyarticular Course
To improve dosing accuracy in smaller weight
children, the use of the MOBIC oral suspension is recommended. MOBIC
oral suspension is available in the strength of 7.5 mg/5 mL. For the
treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, the recommended oral dose
of MOBIC is 0.125 mg/kg once daily up to a maximum of 7.5 mg. There
was no additional benefit demonstrated by increasing the dose above
0.125 mg/kg once daily in these clinical trials.
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis dosing
using the oral suspension should be individualized based on the weight
of the child:
|
0.125 mg/kg |
||
|
Weight |
Dose (1.5 mg/mL) |
Delivered dose |
|
12 kg (26 lb) |
1.0 mL | 1.5 mg |
|
24 kg (54 lb) |
2.0 mL | 3.0 mg |
|
36 kg (80 lb) |
3.0 mL | 4.5 mg |
|
48 kg (106 lb) |
4.0 mL | 6.0 mg |
|
≥60 kg (132 lb) |
5.0 mL | 7.5 mg |
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets:
- 7.5 mg: pastel yellow, round, biconvex, uncoated tablet
containing meloxicam 7.5 mg. Impressed with the Boehringer Ingelheim
logo on one side and the letter “M” on the other. - 15 mg: pastel yellow, oblong, biconvex, uncoated tablet
containing meloxicam 15 mg. Impressed with the tablet code “15” on
one side and the letter “M” on the other.
Oral Suspension:
- yellowish green tinged viscous suspension containing 7.5
mg meloxicam in 5 mL.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Allergic Reactions
MOBIC is contraindicated in patients with
known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactoid reactions and serious
skin reactions) to meloxicam.
MOBIC should not be given to patients who have experienced asthma,
urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other
NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs
have been reported in such patients [
see Warnings
and Precautions (5.7, 5.13)
].
4.2 Coronary Surgery
MOBIC is contraindicated for the treatment
of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft
(CABG) surgery [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)
].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic
Events
Clinical trials
of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three
years’ duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular
(CV) thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can
be fatal. All NSAIDs, both COX-2 selective and nonselective, may have
a similar risk. Patients with known CV disease or risk factors for
CV disease may be at greater risk. To minimize the potential risk
for an adverse CV event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest
effective dose should be used for the shortest duration possible.
Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of
such events, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients
should be informed about the signs and/or symptoms of serious CV events
and the steps to take if they occur.
Two large, controlled, clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID
for the treatment of pain in the first 10 to 14 days following CABG
surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and
stroke [
see Contraindications (4.2)
].
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates
the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with
NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID does increase
the risk of serious GI events [
see Warnings and
Precautions (5.2)
].
5.2 Gastrointestinal
(GI) Effects – Risk of GI Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including MOBIC, can cause serious
gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding,
ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine, or large
intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur
at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated
with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients who develop a serious upper
GI adverse event on NSAID therapy is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers,
gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs, occur in approximately
1% of patients treated for 3 to 6 months, and in about 2% to 4% of
patients treated for one year. These trends continue with longer duration
of use, increasing the likelihood of developing a serious GI event
at some time during the course of therapy. However, even short-term
therapy is not without risk.
Prescribe
NSAIDs, including MOBIC, with extreme caution in those with a prior
history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients with
a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding
who use NSAIDs have a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing
a GI bleed compared to patients with neither of these risk factors.
Other factors that increase the risk for GI bleeding in patients treated
with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants,
longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, older age,
and poor general health status. Most spontaneous reports of fatal
GI events are in elderly or debilitated patients and therefore, special
care should be taken in treating this population.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse GI event
in patients treated with an NSAID, use the lowest effective dose for
the shortest possible duration. Patients and physicians should remain
alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during
MOBIC therapy and promptly initiate additional evaluation and treatment
if a serious GI adverse event is suspected. This should include discontinuation
of MOBIC until a serious GI adverse event is ruled out. For high-risk
patients, consider alternate therapies that do not involve NSAIDs.
5.3 Hepatic Effects
Borderline elevations of one or more liver
tests may occur in up to 15% of patients taking NSAIDs including MOBIC.
These laboratory abnormalities may progress, may remain unchanged,
or may be transient with continuing therapy. Notable elevations of
ALT or AST (approximately three or more times the upper limit of normal)
have been reported in approximately 1% of patients in clinical trials
with NSAIDs. In addition, rare cases of severe hepatic reactions,
including jaundice and fatal fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis and
hepatic failure, some of them with fatal outcomes have been reported
[
see Adverse Reactions (6.1)
].
A patient with symptoms and/or signs suggesting liver dysfunction,
or in whom an abnormal liver test has occurred, should be evaluated
for evidence of the development of a more severe hepatic reaction
while on therapy with MOBIC. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent
with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g.,
eosinophilia, rash, etc.), discontinue MOBIC [
see
Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and
Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
].
5.4 Hypertension
NSAIDs, including MOBIC, can lead to onset
of new hypertension or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, either
of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. NSAIDs,
including MOBIC, should be used with caution in patients with hypertension.
Blood pressure (BP) should be monitored closely during the initiation
of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
Patients taking ACE inhibitors, thiazides,
or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when
taking NSAIDs.
5.5 Congestive Heart
Failure and Edema
Fluid
retention and edema have been observed in some patients taking NSAIDs.
Use MOBIC with caution in patients with fluid retention, hypertension,
or heart failure.
5.6 Renal Effects
Long-term administration of NSAIDs, including
MOBIC, can result in renal papillary necrosis, renal insufficiency,
acute renal failure, and other renal injury. Renal toxicity has also
been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory
role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration
of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug may cause a dose-dependent
reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood
flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at
greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function,
heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics, ACE-inhibitors,
and angiotensin II receptor antagonists, and the elderly. Discontinuation
of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment
state.
A pharmacokinetic study
in patients with mild and moderate renal impairment revealed that
no dosage adjustments in these patient populations are required. Patients
with severe renal impairment have not been studied. The use of MOBIC
in patients with severe renal impairment with CrCl less than 20 mL/min
is not recommended. A study performed in patients on hemodialysis
revealed that although overall Cmax was diminished
in this population, the proportion of free drug not bound to plasma
was increased. Therefore it is recommended that meloxicam dosage in
this population not exceed 7.5 mg per day. Closely monitor the renal
function of patients with impaired renal function who are taking MOBIC
[
see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
].
Use caution when initiating treatment with MOBIC in patients with
considerable dehydration. It is advisable to rehydrate patients first
and then start therapy with MOBIC. Caution is also recommended in
patients with pre-existing kidney disease.
The extent to which metabolites may accumulate in patients
with renal impairment has not been studied with MOBIC. Because some
MOBIC metabolites are excreted by the kidney, monitor patients with
significant renal impairment closely.
5.7 Anaphylactoid Reactions
As with other NSAIDs, anaphylactoid reactions
have occurred in patients without known prior exposure to MOBIC. MOBIC
should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad. This symptom
complex typically occurs in asthmatic patients who experience rhinitis
with or without nasal polyps, or who exhibit severe, potentially fatal
bronchospasm after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs [
see Contraindications (4.1) and Warnings
and Precautions (5.12)
]. Seek emergency help in cases where an anaphylactoid reaction
occurs.
5.8 Adverse Skin Reactions
NSAIDs, including MOBIC, can cause serious
skin adverse events such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson
Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be
fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Inform patients
about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations and discontinue
use of the drug at the first appearance of skin rash or any other
sign of hypersensitivity.
5.9 Pregnancy
Starting at 30 weeks gestation, avoid the
use of MOBIC because it may cause premature closure of the ductus
arteriosus [
see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) and Patient Counseling Information (17.8)
].
5.10 Corticosteroid
Treatment
MOBIC cannot
be expected to substitute for corticosteroids or to treat corticosteroid
insufficiency. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead
to disease exacerbation. Slowly taper patients on prolonged corticosteroid
therapy if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids.
5.11 Masking of Inflammation
and Fever
The pharmacological
activity of MOBIC in reducing fever and inflammation may diminish
the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of
presumed noninfectious, painful conditions.
5.12 Hematological Effects
Anemia may occur in patients receiving NSAIDs,
including MOBIC. This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross
GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis.
Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including MOBIC, should
have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs
or symptoms of anemia.
NSAIDs
inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown to prolong bleeding
time in some patients. Unlike aspirin, their effect on platelet function
is quantitatively less, of shorter duration, and reversible. Carefully
monitor patients treated with MOBIC who may be adversely affected
by alterations in platelet function, such as those with coagulation
disorders or patients receiving anticoagulants.
5.13 Use in Patients
with Pre-existing Asthma
Patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma. The use of
aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma has been associated
with severe bronchospasm, which can be fatal. Since cross reactivity,
including bronchospasm, between aspirin and other NSAIDs has been
reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, MOBIC should not be administered
to patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity and should be used
with caution in patients with pre-existing asthma.
5.14 Monitoring
Because serious GI tract ulcerations and
bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, physicians should monitor
for signs or symptoms of GI bleeding. Patients on long-term treatment
with NSAIDs should have their CBC and a chemistry profile checked
periodically. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver
or renal disease develop, systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia,
rash, etc.) or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, MOBIC should
be discontinued.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions,
adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot
be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug
and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed
elsewhere in the labeling:
- Cardiovascular thrombotic events [
see
Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)
] - Gastrointestinal effects – risk of GI ulceration, bleeding,
and perforation [
see Boxed Warning and Warnings
and Precautions (5.2)
] - Hepatic effects [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)
] - Hypertension [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)
] - Congestive heart failure and edema [
see
Warnings and Precautions (5.5)
] - Renal effects [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)
] - Anaphylactoid reactions [
see Warnings
and Precautions (5.7)
] - Adverse skin reactions [
see Warnings and
Precautions (5.8)
]
6.1 Clinical Trials
Experience
Osteoarthritis and
Rheumatoid Arthritis
The MOBIC Phase 2/3 clinical trial database includes
10,122 OA patients and 1012 RA patients treated with MOBIC 7.5 mg/day,
3505 OA patients and 1351 RA patients treated with MOBIC 15 mg/day.
MOBIC at these doses was administered to 661 patients for at least
6 months and to 312 patients for at least one year. Approximately
10,500 of these patients were treated in ten placebo- and/or active-controlled
osteoarthritis trials and 2363 of these patients were treated in ten
placebo- and/or active-controlled rheumatoid arthritis trials. Gastrointestinal
(GI) adverse events were the most frequently reported adverse events
in all treatment groups across MOBIC trials.
A 12-week multicenter, double-blind, randomized trial
was conducted in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee or hip to
compare the efficacy and safety of MOBIC with placebo and with an
active control. Two 12-week multicenter, double-blind, randomized
trials were conducted in patients with rheumatoid arthritis to compare
the efficacy and safety of MOBIC with placebo.
Table 1a depicts adverse events that occurred in ≥2%
of the MOBIC treatment groups in a 12-week placebo- and active-controlled
osteoarthritis trial.
Table 1b
depicts adverse events that occurred in ≥2% of the MOBIC treatment
groups in two 12-week placebo-controlled rheumatoid arthritis trials.
|
Placebo |
MOBIC 7.5 mg daily |
MOBIC 15 mg daily |
Diclofenac 100 mg daily |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
No. of Patients |
157 |
154 |
156 |
153 |
|
1 WHO preferred terms edema, edema dependent, edema peripheral, and edema legs combined 2 WHO preferred terms rash, rash erythematous, and rash maculo-papular combined |
||||
|
Gastrointestinal |
17.2 | 20.1 | 17.3 | 28.1 |
| Abdominal pain | 2.5 | 1.9 | 2.6 | 1.3 |
| Diarrhea | 3.8 | 7.8 | 3.2 | 9.2 |
| Dyspepsia | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 6.5 |
| Flatulence | 4.5 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.9 |
| Nausea | 3.2 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 7.2 |
|
Body as a Whole |
||||
| Accident household | 1.9 | 4.5 | 3.2 | 2.6 |
| Edema1 | 2.5 | 1.9 | 4.5 | 3.3 |
| Fall | 0.6 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 1.3 |
| Influenza-like symptoms | 5.1 | 4.5 | 5.8 | 2.6 |
|
Central and Peripheral Nervous System |
||||
| Dizziness | 3.2 | 2.6 | 3.8 | 2.0 |
| Headache | 10.2 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 5.9 |
|
Respiratory |
||||
| Pharyngitis | 1.3 | 0.6 | 3.2 | 1.3 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 1.9 | 3.2 | 1.9 | 3.3 |
|
Skin |
||||
| Rash2 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 0.6 | 2.0 |
|
Placebo |
MOBIC 7.5 mg daily |
MOBIC 15 mg daily |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
No. of Patients |
469 |
481 |
477 |
|
1 MedDRA high level term (preferred terms): dyspeptic signs and symptoms (dyspepsia, dyspepsia aggravated, eructation, gastrointestinal irritation), upper respiratory tract infections-pathogen unspecified (laryngitis NOS, pharyngitis NOS, sinusitis NOS), joint related signs and symptoms (arthralgia, arthralgia aggravated, joint crepitation, joint effusion, joint swelling) 2 MedDRA preferred term: nausea, abdominal pain NOS, influenza-like illness, headaches NOS, and rash NOS |
|||
|
Gastrointestinal Disorders |
14.1 | 18.9 | 16.8 |
| Abdominal pain NOS2 | 0.6 | 2.9 | 2.3 |
| Dyspeptic signs and symptoms1 | 3.8 | 5.8 | 4.0 |
| Nausea2 | 2.6 | 3.3 | 3.8 |
|
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions |
|||
| Influenza-like illness2 | 2.1 | 2.9 | 2.3 |
|
Infection and Infestations Upper respiratory tract infections-pathogen class unspecified1 |
4.1 | 7.0 | 6.5 |
|
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders Joint related signs and symptoms1 |
1.9 | 1.5 | 2.3 |
|
Nervous System Disorders |
|||
| Headaches NOS2 | 6.4 | 6.4 | 5.5 |
|
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Rash NOS2 |
1.7 | 1.0 | 2.1 |
The adverse events that occurred
with MOBIC in ≥2% of patients treated short-term (4 to 6 weeks) and
long-term (6 months) in active-controlled osteoarthritis trials are
presented in Table 2.
|
4 to 6 Weeks Controlled Trials |
6 Month Controlled Trials |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MOBIC 7.5 mg daily |
MOBIC 15 mg daily |
MOBIC 7.5 mg daily |
MOBIC 15 mg daily |
|
|
No. of Patients |
8955 |
256 |
169 |
306 |
|
1 WHO preferred terms edema, edema dependent, edema peripheral, and edema legs combined 2 WHO preferred terms rash, rash erythematous, and rash maculo-papular combined |
||||
|
Gastrointestinal |
11.8 | 18.0 | 26.6 | 24.2 |
| Abdominal pain | 2.7 | 2.3 | 4.7 | 2.9 |
| Constipation | 0.8 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 2.6 |
| Diarrhea | 1.9 | 2.7 | 5.9 | 2.6 |
| Dyspepsia | 3.8 | 7.4 | 8.9 | 9.5 |
| Flatulence | 0.5 | 0.4 | 3.0 | 2.6 |
| Nausea | 2.4 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 7.2 |
| Vomiting | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 2.6 |
|
Body as a Whole |
||||
| Accident household | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 2.9 |
| Edema1 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 1.6 |
| Pain | 0.9 | 2.0 | 3.6 | 5.2 |
|
Central and Peripheral Nervous System |
||||
| Dizziness | 1.1 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 2.6 |
| Headache | 2.4 | 2.7 | 3.6 | 2.6 |
|
Hematologic |
||||
| Anemia | 0.1 | 0.0 | 4.1 | 2.9 |
|
Musculoskeletal |
||||
| Arthralgia | 0.5 | 0.0 | 5.3 | 1.3 |
| Back pain | 0.5 | 0.4 | 3.0 | 0.7 |
|
Psychiatric |
||||
| Insomnia | 0.4 | 0.0 | 3.6 | 1.6 |
|
Respiratory |
||||
| Coughing | 0.2 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 1.0 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 0.2 | 0.0 | 8.3 | 7.5 |
|
Skin |
||||
| Pruritus | 0.4 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 0.0 |
| Rash2 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 3.0 | 1.3 |
|
Urinary |
||||
| Micturition frequency | 0.1 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 1.3 |
| Urinary tract infection | 0.3 | 0.4 | 4.7 | 6.9 |
Higher doses of MOBIC (22.5 mg and
greater) have been associated with an increased risk of serious GI
events; therefore, the daily dose of MOBIC should not exceed 15 mg.
Pauciarticular and
Polyarticular Course Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA)
Three hundred and
eighty-seven patients with pauciarticular and polyarticular course
JRA were exposed to MOBIC with doses ranging from 0.125 to 0.375 mg/kg
per day in three clinical trials. These studies consisted of two 12-week
multicenter, double-blind, randomized trials (one with a 12-week open-label
extension and one with a 40-week extension) and one 1-year open-label
PK study. The adverse events observed in these pediatric studies with
MOBIC were similar in nature to the adult clinical trial experience,
although there were differences in frequency. In particular, the following
most common adverse events, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, headache,
and pyrexia, were more common in the pediatric than in the adult trials.
Rash was reported in seven (<2%) patients receiving MOBIC. No unexpected
adverse events were identified during the course of the trials. The
adverse events did not demonstrate an age or gender-specific subgroup
effect.
The following is a list
of adverse drug reactions occurring in <2% of patients receiving
MOBIC in clinical trials involving approximately 16,200 patients.
|
Body as a Whole |
allergic reaction, face edema, fatigue, fever, hot flushes, malaise, syncope, weight decrease, weight increase |
|
Cardiovascular |
angina pectoris, cardiac failure, hypertension, hypotension, myocardial infarction, vasculitis |
|
Central and Peripheral Nervous System |
convulsions, paresthesia, tremor, vertigo |
|
Gastrointestinal |
colitis, dry mouth, duodenal ulcer, eructation, esophagitis, gastric ulcer, gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hematemesis, hemorrhagic duodenal ulcer, hemorrhagic gastric ulcer, intestinal perforation, melena, pancreatitis, perforated duodenal ulcer, perforated gastric ulcer, stomatitis ulcerative |
|
Heart Rate and Rhythm |
arrhythmia, palpitation, tachycardia |
|
Hematologic |
leukopenia, purpura, thrombocytopenia |
|
Liver and Biliary System |
ALT increased, AST increased, bilirubinemia, GGT increased, hepatitis |
|
Metabolic and Nutritional |
dehydration |
|
Psychiatric |
abnormal dreaming, anxiety, appetite increased, confusion, depression, nervousness, somnolence |
|
Respiratory |
asthma, bronchospasm, dyspnea |
|
Skin and Appendages |
alopecia, angioedema, bullous eruption, photosensitivity reaction, pruritus, sweating increased, urticaria |
|
Special Senses |
abnormal vision, conjunctivitis, taste perversion, tinnitus |
|
Urinary System |
albuminuria, BUN increased, creatinine increased, hematuria, renal failure |
6.2 Post Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been
identified during post approval use of MOBIC. Because these reactions
are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is
not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish
a causal relationship to drug exposure. Decisions about whether to
include an adverse event from spontaneous reports in labeling are
typically based on one or more of the following factors: (1) seriousness
of the event, (2) number of reports, or (3) strength of causal relationship
to the drug. Adverse reactions reported in worldwide post marketing
experience or the literature include: acute urinary retention; agranulocytosis;
alterations in mood (such as mood elevation); anaphylactoid reactions
including shock; erythema multiforme; exfoliative dermatitis; interstitial
nephritis; jaundice; liver failure; Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and
toxic epidermal necrolysis.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
See also Clinical Pharmacology (12.3).
7.1 ACE-inhibitors
NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive
effect of ACE-inhibitors. This interaction should be given consideration
in patients taking MOBIC concomitantly with ACE-inhibitors.
7.2 Aspirin
When MOBIC is administered with aspirin
(1000 mg three times daily) to healthy volunteers, an increase in
the AUC (10%) and Cmax (24%) of meloxicam was
noted. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known;
however, as with other NSAIDs concomitant administration of meloxicam
and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential
for increased adverse effects.
Concomitant administration of low-dose aspirin with MOBIC may result
in an increased rate of GI ulceration or other complications, compared
to use of MOBIC alone. MOBIC is not a substitute for aspirin for cardiovascular
prophylaxis.
7.3 Diuretics
Clinical studies, as well as post marketing
observations, have shown that NSAIDs can reduce the natriuretic effect
of furosemide and thiazides in some patients. This response has been
attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. However,
studies with furosemide agents and meloxicam have not demonstrated
a reduction in natriuretic effect. Furosemide single and multiple
dose pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics are not affected by multiple
doses of meloxicam. Nevertheless, during concomitant therapy with
MOBIC, patients should be observed closely for signs of renal failure
[
see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)
], as well as to ensure diuretic
efficacy.
7.4 Lithium
In a study conducted in healthy subjects,
mean pre-dose lithium concentration and AUC were increased by 21%
in subjects receiving lithium doses ranging from 804 to 1072 mg twice
daily with meloxicam 15 mg every day as compared to subjects receiving
lithium alone. These effects have been attributed to inhibition of
renal prostaglandin synthesis by MOBIC. Closely monitor patients on
lithium treatment for signs of lithium toxicity when MOBIC is introduced,
adjusted, or withdrawn.
7.5 Methotrexate
NSAIDs have been reported to competitively
inhibit methotrexate accumulation in rabbit kidney slices. Therefore,
NSAIDs may reduce the elimination of methotrexate, thereby enhancing
the toxicity of methotrexate. Use caution when MOBIC is administered
concomitantly with methotrexate [
see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
].
7.6 Cyclosporine
MOBIC, like other NSAIDs, may affect renal
prostaglandins, thereby altering the renal toxicity of certain drugs.
Therefore, concomitant therapy with MOBIC may increase cyclosporine’s
nephrotoxicity. Use caution when MOBIC is administered concomitantly
with cyclosporine.
7.7 Warfarin
The effects of warfarin and NSAIDs on GI
bleeding are synergistic, such that users of both drugs together have
a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone.
Monitor anticoagulant activity, particularly
in the first few days after initiating or changing MOBIC therapy in
patients receiving warfarin or similar agents, since these patients
are at an increased risk of bleeding than with the use of either drug
alone. Use caution when administering MOBIC with warfarin since patients
on warfarin may experience changes in INR and an increased risk of
bleeding complications when a new medication is introduced [
see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
].
7.8 Kayexalate® (sodium
polystyrene sulfonate)
Cases of intestinal necrosis (possibly fatal) have been described
in patients who received concomitant sorbitol and Kayexalate® (sodium
polystyrene sulfonate). Due to the presence of sorbitol in MOBIC
Oral Suspension, use with Kayexalate® is not recommended.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C;
Category D starting 30 weeks gestation
There are no adequate and well-controlled
studies in pregnant women. Meloxicam crosses the placental barrier.
Prior to 30 weeks gestation, use MOBIC during pregnancy only if the
potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Starting
at 30 weeks gestation, avoid MOBIC and other NSAIDs, in pregnant women
as premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus may occur.
If this drug is used during this time period in pregnancy, inform
the patient of the potential hazard to a fetus [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Patient Counseling Information (17.8)
].
Teratogenic Effects
Meloxicam was not
teratogenic when administered to pregnant rats during fetal organogenesis
at oral doses up to 4 mg/kg/day (2.6-fold greater than the maximum
recommended human daily dose [MRHD] based on body surface area [BSA]
comparison). Administration of meloxicam to pregnant rabbits throughout
embryogenesis produced an increased incidence of septal defects of
the heart at an oral dose of 60 mg/kg/day. The no effect level was
20 mg/kg/day (26-fold greater than the MRHD based on BSA conversion).
Nonteratogenic Effects
In rats and rabbits,
embryolethality occurred at oral meloxicam doses of 1 mg/kg/day and
5 mg/kg/day, respectively (0.65- and 6.5-fold greater, respectively,
than the MRHD based on BSA comparison) when administered throughout
organogenesis.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
The effects of MOBIC on labor and delivery of pregnant women are
unknown. Oral administration of meloxicam to pregnant rats during
late gestation through lactation increased the incidence of dystocia,
delayed parturition, and decreased offspring survival at meloxicam
doses of 0.125 mg/kg/day or greater (at least 12.5 times lower than
the maximum recommended human daily dose based on body surface area
comparison).
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk; however,
meloxicam was excreted in the milk of lactating rats at concentrations
higher than those in plasma. Because many drugs are excreted in human
milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in
nursing infants from MOBIC, a decision should be made whether to discontinue
nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance
of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of meloxicam in pediatric JRA patients
from 2 to 17 years of age has been evaluated in three clinical trials
[
see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Adverse Reactions (6.1), and Clinical Studies (14.2)
].
8.5 Geriatric Use
As with any NSAID, caution should be exercised in treating the elderly
(65 years and older).
Of the
total number of subjects in clinical studies, 5157 were age 65 and
over (4044 in OA studies and 1113 in RA studies). No overall differences
in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and
younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified
differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients,
but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled
out.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is necessary in patients
with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. Patients with severe hepatic
impairment have not been adequately studied. Since meloxicam is significantly
metabolized in the liver; the use of meloxicam in these patients should
be done with caution [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
].
8.7 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is necessary in patients
with mild to moderate renal impairment. Patients with severe renal
impairment have not been studied. The use of MOBIC in subjects with
severe renal impairment is not recommended. Following a single dose
of meloxicam, the free Cmax plasma concentrations
were higher in patients with renal failure on chronic hemodialysis
(1% free fraction) in comparison to healthy volunteers (0.3% free
fraction). Therefore, it is recommended that meloxicam dosage in this
population not exceed 7.5 mg per day. Hemodialysis did not lower the
total drug concentration in plasma; therefore, additional doses are
not necessary after hemodialysis. Meloxicam is not dialyzable [
see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
].
8.8 Females of Reproductive Potential
Data from several small studies in humans and from
studies in animals indicate that NSAIDs, including MOBIC, may be associated
with a reversible delay in ovulation. Therefore, in women who have
difficulties conceiving, or who are undergoing investigation of infertility,
use of meloxicam is not recommended.
10 OVERDOSAGE
There
is limited experience with meloxicam overdose. Four cases have taken
6 to 11 times the highest recommended dose; all recovered. Cholestyramine
is known to accelerate the clearance of meloxicam.
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdose include lethargy,
drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which are generally
reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur.
Severe poisoning may result in hypertension, acute renal failure,
hepatic dysfunction, respiratory depression, coma, convulsions, cardiovascular
collapse, and cardiac arrest. Anaphylactoid reactions have been reported
with therapeutic ingestion of NSAIDs, and may occur following an overdose.
Patients should be managed with symptomatic
and supportive care following an NSAID overdose. Administration of
activated charcoal is recommended for patients who present 1 to 2
hours after overdose. For substantial overdose or severely symptomatic
patients, activated charcoal may be administered repeatedly. Accelerated
removal of meloxicam by 4 g oral doses of cholestyramine given three
times a day was demonstrated in a clinical trial. Administration of
cholestyramine may be useful following an overdose. Forced diuresis,
alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be
useful due to high protein binding.
For additional information about overdose treatment, call a poison
control center (1-800-222-1222).
11 DESCRIPTION
Meloxicam, an oxicam derivative, is a member
of the enolic acid group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Each pastel yellow MOBIC tablet contains 7.5 mg or 15 mg meloxicam
for oral administration. Each bottle of MOBIC oral suspension contains
7.5 mg meloxicam per 5 mL. Meloxicam is chemically designated as 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-2-thiazolyl)-2H-1,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide-1,1-dioxide.
The molecular weight is 351.4. Its empirical formula is C14H13N3O4S2 and it has the
following structural formula:
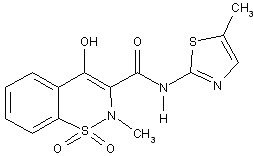
Meloxicam is a pastel yellow solid, practically insoluble
in water, with higher solubility observed in strong acids and bases.
It is very slightly soluble in methanol. Meloxicam has an apparent
partition coefficient (log P)app = 0.1 in n-octanol/buffer pH 7.4. Meloxicam has pKa values of 1.1
and 4.2.
MOBIC is available as
a tablet for oral administration containing 7.5 mg or 15 mg meloxicam,
and as an oral suspension containing 7.5 mg meloxicam per 5 mL.
The inactive ingredients in MOBIC tablets
include colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, lactose monohydrate,
magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, and sodium
citrate dihydrate.
The inactive
ingredients in MOBIC oral suspension include colloidal silicon dioxide,
hydroxyethylcellulose, sorbitol, glycerol, xylitol, monobasic sodium
phosphate (dihydrate), saccharin sodium, sodium benzoate, citric acid
(monohydrate), raspberry flavor, and purified water.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of meloxicam, like that of other NSAIDs,
may be related to prostaglandin synthetase (cyclo-oxygenase) inhibition
which is involved in the initial steps of the arachidonic acid cascade,
resulting in the reduced formation of prostaglandins, thromboxanes
and prostacylin. It is not completely understood how reduced synthesis
of these compounds results in therapeutic efficacy.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Meloxicam exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic
activities.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The absolute bioavailability
of meloxicam capsules was 89% following a single oral dose of 30 mg
compared with 30 mg IV bolus injection. Following single intravenous
doses, dose-proportional pharmacokinetics were shown in the range
of 5 mg to 60 mg. After multiple oral doses the pharmacokinetics of
meloxicam capsules were dose-proportional over the range of 7.5 mg
to 15 mg. Mean Cmax was achieved within four
to five hours after a 7.5 mg meloxicam tablet was taken under fasted
conditions, indicating a prolonged drug absorption. With multiple
dosing, steady-state concentrations were reached by Day 5. A second
meloxicam concentration peak occurs around 12 to 14 hours post-dose
suggesting biliary recycling.
Meloxicam oral suspension doses of 7.5 mg/5 mL and 15 mg/10 mL have
been found to be bioequivalent to meloxicam 7.5 mg and 15 mg capsules,
respectively. Meloxicam capsules have been shown to be bioequivalent
to MOBIC tablets.
|
Steady State |
Single Dose |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Pharmacokinetic Parameters (% CV) |
Healthy male adults (Fed)2 |
Elderly males (Fed)2 |
Elderly females (Fed)2 |
Renal failure (Fasted) |
Hepatic insufficiency (Fasted) |
|
|
7.5 mg3 tablets |
15 mg capsules |
15 mg capsules |
15 mg capsules |
15 mg capsules |
||
|
N |
18 |
5 |
8 |
12 |
12 |
|
|
1 The parameter values in the table are from various studies 2 not under high fat conditions 3 MOBIC tablets 4 Vz/f =Dose/(AUC•Kel) |
||||||
| Cmax | [µg/mL] | 1.05 (20) | 2.3 (59) | 3.2 (24) | 0.59 (36) | 0.84 (29) |
| tmax | [h] | 4.9 (8) | 5 (12) | 6 (27) | 4 (65) | 10 (87) |
| t1/2 | [h] | 20.1 (29) | 21 (34) | 24 (34) | 18 (46) | 16 (29) |
| CL/f | [mL/min] | 8.8 (29) | 9.9 (76) | 5.1 (22) | 19 (43) | 11 (44) |
| Vz/f4 | [L] | 14.7 (32) | 15 (42) | 10 (30) | 26 (44) | 14 (29) |
Administration
of meloxicam capsules following a high fat breakfast (75 g of fat)
resulted in mean peak drug levels (i.e., Cmax) being increased by approximately 22% while the extent of absorption
(AUC) was unchanged. The time to maximum concentration (Tmax) was achieved between 5 and 6 hours. In comparison,
neither the AUC nor the Cmax values for meloxicam
suspension were affected following a similar high fat meal, while
mean Tmax values were increased to approximately
7 hours. No pharmacokinetic interaction was detected with concomitant
administration of antacids. Based on these results, MOBIC can be administered
without regard to timing of meals or concomitant administration of
antacids.
The mean volume of
distribution (Vss) of meloxicam is approximately 10 L. Meloxicam is
~99.4% bound to human plasma proteins (primarily albumin) within the
therapeutic dose range. The fraction of protein binding is independent
of drug concentration, over the clinically relevant concentration
range, but decreases to ~99% in patients with renal disease. Meloxicam
penetration into human red blood cells, after oral dosing, is less
than 10%. Following a radiolabeled dose, over 90% of the radioactivity
detected in the plasma was present as unchanged meloxicam.
Meloxicam concentrations in synovial fluid,
after a single oral dose, range from 40% to 50% of those in plasma.
The free fraction in synovial fluid is 2.5 times higher than in plasma,
due to the lower albumin content in synovial fluid as compared to
plasma. The significance of this penetration is unknown.
Meloxicam is extensively
metabolized in the liver. Meloxicam metabolites include 5′-carboxy
meloxicam (60% of dose), from P-450 mediated metabolism formed by
oxidation of an intermediate metabolite 5′-hydroxymethyl meloxicam
which is also excreted to a lesser extent (9% of dose). In
vitro studies indicate that CYP2C9 (cytochrome P450 metabolizing
enzyme) plays an important role in this metabolic pathway with a minor
contribution of the CYP3A4 isozyme. Patients’ peroxidase activity
is probably responsible for the other two metabolites which account
for 16% and 4% of the administered dose, respectively. All the four
metabolites are not known to have any in vivo pharmacological
activity.
Meloxicam excretion
is predominantly in the form of metabolites, and occurs to equal extents
in the urine and feces. Only traces of the unchanged parent compound
are excreted in the urine (0.2%) and feces (1.6%). The extent of
the urinary excretion was confirmed for unlabeled multiple 7.5 mg
doses: 0.5%, 6%, and 13% of the dose were found in urine in the form
of meloxicam, and the 5′-hydroxymethyl and 5′-carboxy metabolites,
respectively. There is significant biliary and/or enteral secretion
of the drug. This was demonstrated when oral administration of cholestyramine
following a single IV dose of meloxicam decreased the AUC of meloxicam
by 50%.
The mean elimination
half-life (t1/2) ranges from 15 hours to 20
hours. The elimination half-life is constant across dose levels indicating
linear metabolism within the therapeutic dose range. Plasma clearance
ranges from 7 to 9 mL/min.
Pediatric
After single (0.25 mg/kg) dose administration and after achieving
steady state (0.375 mg/kg/day), there was a general trend of approximately
30% lower exposure in younger patients (2 to 6 years old) as compared
to the older patients (7 to 16 years old). The older patients had
meloxicam exposures similar (single dose) or slightly reduced (steady
state) to those in the adult patients, when using AUC values normalized
to a dose of 0.25 mg/kg [
see Dosage and Administration (2.4)
]. The meloxicam
mean (SD) elimination half-life was 15.2 (10.1) and 13.0 hours (3.0)
for the 2 to 6 year old patients, and 7 to 16 year old patients, respectively.
In a covariate analysis, utilizing population
pharmacokinetics body-weight, but not age, was the single predictive
covariate for differences in the meloxicam apparent oral plasma clearance.
The body-weight normalized apparent oral clearance values were adequate
predictors of meloxicam exposure in pediatric patients.
The pharmacokinetics of MOBIC in pediatric
patients under 2 years of age have not been investigated.
Geriatric
Elderly males (≥65 years of age) exhibited meloxicam plasma concentrations
and steady-state pharmacokinetics similar to young males. Elderly
females (≥65 years of age) had a 47% higher AUCss and 32% higher Cmax,ss as compared to younger
females (≤55 years of age) after body weight normalization. Despite
the increased total concentrations in the elderly females, the adverse
event profile was comparable for both elderly patient populations.
A smaller free fraction was found in elderly female patients in comparison
to elderly male patients.
Gender
Young females exhibited slightly lower plasma concentrations relative
to young males. After single doses of 7.5 mg MOBIC, the mean elimination
half-life was 19.5 hours for the female group as compared to 23.4
hours for the male group. At steady state, the data were similar
(17.9 hours vs 21.4 hours). This pharmacokinetic difference due to
gender is likely to be of little clinical importance. There was linearity
of pharmacokinetics and no appreciable difference in the Cmax or Tmax across genders.
Hepatic Impairment
Following a single 15 mg dose of meloxicam there was
no marked difference in plasma concentrations in patients with mild
(Child-Pugh Class I) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class II) hepatic impairment
compared to healthy volunteers. Protein binding of meloxicam was
not affected by hepatic impairment. No dosage adjustment is necessary
in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. Patients with
severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class III) have not been adequately
studied [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)
].
Renal Impairment
Meloxicam pharmacokinetics have been investigated in
subjects with mild and moderate renal impairment. Total drug plasma
concentrations of meloxicam decreased and total clearance of meloxicam
increased with the degree of renal impairment while free AUC values
were similar in all groups. The higher meloxicam clearance in subjects
with renal impairment may be due to increased fraction of unbound
meloxicam which is available for hepatic metabolism and subsequent
excretion. No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with mild
to moderate renal impairment. Patients with severe renal impairment
have not been adequately studied. The use of MOBIC in subjects with
severe renal impairment is not recommended [
see
Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and
Use in Specific Populations (8.7)
].
Hemodialysis
Following a single dose of meloxicam, the free Cmax plasma concentrations were higher in patients with renal failure
on chronic hemodialysis (1% free fraction) in comparison to healthy
volunteers (0.3% free fraction). Hemodialysis did not lower the total
drug concentration in plasma; therefore, additional doses are not
necessary after hemodialysis. Meloxicam is not dialyzable [
see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.6), and Use in Specific Populations (8.7)
].
Aspirin:
When MOBIC is administered with aspirin
(1000 mg three times daily) to healthy volunteers, it tended to increase
the AUC (10%) and Cmax (24%) of meloxicam.
The clinical significance of this interaction is not known [
see Drug Interactions (7.2)
].
Cholestyramine:
Pretreatment for four
days with cholestyramine significantly increased the clearance of
meloxicam by 50%. This resulted in a decrease in t1/2, from 19.2 hours to 12.5 hours, and a 35% reduction in AUC. This
suggests the existence of a recirculation pathway for meloxicam in
the gastrointestinal tract. The clinical relevance of this interaction
has not been established.
Cimetidine:
Concomitant administration
of 200 mg cimetidine four times daily did not alter the single-dose
pharmacokinetics of 30 mg meloxicam.
Digoxin:
Meloxicam 15 mg once
daily for 7 days did not alter the plasma concentration profile of
digoxin after β-acetyldigoxin administration for 7 days at clinical
doses. In vitro testing found no protein binding
drug interaction between digoxin and meloxicam.
Lithium:
In a
study conducted in healthy subjects, mean pre-dose lithium concentration
and AUC were increased by 21% in subjects receiving lithium doses
ranging from 804 to 1072 mg twice daily with meloxicam 15 mg QD every
day as compared to subjects receiving lithium alone [
see Drug Interactions (7.4)
].
Methotrexate:
A study in 13 rheumatoid arthritis
(RA) patients evaluated the effects of multiple doses of meloxicam
on the pharmacokinetics of methotrexate taken once weekly. Meloxicam
did not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of single
doses of methotrexate. In vitro, methotrexate did
not displace meloxicam from its human serum binding sites [
see Drug Interactions (7.5)
].
Warfarin:
The effect of meloxicam on
the anticoagulant effect of warfarin was studied in a group of healthy
subjects receiving daily doses of warfarin that produced an INR (International
Normalized Ratio) between 1.2 and 1.8. In these subjects, meloxicam
did not alter warfarin pharmacokinetics and the average anticoagulant
effect of warfarin as determined by prothrombin time. However, one
subject showed an increase in INR from 1.5 to 2.1. Caution should
be used when administering MOBIC with warfarin since patients on warfarin
may experience changes in INR and an increased risk of bleeding complications
when a new medication is introduced [
see Drug Interactions (7.7)
].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: There
was no increase in tumor incidence in long-term carcinogenicity studies
in rats (104 weeks) and mice (99 weeks) administered meloxicam at
oral doses up to 0.8 mg/kg/day in rats and up to 8.0 mg/kg/day in
mice (up to 0.5- and 2.6-fold, respectively, the maximum recommended
human daily dose based on body surface area comparison).
Mutagenesis: Meloxicam
was not mutagenic in an Ames assay, or clastogenic in a chromosome
aberration assay with human lymphocytes and an in vivo micronucleus test in mouse bone marrow.
Impairment of Fertility: Meloxicam
did not impair male and female fertility in rats at oral doses up
to 9 mg/kg/day in males and 5 mg/kg/day in females (up to 5.8- and
3.2-fold greater, respectively, than the maximum recommended human
daily dose based on body surface area comparison).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Osteoarthritis
and Rheumatoid Arthritis
The use of MOBIC for the treatment of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis
of the knee and hip was evaluated in a 12-week, double-blind, controlled
trial. MOBIC (3.75 mg, 7.5 mg, and 15 mg daily) was compared to placebo.
The four primary endpoints were investigator’s global assessment,
patient global assessment, patient pain assessment, and total WOMAC
score (a self-administered questionnaire addressing pain, function,
and stiffness). Patients on MOBIC 7.5 mg daily and MOBIC 15 mg daily
showed significant improvement in each of these endpoints compared
with placebo.
The use of MOBIC
for the management of signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis was evaluated
in six double-blind, active-controlled trials outside the U.S. ranging
from 4 weeks’ to 6 months’ duration. In these trials, the efficacy
of MOBIC, in doses of 7.5 mg/day and 15 mg/day, was comparable to
piroxicam 20 mg/day and diclofenac SR 100 mg/day and consistent with
the efficacy seen in the U.S. trial.
The use of MOBIC for the treatment of the signs and
symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis was evaluated in a 12-week, double-blind,
controlled multinational trial. MOBIC (7.5 mg, 15 mg, and 22.5 mg
daily) was compared to placebo. The primary endpoint in this study
was the ACR20 response rate, a composite measure of clinical, laboratory,
and functional measures of RA response. Patients receiving MOBIC
7.5 mg and 15 mg daily showed significant improvement in the primary
endpoint compared with placebo. No incremental benefit was observed
with the 22.5 mg dose compared to the 15 mg dose.
14.2 Juvenile Rheumatoid
Arthritis (JRA) Pauciarticular and Polyarticular Course
The use of MOBIC for the treatment of the
signs and symptoms of pauciarticular or polyarticular course Juvenile
Rheumatoid Arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older was evaluated
in two 12-week, double-blind, parallel-arm, active-controlled trials.
Both studies included three arms: naproxen
and two doses of meloxicam. In both studies, meloxicam dosing began
at 0.125 mg/kg/day (7.5 mg maximum) or 0.25 mg/kg/day (15 mg maximum),
and naproxen dosing began at 10 mg/kg/day. One study used these doses
throughout the 12-week dosing period, while the other incorporated
a titration after 4 weeks to doses of 0.25 mg/kg/day and 0.375 mg/kg/day
(22.5 mg maximum) of meloxicam and 15 mg/kg/day of naproxen.
The efficacy analysis used the ACR Pediatric
30 responder definition, a composite of parent and investigator assessments,
counts of active joints and joints with limited range of motion, and
erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The proportion of responders were
similar in all three groups in both studies, and no difference was
observed between the meloxicam dose groups.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE
AND HANDLING
MOBIC is
available as a pastel yellow, round, biconvex, uncoated tablet containing
meloxicam 7.5 mg or as a pastel yellow, oblong, biconvex, uncoated
tablet containing meloxicam 15 mg. The 7.5 mg tablet is impressed
with the Boehringer Ingelheim logo on one side, and on the other side,
the letter “M”. The 15 mg tablet is impressed with the tablet code
“15” on one side and the letter “M” on the other. MOBIC is also available
as a yellowish green tinged viscous oral suspension containing 7.5
mg meloxicam in 5 mL.
MOBIC tablets
7.5 mg: NDC 0597-0029-01; Bottles of 100
MOBIC tablets 15 mg: NDC 0597-0030-01; Bottles of
100
MOBIC oral suspension 7.5
mg/5 mL: NDC 0597-0034-01; Bottles of 100 mL
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C-30°C
(59°F-86°F).
Keep MOBIC tablets in a dry place.
Dispense tablets in a tight container.
Keep oral suspension container tightly closed.
Keep this and all medications out of the reach of children.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved Medication Guide
Patients
should be informed of the following information before initiating
therapy with an NSAID and periodically during the course of ongoing
therapy.
17.1 Medication Guide
Inform patients of the availability of
a Medication Guide for NSAIDs that accompanies each prescription dispensed,
and instruct them to read the Medication Guide prior to using MOBIC.
17.2 Cardiovascular
Effects
NSAIDs including
MOBIC may cause serious CV side effects, such as MI or stroke, which
may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious CV
events can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert
for the signs and symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness,
slurring of speech, and should ask for medical advice when observing
any indicative sign or symptoms. Patients should be apprised of the
importance of this follow-up [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)
].
17.3 Gastrointestinal
Effects
NSAIDs including
MOBIC, can cause GI discomfort and, rarely, serious GI side effects,
such as ulcers and bleeding, which may result in hospitalization and
even death. Although serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can
occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs
and symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, and should ask for medical
advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms including epigastric
pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis. Patients should be apprised
of the importance of this follow-up [
see Warnings
and Precautions (5.2)
].
17.4 Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients of the warning signs and
symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus,
jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and «flu-like» symptoms).
If these occur, instruct patients to stop therapy and seek immediate
medical therapy [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)
].
17.5 Adverse Skin Reactions
NSAIDs including MOBIC, can cause serious
skin side effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson
Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which may result
in hospitalization and even death. Although serious skin reactions
may occur without warning, patients should be alert for the signs
and symptoms of skin rash and blisters, fever, or other signs of hypersensitivity
such as itching, and should ask for medical advice when observing
any indicative signs or symptoms. Advise patients to stop the drug
immediately if they develop any type of rash and contact their physicians
as soon as possible [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)
].
17.6 Weight Gain and
Edema
Advise patients
to promptly report signs or symptoms of unexplained weight gain or
edema to their physicians [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)
].
17.7 Anaphylactoid Reactions
Inform patients of the signs of an anaphylactoid
reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat).
Instruct patients seek immediate emergency help [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)
].
17.8 Effects During
Pregnancy
Starting at
30 weeks gestation, MOBIC should be avoided as premature closure of
the ductus arteriosus in the fetus may occur [
see
Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and
Use in Specific Populations (8.1)
].
17.9 Effects on Female Fertility
Advise females of reproductive potential who desire
pregnancy that NSAIDs, including MOBIC, may be associated with a reversible
delay in ovulation. For women who have difficulties conceiving, or
who are undergoing investigation of infertility, use of meloxicam
is not recommended [see Use in Specific Populations (8.8)
].
Kayexalate is a registered trademark of
Sanofi-Aventis
Please address medical inquiries to (800) 542-6257 or (800) 459-9906
TTY.
Distributed
by: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Ridgefield,
CT 06877 USA
Licensed from: Boehringer
Ingelheim International GmbH
Copyright 2012 Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
10003990/08
IT1400KC122012
090340141/9
OT1407G
Medication Guide for Non-Steroidal
Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
(See
the end of this Medication Guide for a list of prescription NSAID
medicines.)
What is the most important information I should know
about medicines called Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID
medicines may increase the chance of a heart attack or stroke that
can lead to death.
This chance increases:
- with longer use of NSAID medicines
- in people who have heart disease
NSAID medicines should
never be used right before or after a heart surgery called a «coronary
artery bypass graft (CABG).»
NSAID medicines can cause ulcers and
bleeding in the stomach and intestines at any time during treatment.
Ulcers and bleeding:
- can happen without warning symptoms
- may cause death
The chance of a person
getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
- taking medicines called «corticosteroids» and «anticoagulants»
- longer use
- smoking
- drinking alcohol
- older age
- having poor health
NSAID medicines should
only be used:
- exactly as prescribed
- at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
- for the shortest time needed
What are Non-Steroidal
Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines are used to treat pain and redness,
swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as:
- different types of arthritis
- menstrual cramps and other types of short-term pain
Who should not take
a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)?
Do not
take an NSAID medicine:
- if you had an asthma attack, hives, or other allergic reaction
with aspirin or any other NSAID medicine - for pain right before or after heart bypass surgery
Tell your healthcare
provider:
- about all of your medical conditions.
- about all of the medicines you take. NSAIDs and some other
medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects.
Keep a list of your medicines to show to your healthcare
provider and pharmacist.
- if you are pregnant.
NSAID medicines should
not be used by pregnant women late in their pregnancy.
- if you are breastfeeding.
Talk to your doctor.
What are the possible
side effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
Serious
side effects include:
- heart attack
- stroke
- high blood pressure
- heart failure from body swelling (fluid retention)
- kidney problems including kidney failure
- bleeding and ulcers in the stomach and intestine
- low red blood cells (anemia)
- life-threatening skin reactions
- life-threatening allergic reactions
- liver problems including liver failure
- asthma attacks in people who have asthma
Other side effects
include:
- stomach pain
- constipation
- diarrhea
- gas
- heartburn
- nausea
- vomiting
- dizziness
Get emergency help
right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- chest pain
- weakness in one part or side of your body
- slurred speech
- swelling of the face or throat
Stop your NSAID medicine
and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the
following symptoms:
- nausea
- more tired or weaker than usual
- itching
- your skin or eyes look yellow
- stomach pain
- flu-like symptoms
- vomit blood
- there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and
sticky like tar - unusual weight gain
- skin rash or blisters with fever
- swelling of the arms and legs, hands and feet
These are not all the side effects
with NSAID medicines. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist
for more information about NSAID medicines.
Call your doctor for medical advice
about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Other
information about Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Aspirin is an NSAID medicine but it does not increase the
chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain,
stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach
and intestines. - Some of these NSAID medicines are sold in lower doses without
a prescription (over-the-counter). Talk to your healthcare provider
before using over-the-counter NSAIDs for more than 10 days.
NSAID
medicines that need a prescription
|
Generic Name |
Tradename |
| Celecoxib | Celebrex |
| Diclofenac | Cataflam, Voltaren, Arthrotec (combined with misoprostol) |
| Diflunisal | Dolobid |
| Etodolac | Lodine, Lodine XL |
| Fenoprofen | Nalfon, Nalfon 200 |
| Flurbiprofen | Ansaid |
| Ibuprofen | Motrin, Tab-Profen, Vicoprofen* (combined with hydrocodone), Combunox (combined with oxycodone) |
| Indomethacin | Indocin, Indocin SR, Indo-Lemmon, Indomethagan |
| Ketoprofen | Oruvail |
| Ketorolac | Toradol |
| Mefenamic Acid | Ponstel |
| Meloxicam | Mobic |
| Nabumetone | Relafen |
| Naproxen | Naprosyn, Anaprox, Anaprox DS, EC-Naprosyn, Naprelan, Naprapac (copackaged with lansoprazole) |
| Oxaprozin | Daypro |
| Piroxicam | Feldene |
| Sulindac | Clinoril |
| Tolmetin | Tolectin, Tolectin DS, Tolectin 600 |
*Vicoprofen contains the same dose
of ibuprofen as over-the-counter (OTC) NSAIDs, and is usually used
for less than 10 days to treat pain. The OTC NSAID label warns that
long term continuous use may increase the risk of heart attack or
stroke.
This
Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Mobic® (meloxicam) Tablets Label
7.5 mg/100 Tablets
NDC: 0597002901
Mobic® (meloxicam) Tablets Label
15 mg/100 Tablets
NDC: 0597003001

Mobic® (meloxicam) Oral Suspension
7.5 mg/5 mL
NDCL: 0597003401

Mobic
meloxicam SUSPENSION
Product Information |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Type | Human prescription drug label | Item Code (Source) | NDC:0597-0034 |
| Route of Administration | ORAL | DEA Schedule |
Active Ingredient/Active Moiety |
||
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient Name | Basis of Strength | Strength |
| MELOXICAM MELOXICAM | 7.5 mg |
Inactive Ingredients |
|
|---|---|
| Ingredient Name | Strength |
| SILICON DIOXIDE | |
| HYDROXYETHYL CELLULOSE (2000 CPS AT 1%) | |
| sorbitol | |
| Xylitol | |
| sodium phosphate, monobasic, dihydrate | |
| saccharin sodium | |
| SODIUM BENZOATE | |
| CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE | |
| water |
Product Characteristics |
||
|---|---|---|
| Color | ||
| GREEN |
Packaging |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Item Code | Package Description | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| 1 | 100 in 1 BOTTLE, GLASS | |||
| 2 | NDC:0597-0034-01 | 1 in 1 CARTON |
Marketing Information |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA021530 | 2005-11-01 |
Mobic
meloxicam TABLET
Product Information |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Type | Human prescription drug label | Item Code (Source) | NDC:0597-0029 |
| Route of Administration | ORAL | DEA Schedule |
Active Ingredient/Active Moiety |
||
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient Name | Basis of Strength | Strength |
| MELOXICAM MELOXICAM | 7.5 mg |
Product Characteristics |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Size | Imprint Code | Shape |
| YELLOW | 8 mm | M; | ROUND |
Packaging |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Item Code | Package Description | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| 1 | NDC:0597-0029-01 | 100 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC |
Marketing Information |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA020938 | 2000-06-01 |
Mobic
meloxicam TABLET
Product Information |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Type | Human prescription drug label | Item Code (Source) | NDC:0597-0030 |
| Route of Administration | ORAL | DEA Schedule |
Active Ingredient/Active Moiety |
||
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient Name | Basis of Strength | Strength |
| MELOXICAM MELOXICAM | 15 mg |
Product Characteristics |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Size | Imprint Code | Shape |
| YELLOW | 11 mm | M;15 | OVAL |
Packaging |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Item Code | Package Description | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| 1 | NDC:0597-0030-01 | 100 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC |
Marketing Information |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA020938 | 2000-10-01 |
