-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Troubleshooting
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator
User Manual
Related Manuals for Respironics V60
Summary of Contents for Respironics V60
-
Page 1
Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator User Manual… -
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Table of contents Warnings, cautions, and notes ……. 1-1 Definitions ……….1-1 General.
-
Page 4
Leak adaptation ……..4-5 Auto-Trak+ (optional) . -
Page 5
Standby ……….6-20 Help function . -
Page 6
Repacking and shipping ……..10-9 Technical specifications ……..11-1 Control settings . -
Page 7
Electromagnetic compatibility declaration ….. . D-1 Electromagnetic emissions ……D-2 Electromagnetic immunity . -
Page 8
viii… -
Page 9: Warnings, Cautions, And Notes
Chapter 1. Warnings, cautions, and notes Before using the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator on a patient, familiarize yourself with this user manual, particularly the safety considerations listed. Be aware, however, that this manual is a reference only. It is not intended to supersede your institution’s protocol regarding the safe use of assisted…
-
Page 10
Do not leave the ventilator unattended when stationed on an incline. WARNING: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator may cause radio interference or may disrupt the operation of nearby equipment. It may be necessary to take mitigation measures, such as re-orienting or relocating the ventilator or shielding the location. -
Page 11
EMC emissions or decrease the EMC immunity performance of the equipment. WARNING: Do not use the ventilator in an MRI environment. The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is MR Unsafe. Keep it outside the MRI scan room (Zone IV). It represents a projectile hazard. -
Page 12: Preparing For Ventilation
To reduce the risk of fire, do not use a high-pressure oxygen hose that is worn or contaminated with combustible materials like grease or oil. WARNING: The Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is designed to use ambient air and high pressure 100% oxygen. No other gases should be used. WARNING: Do not use the ventilator with helium or helium mixtures.
-
Page 13
For example, positioning the ventilator next to a curtain that blocks the flow of cooling air can cause the equipment to overheat. Use the V60/V60 Plus in an upright position that does not block the air inlet. -
Page 14
Philips-supplied cord securely in place. WARNING: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator should not be positioned in a way that makes it difficult to disconnect from mains power if necessary. Disconnect from supply mains by removing the power cord from the wall outlet. The AC mains plug is used as disconnection device. -
Page 15: Operation
SIS adapters such as the O transport manifold. NOTE: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is a single-limb device with substantial intentional and unintentional leak in the ventilator breathing system. Under those conditions, CO cannot be measured accurately. Therefore, we do not recommend the use of CO monitoring.
-
Page 16: Alarms And Messages
— Do not short-circuit the battery or allow metallic or conductive objects to contact the battery connector housing. — Use the battery with the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator only. WARNING: Modification of the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator and associated equipment is not permitted and may compromise ventilator operation and patient safety.
-
Page 17: First-Time Installation
(or as stipulated by your institution). CAUTION: To ensure proper system performance, use a Respironics-approved air inlet filter. CAUTION: Because some environments cause a quicker collection of lint and dust than others, inspect the filters more often when needed.
-
Page 18: Diagnostic Mode
To prevent possible patient injury due to nonannunciating alarms, verify the operation of any remote alarm device before use. WARNING: To ensure the functionality of the remote alarm, connect only Respironics- approved cables to the remote alarm port. CAUTION: The remote alarm port is intended to connect only to an SELV (safety extra-low voltage and ungrounded system with basic insulation to ground), in accordance with IEC 60601-1.
-
Page 19: Symbols
Chapter 2. Symbols Refer to these tables to interpret symbols used on the ventilator labels, backup battery labels, and packaging and on the ventilator screen. To interpret symbols pertaining to accessories, refer to their instructions for use. Table 2-1: Symbols used on ventilator labels, battery, and packaging Symbol Description Warning: Risk of explosion.
-
Page 20
Symbols Table 2-1: Symbols used on ventilator labels, battery, and packaging Symbol Description Stacking limit by number This end up Type B applied part, which is equipment that provides a particular degree of protection against electric shock, particularly in regard to allowable leakage current and of the protective earth connection Requires alternating current (AC) Degree of fluid ingress protection provided by the enclosure (drip-proof) -
Page 21
Symbols Table 2-1: Symbols used on ventilator labels, battery, and packaging Symbol Description Manufacturer. Symbol accompanied by manufacturer’s name and address. EC representative Serial number Order number Lot or batch number Model number Use by date RS-232 serial input/output USB port Oxygen (Yellow) Warning Ethernet connection… -
Page 22
Noninvasive ventilation (patient with mask) Invasive ventilation (intubated patient) The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is MR Unsafe and presents a projectile haz- ard. Keep the ventilator outside MRI scan room (Zone IV). Do not block the cooling fan Inlet (at the rear of the ventilator). -
Page 23
Symbols Table 2-1: Symbols used on ventilator labels, battery, and packaging Symbol Description Recycle (Taiwan) 廢 電 池 請 回 收 RoHS (China). Administrative Measure on the Control of Pollution Caused by Electronic Information Products. Contains RoHS substances with 50 years environmentally friendly use period (EFUP). uR UL recognition symbol Direct current (DC). -
Page 24
Table 2-1: Symbols used on ventilator labels, battery, and packaging Symbol Description Auto-Trak+ software option High flow therapy Note: 3.00 software and above. HFT is optional for model V60 and included with model V60 Plus. Table 2-2: Symbols used on graphical user interface Symbol Description… -
Page 25
Symbols Table 2-2: Symbols used on graphical user interface (continued) Symbol Description Cancel button. Cancels set values. +2:00 minutes button. Adds two minutes to 100% O delivery. Ventilator is powered by AC power and the battery is installed. Ventilator is powered by AC power and the battery is not installed. Ventilator is powered by the battery. -
Page 26
Flow, liters per minute. BTPS compensated. Volume, milliliters User-set Ramp Time. Ramp graphic fills in as Ramp Time progresses. Ramp Time is OFF (no ramp time set). Intentional leak. The number corresponds to the leak symbol printed on Philips Respironics masks. -
Page 27: General Information
Philips-recommended patient circuits, interfaces (masks), humidifiers, and other accessories. Indications for use The Respironics V60/V60 Plus is an assist ventilator and is indicated for use to augment patient breathing. The ventilator is indicated for spontaneously breathing individuals who require mechanical ventilation: patients with respiratory failure, chronic respiratory insufficiency, or obstructive sleep apnea in a hospital or other institutional settings under the direction of a physician.
-
Page 28: Contraindications
General information Contraindications The Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is contraindicated for patients with any of the following conditions: • Lack of spontaneous respiratory drive • Inability to maintain a patent airway or adequately clear secretions • At risk for aspiration of gastric contents •…
-
Page 29: General Description
Flow and O percentage settings are selected by the clinician. HFT is available for 3.00 software and above, as well as for the V60 Plus. Auto-Trak Sensitivity allows the ventilator to automatically compensate for intentional and unintentional leaks by maintaining a stable baseline and adjusting trigger and cycle thresholds for optimum patient-to-ventilator synchrony.
-
Page 30: Physical Description
RS-232 port. Physical description Patient circuits, masks/patient interfaces, and accessories Figure 3-2 shows the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator with its patient circuit and accessories. Appendix C provides ordering information for parts and accessories.
-
Page 31
General information Bacteria filter Mask Oxygen monitor Humidifier Patient circuit Oxygen cylinder Figure 3-2: Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator with accessories… -
Page 32: Ventilator Unit
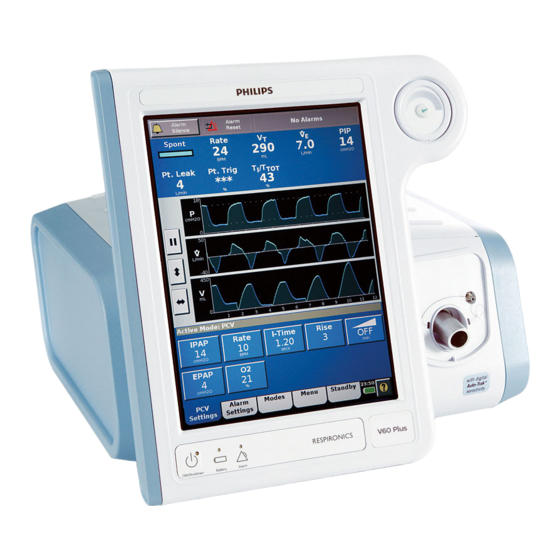
General information Ventilator unit Figure 3-3 through Figure 3-5 show the controls, indicators, and other important parts of the ventilator unit. Key panel Figure 3-3: Front view Number Description Graphical user interface. Color LCD (liquid crystal display) with touchscreen. Navigation ring. Lets you adjust values and navigate the graphical user interface by rotating the finger on its touchpad.
-
Page 33
General information Number Description Battery (charged) LED. Flashes when battery is charging. On continuously when battery is charged. Off when ventilator is running on battery, when a battery er- ror or failure is detected, or when the ventilator is off and AC power is not con- nected. -
Page 34
General information 5 4 3 2 Figure 3-5: Rear view Number Description Backup battery (compartment under side panel). Remote alarm/nurse call connector Reserved for future use Power cord retainer Power cord RS-232 serial connector (female DB-25). Connects to hospital information systems and other serial devices. -
Page 35: About The Backup Battery
General information About the backup WARNING: To reduce the risk of power failure to the ventilator, pay close attention to the battery’s charge level. The battery’s operation time is approximate and battery is affected by ventilator settings, discharge and recharge cycles, battery age, and ambient temperature.
-
Page 36
General information CAUTION: Avoid allowing the ventilator battery to become completely discharged. Otherwise, the battery may become over-discharged and require long recharge times of up to 16 hours or more. The over- discharged condition may permanently damage the battery so that it is unable to recharge. -
Page 37: About The Graphical User Interface
General information About the graphical Through the graphical user interface (Figure 3-7) you make ventilator settings and view ventilator and patient data. During ventilation, the upper screen user interface displays alarms and patient data. The middle screen displays real-time waveforms and alarm and informational messages. The lower screen lets you access modes and other ventilator settings, display help information, and see the power status.
-
Page 38: Navigating The Graphical User Interface
General information Navigating the graphical user interface Select a function by touching the desired tab or button on the touchscreen. Use this as the primary method to control the ventilator. You can use the navigation ring as an alternative to the following touchscreen functions: Touchscreen equivalent Navigation ring equivalent…
-
Page 39: Starting Up The Ventilator
General information Starting up the NOTE: Upon power-on the ventilator automatically runs a test of the backup audible alarm followed by the primary audible alarm. You should hear ventilator a high-pitched tone, followed by a beep. If you do not hear all of these sounds, discontinue use of the ventilator and have it serviced.
-
Page 40
General information 3-14… -
Page 41
Chapter 4. Principles of operation System operational The Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is a microprocessor-controlled pneumatic system that delivers a mixture of air and oxygen. It is powered by overview AC with battery backup to protect against power failure or unstable power and to facilitate intrahospital transport. -
Page 42: Principles Of Operation
CO removal. Breath delivery Control variable Breaths delivered by the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator are pressure characteristics controlled. In the AVAPS mode, the ventilator’s applied pressure is automatically adjusted over a period of time to maintain a target tidal volume.
-
Page 43: Pressure Rise Time
Auto-Trak Sensitivity An important characteristic of the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is its ability to recognize and compensate for intentional and unintentional leaks in the system, and to automatically adjust its triggering and cycling algorithms to maintain optimum performance in the presence of leaks.
-
Page 44
Principles of operation Shape signal method of cycling and triggering. The shape signal or “shadow trigger” method uses a mathematical model derived from the flow signal. A new flow signal (shape signal) is generated by offsetting the signal from the actual flow and delaying it (Figure 4-2). -
Page 45: Leak Adaptation
Principles of operation Leak adaptation Noninvasive ventilation in particular may involve considerable leakage around the mask or through the mouth. Some leakage is known or intentional: it is a characteristic of the mask/patient interface design. So that it can accurately adjust its baseline flow, the ventilator has you enter the intentional leakage value specific to the mask/patient interface (“Selecting the mask and exhalation port”…
-
Page 46: Auto-Trak+ (Optional)
Volume adjustment Figure 4-5: Tidal volume adjustment Auto-Trak+ (optional) The Auto-Trak+ option for the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator lets you further adjust the level of Auto-Trak Sensitivity, a feature that recognizes and compensates for intentional and unintentional leaks. This algorithm has multiple breath trigger and cycle thresholds.
-
Page 47: Ventilation Modes
Patient alarms are not available during high flow therapy. This therapy is not considered a breath delivery mode. HFT requires 3.00 software and above. Ventilation modes The Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator operates in the following ventilation modes: • CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) mode •…
-
Page 48: Cpap Mode
Principles of operation CPAP mode In the CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) mode, the ventilator functions as a demand flow system, with the patient triggering all breaths and determining their timing and size. The patient triggers and cycles based on the ventilator’s Auto-Trak Sensitivity algorithms.
-
Page 49: Pcv Mode
Principles of operation PCV mode The PCV (pressure-controlled ventilation) mode delivers pressure-controlled breaths, either triggered by the ventilator (Timed) or the patient (Spont). The control settings active in the PCV mode are shown in Figure 4-8. The IPAP setting defines the applied inspiratory pressure for all breaths. If the patient fails to trigger a breath through Auto-Trak within the interval determined by the rate setting, the ventilator triggers a mandatory breath.
-
Page 50: S/T Mode
Principles of operation S/T mode The S/T (spontaneous/timed) mode guarantees breath delivery at the user-set rate. It delivers pressure-controlled, time-cycled mandatory and pressure- supported spontaneous breaths, all at the IPAP pressure level. If the patient fails to trigger a breath within the interval determined by the Rate setting, the ventilator triggers a mandatory breath with the set I-Time.
-
Page 51: Avaps Mode
Principles of operation AVAPS mode NOTE: When you adjust AVAPS minimum and maximum pressures, remember that IPAP is adjusted to meet the target value. If the calculated target pressure is outside of the minimum and maximum pressure range, the target volume will not be achieved. Unlike most pressure modes, the AVAPS (average volume-assured pressure support) mode delivers a target tidal volume.
-
Page 52
Principles of operation Max P Mandatory (Timed) Rise breath Min P EPAP I-Time Patient-triggered (Spont) 1/Rate spontaneous breath Time Figure 4-13: AVAPS waveforms 4-12… -
Page 53: Ppv Mode (Optional)
Principles of operation PPV mode (optional) The PPV (proportional pressure ventilation) mode provides patient-triggered breaths that deliver pressure in proportion to patient effort. Additionally a user- settable backup rate activates machine-triggered, pressure-limited, and time- cycled breaths in the case of apnea. In the PPV mode, patient effort determines the pressure, flow, and tidal volume delivered by the ventilator.
-
Page 54
Principles of operation setting. If the patient fails to trigger a breath within the interval determined by the Rate control, the ventilator triggers a Timed (backup) breath with the set I-Time, Rise, and IPAP settings. The control settings active in the PPV mode are shown in Figure 4-14. Figure 4-14: PPV controls Figure 4-15 shows PPV mode waveforms. -
Page 55: Oxygen Mixing
Principles of operation Oxygen mixing The ventilator’s oxygen mixer regulates and proportions oxygen into the air from the blower according to the O setting. The delivered oxygen accuracy is ±5% of the set value up to the maximum oxygen flow available. The ventilator can deliver up to 240 L/min of air/oxygen mix to assist in managing uncontrolled leaks during noninvasive ventilation.
-
Page 56
Principles of operation 4-16… -
Page 57: Setting Up The Ventilator For Use
The Analytical Industries 2000M monitor includes user-settable high and low oxygen % alarms and is approved for use with the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator. Refer to the monitor instructions for use for detailed instructions on the proper setup and operation of the oxygen monitor.
-
Page 58: Connecting To Ac Power
WARNING: Do not use extension cords, adapters, or power cords with the ventilator that are not approved by Respironics. WARNING: To prevent unintentional disconnection of the power cord, always use the correct, Philips-supplied power cord and lock it into place with the power cord retainer before you switch the ventilator on.
-
Page 59: Installing The Patient Circuit
To prevent patient or ventilator contamination, always use a main flow bacteria filter on the patient gas outlet port. Filters not approved by Respironics may degrade system performance. WARNING: During ventilation, patient exhalate is released into room air. Use of a patient circuit with a filter on its exhalation port is recommended.
-
Page 60
Setting up the ventilator for use Assemble the patient circuit, including the main flow (inspiratory) bacteria filter, proximal pressure line, oxygen sensor tee, and if desired, humidifier and nebulizer. Figure 5-2 and Figure 5-3 show circuit configurations for noninvasive and invasive ventilation. Follow the manufacturers’ instructions for use for the individual parts. -
Page 61
Setting up the ventilator for use NOTE: This circuit setup is recommended for noninvasive ventilation. Proximal pressure port Ventilator outlet Oxygen sensor tee Bacteria filter Proximal pressure line Figure 5-2: Noninvasive patient circuit, without humidification… -
Page 62: Connecting External Devices
The Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator can communicate with a Philips patient monitor using the IntelliBridge Open Interface. See “Using Philips monitors and the IntelliBridge or VueLink Open Interfaces” on page B-2. The ventilator also supports the VueLink Open Interface.
-
Page 63: Before Placing A Patient On The Ventilator
Setting up the ventilator for use Before placing a WARNING: To ensure the ventilator’s safe operation, always verify ventilator operation as described in “Verify ventilator operation” on page 5-7 before patient on the using the ventilator on a patient. If the ventilator fails any tests, remove it ventilator from clinical use immediately.
-
Page 64: Running Alarm Tests
Setting up the ventilator for use d. VERIFY that the blue “Running on Internal Battery” message is displayed. 6. Install a fully-charged battery and reconnect the ventilator to AC power. 7. Repeat step 5 to verify that the ventilator switches over to battery power.
-
Page 65: Low Tidal Volume
Setting up the ventilator for use Low Tidal Volume 1. Raise the Lo V alarm setting above the displayed, measured V 2. VERIFY that the alarm is activated. Low Tidal Volume 3. Turn the Lo V alarm setting OFF. 4. VERIFY that the alarm resets. Patient Disconnect 1.
-
Page 66: Using The Ventilator For Intra-Hospital Transport
WARNING: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator requires a pressurized oxygen supply that provides a minimum flow of 175 SLPM. Do not use any devices such as valves, hoses, Grab n’ Go regulators or other brands of combined cylinder/ regulators that limit supply of oxygen flow below 175 SLPM.
-
Page 67: Storing The Ventilator Between Patient Use
Setting up the ventilator for use 95 100 Leak of 10 L/min Leak of 20 L/min Leak of 30 L/min Leak of 40 L/min Leak of 50 L/min a. V = 500 mL, Rate = 40 BPM, EPAP = 6 cmH O, IPAP = 18 cmH 95 100 Leak of 20 L/min…
-
Page 68: Mri Safety Information
Setting up the ventilator for use MRI safety WARNING: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is MR Unsafe. Keep it outside the MRI scan room (Zone IV). It represents a projectile hazard. information 5-12…
-
Page 69: Operation
Chapter 6. Operation WARNING: To ensure the ventilator’s safe operation, always verify ventilator operation as described in “Verify ventilator operation” on page 5-7 before using the ventilator on a patient. If the ventilator fails any tests, remove it from clinical use immediately. Do not use the ventilator until necessary repairs are completed and all tests have passed.
-
Page 70: Changing The Mode
Operation Changing the mode The active ventilation mode is displayed in the bottom, left-hand corner of the screen. Change the mode as follows. For details on modes, see “Ventilation modes” on page 4-7. 1. Open the Modes window. 2. Select the desired mode. Active mode 3.
-
Page 71: Changing Control Settings
Operation Changing control Table 6-3 on page 6-23 is an alphabetical list of the control settings with their ranges. Table 11-2 on page 11-2 shows the control settings applicable to the settings different modes. For more information on control settings as they apply in the different ventilation modes, see “Ventilation modes”…
-
Page 72: Changing Individual Ventilator Settings
Operation Changing individual ventilator settings You can make ventilator settings from the Settings window. 1. Open the Settings window. 2. Select the desired setting. As an example we will show the IPAP adjustment. 3. The setting window opens. Adjust the setting. Select Accept to apply. Adjustment Setting range scale arrow button…
-
Page 73: Using The Ramp Time Function
Operation Using the Ramp Time The Ramp Time function helps your patient adapt to ventilation by gradually increasing inspiratory and expiratory pressure (IPAP and EPAP/CPAP) from function subtherapeutic to user-set pressures over a user-set interval. Table 6-3 on page 6-23 describes this function’s principles of operation. Follow these instructions to use the Ramp Time function: 1.
-
Page 74: Using The 100% O2 Function
Operation Using the 100% O NOTE: The 100% O feature is available in Revision 2.30 software and above. function The 100% O function delivers 100% oxygen to the patient. It is available during Screen Lock status. Follow these instructions to use the 100% O function: 1.
-
Page 75: Using Ppv
Operation Using PPV Follow these instructions to set up the ventilator in the PPV mode, referring to Figure 6-3. For principles of operation, see “PPV mode (optional)” on page 4-13. 1. Open the PPV Settings window. 2. Set EPAP, O , alarm limits, and backup settings to appropriate values.
-
Page 76
Operation Max V Inspiration terminated Max V Sudden increase in flow Time Figure 6-1: PPV waveform – Max V limit When the Max P (PPV maximum pressure limit) is reached, pressure is limited but the breath is not terminated, and a message is displayed. After the limit is reached in three consecutive breaths, the audible alarm sounds. -
Page 77: Guidelines For Using Ppv
Operation Guidelines for using PPV NOTE: The guidelines below are based on recommendations by clinicians. They do not replace the clinical judgment of a physician and should not, on their own, be used for clinical decision making. Determining Max R and Max E settings It is recommended you set Max R (flow assist) and Max E (volume assist) to initial values and then titrate them based on the patient’s disease process: •…
-
Page 78
Operation 2. Adjust Max E: a. Evaluate the patient. Check whether any of these conditions is true: • The patient says they are getting too much air, pressure, or volume • The patient is using accessory muscles to actively stop inspiration •… -
Page 79
Operation Start Max R Make initial settings: titration EPAP: 4 cmH : Current setting or per prescription Max P: 25 cmH Does the patient say the air Max V: 1000 to 1500 mL is coming too fast ? PPV %: 80 to 100% Max E: 5 cmH Max R: 2 cmH O/L/s… -
Page 80: Changing Alarm Settings
Operation Changing alarm WARNING: To prevent possible patient injury, avoid setting alarm limits to extreme values, which can render the alarm system useless. settings Some ventilator alarm settings are operator adjustable. You can adjust these at any time. Table 6-4 on page 6-26 lists the alarm settings and their ranges. Review and adjust the alarm settings as follows: 1.
-
Page 81
Description ET/Trach ET or tracheostomy tube Leak 1 Mask with minimal intentional leak characteristics. En- ter Leak 1 for any of these Philips Respironics masks: • Contour Deluxe nasal mask • PerformaTrak mask • AF531, AF541 (EE) Leak 2 Mask with medium intentional leak characteristics. En- ter Leak 2 for this mask: •… -
Page 82
Not allowed with current mask is displayed. NOTE: In ventilation modes, ET/tracheostomy tubes and most Philips Respironics masks require the use of an exhalation port. If you selected ET/Trach or Leak 1 as a mask/patient interface, you may not select None as an exhalation port. -
Page 83
Exhalation port test Port type recommended? Philips Respironics Disposable Exhalation Port Whisper Swivel Philips Respironics Whisper Swivel Philips Respironics Plateau Exhalation Valve Other Exhalation port not supplied by Philips Respi- ronics. None No inline circuit exhalation port NOTE: If you select None, refer to the manufacturer’s instructions to make sure the mask selected contains an exhalation port. -
Page 84: Running The Exhalation Port Test
Operation Running the The exhalation port test is required and its window is automatically displayed when PEV or Other is selected. exhalation port test Procedure Run the test as follows: 1. Disconnect the patient circuit from the mask/patient interface. 2. Occlude the circuit outlet. Select Start Test. 3.
-
Page 85: Troubleshooting
Operation 5. Reconnect the patient circuit to the mask/interface. 6. Select Start Ventilation to initiate ventilation. Troubleshooting If Test Failed is displayed, check for leaks in the patient circuit, and install an exhalation device with lower leak characteristics. Repeat test. If the exhalation port test fails again, the intentional leak is unknown and Tot.Leak rather than Pt.
-
Page 86: Mask/Port
Operation Mask/Port See “Selecting the mask and exhalation port” on page 6-12. Vent Info (ventilator information) The Ventilator Information window displays software version and other information specific to your ventilator. Screen Lock Screen Lock deactivates all buttons and tabs on the touchscreen except Alarm Silence, Alarm Reset, the Alarm/Message button, and Help.
-
Page 87
Operation 2. Select the desired adjustment. As an example, the E-Cycle adjustment is shown below. 3. The setting window opens. Adjust the setting, referring to the pressure-time graphic which represents the effect on I-Time. Select Accept to apply. Proposed value When Auto-Trak+ is active (when either Trigger or E-Cycle is set to a value other than Normal), the ventilator setting window displays Auto-Trak+. -
Page 88: Standby
Operation Standby Standby lets you safely suspend ventilation to temporarily disconnect the patient from the ventilator or to set up the ventilator before connecting the patient. Alarms are disabled during standby. You can also change ventilator settings and most menu functions during standby.
-
Page 89
Operation 2. Disconnect the patient from the ventilator now. The ventilator enters standby and displays the Standby screen. 3. To resume ventilation, reconnect the patient. When the ventilator senses a patient breathing effort, ventilation automatically resumes in the previous mode. NOTE: You can also manually resume ventilation with the Restart Mode button. -
Page 90: Help Function
Operation Help function Select the help button to display additional information. Help messages are displayed: Help message 6-22…
-
Page 91: Table Of Modes And Control Settings
Operation Table of modes and control settings Table 6-3: Modes and control settings with ranges Setting Description Range Modes Modes Ventilation mode AVAPS, CPAP, S/T, PCV Optional: PPV Control settings C-Flex Enhances traditional CPAP by reducing the OFF, 1 to 3 Pressure relief pressure at the beginning of exhalation––a time when patients may be uncomfortable…
-
Page 92
Operation Table 6-3: Modes and control settings with ranges (continued) Setting Description Range I-Time (Inspira- Time to deliver the required gas. Inverse ra- 0.30 to tory Time) tio ventilation is not allowed. 3.00 secs Resulting I:E Shows where I:E ratio ratio becomes inverse Max E… -
Page 93
Operation Table 6-3: Modes and control settings with ranges (continued) Setting Description Range Min P (AVAPS The minimum pressure to be applied. 5 to 30 cmH Minimum IPAP Pressure) NOTE: When you adjust the AVAPS minimum and maximum pressures, remember that IPAP is adjusted to meet the target value. -
Page 94
Operation Table 6-3: Modes and control settings with ranges (continued) Setting Description Range Trigger Trigger Sensitivity. Auto-Trak+ employs several algorithms to determine the point at which Normal, +1 to (optional) the inspiration begins. The larger the value, the more sensitive the trigger (that is, the pa- tient can trigger inspiration with less effort). -
Page 95
Operation Table 6-4: Alarm settings (continued) Setting Description Range NOTE: In the S/T and PCV modes, the LIP alarm should be set 3-5 cmH O below the IPAP level. When set in this manner, the alarm works in conjunction with the LIP T alarm to indicate if there is a failure to trigger between the two pressure levels. -
Page 96
Operation 6-28… -
Page 97
Chapter 7. High flow therapy The high flow therapy (HFT) feature is available for 3.00 software and above, as well as V60 Plus. HFT is accessed from the Standby mode. For more information, see “Standby” on page 6-20. For principles of operation, see “High flow therapy” on page 4-6. -
Page 98: High Flow Therapy
High flow therapy High flow nasal Use either the AC611 high flow nasal cannula with FEP Connector (Figure 7-1) or the AC611 high flow nasal cannula 22 mm (Figure 7-2), which connects cannula setup directly to the patient circuit. Using the FEP Connect for high flow therapy NOTE: This section applies only if you are using the AC611 high flow nasal cannula with filter exhalation port (FEP) connector (“FEP Connect”)
-
Page 99: Changing From Ventilation To High Flow Therapy (Hft)
High flow therapy Proximal pressure port Proximal pressure line Tubing clips Changing from ventilation to high flow therapy (HFT) Follow the instructions in this chapter. Immediately after starting HFT disconnect the proximal pressure line from the ventilator. Changing from high flow therapy (HFT) to ventilation Follow the instructions in this chapter.
-
Page 100: Connecting Directly To A 22 Mm Circuit
22 mm connector DEP/FEP Figure 7-2: High flow nasal cannula, 22 mm connection Changing from an NIV Follow these instructions to use the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator for high flow therapy (HFT). mode to high flow therapy 1. Select Standby. The Entering Standby window opens.
-
Page 101: Viewing And Pausing The Hft Graph
High flow therapy 5. From the Active Mode window, you can adjust Flow and O 6. Press Start HFT. 7. The High Flow Therapy Active message is displayed during HFT. 8. Apply the HFT interface to the patient. 9. Note the low priority alarm stating that patient alarms are disabled during HFT.
-
Page 102: Changing From High Flow Therapy To An Niv Mode
High flow therapy Changing from high 1. Verify that the high flow nasal cannula is removed from the patient and disconnected from patient circuit. flow therapy to an NIV mode 2. Select Standby to open the Standby window. 3. Press the Enter Standby button. 4.
-
Page 103
High flow therapy Table 7-1: HFT Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Cannot Reach Target Displays when HFT (high Check the patient. Check Flow flow therapy) is active. In- that the high flow nasal (66) dicates that flow target is… -
Page 104
High flow therapy… -
Page 105: Patient Monitoring
Chapter 8. Patient monitoring The ventilator displays numeric patient data in the patient data window and real-time graphics in the waveform window (Figure 8-1). Numeric patient data is updated every breath.Table 8-1 on page 8-2 lists the ventilator’s monitored parameters. Breath phase/trigger indicator…
-
Page 106: Table Of Monitored Parameters
Patient monitoring Table of monitored parameters Table 8-1: Monitored parameters Parameter Definition Patient data window Breath phase/trigger indicator Spont (spontaneous): Inspiratory phase, patient-triggered breath (color: turquoise) Timed: Inspiratory phase, ventilator-triggered breath (color: orange) Exhale: Expiratory phase (color: blue) Peak inspiratory pressure. The highest patient pressure during the previous breath cycle. Pt.
-
Page 107: Freezing And Unfreezing Waveforms
Patient monitoring Freezing and Freeze waveforms for extended viewing by selecting the pause button to the left of the waveform window. unfreezing waveforms The cursor makes one complete sweep across the waveform and then displays the pause in progress symbol. The graphic display is then frozen, and the cursor is visible in the middle of the display (Figure 8-2).
-
Page 108
Patient monitoring… -
Page 109
Chapter 9. Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Alarms and messages on the ventilator alert you to situations that require your attention. The ventilator can also actuate remote alarms. Figure 9-1 on page 2 shows the visual alarm characteristics. Table 9-3 on page 9-7 summarizes the different types of alarm and tells you how to respond to each. -
Page 110: Alarms, Messages, And Troubleshooting
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Alarm status bar (nonalarm status) No active alarms Alarm Reset Alarm button button (active) (active) Up arrows indicate that you can hide message in Alarms/ Messages list Alarm status bar Alarm Silence (active alarm status) button (active) Autoreset alarm (strikeout line through message) Waveforms…
-
Page 111
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-1: Alarm summary Alarm LED on front Alarm message in Remote Status panel Alarm status bar Alarms list Audio Action required alarm No alarms None None Autoreset Red (high- Background color alarm priority) or yellow same as that of (low-priority) active alarm. -
Page 112: Setting Alarm Loudness
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Figure 9-2: Vent Inoperative screen Setting alarm You can set the alarm loudness from the Menu window (see “Loudness” on page 6-17). loudness…
-
Page 113: Silencing Alarms
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Silencing alarms Silence an alarm for 2 minutes by selecting the Alarm Silence button. The button icon is replaced by this one. A timer shows time remaining in the 2-minute alarm silence period. Select Alarm Silence again at any time to reset the counter to 2:00 minutes. During patient maneuvers, you can pre-silence audible alarms as desired.
-
Page 114: Hiding/Displaying Alarm Messages
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Hiding/displaying To hide an alarm or informational message in the Alarms or Messages list, touch the flashing alarm indicator button or informational message button alarm messages when up arrows are present. To display messages, touch the flashing alarm indicator or Informational Message button when down arrows are present.
-
Page 115: Alarms And Other Messages
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-2: Symptom-based troubleshooting (continued) Symptom Recommended Action The estimated exhaled tidal volume reading (V ) is inaccurate. Check the patient. Check for large leaks. Make sure ventilator and alarm settings are appropriate. Make sure an approved patient circuit is in use. Adjust the mask to ensure proper fit and adequate leak com- pensation.
-
Page 116
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-3: Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Cannot Reach Target Displays when HFT (high Check the patient. Check Flow flow therapy) is active. In- that the high flow nasal (53) dicates that flow target is… -
Page 117
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-3: Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Low Internal Battery Battery can provide oper- Connect ventilator to AC High ating power for only an ad- power. -
Page 118
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-3: Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Low Rate A low-priority alarm if the Check the patient. Con- Low/ measured respiratory rate firm ventilator and alarm High is less than the Lo Rate… -
Page 119
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-3: Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Patient Circuit Oc- Displays when HFT (high Check the patient. Check High cluded flow therapy) is active. -
Page 120
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-3: Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able PPV Maximum Vol- Estimated delivered pa- Check the patient. Con- Infor- tient tidal volume is great- firm ventilator and alarm mation/ er than the PPV maximum… -
Page 121
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-3: Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Using Default Set- Displayed after power on Check the patient. Check Infor- tings if setting values are cor- and adjust settings as re- mation… -
Page 122
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-4: Check Vent alarm messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Check Vent: Aux Backup alarm problem Check the patient. Provide High Supply Failed alternative ventilation. -
Page 123
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-4: Check Vent alarm messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Check Vent: CPU Technical failure Check the patient. Provide High PCBA ADC Failed alternative ventilation. -
Page 124
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-4: Check Vent alarm messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Check Vent: O Pres- Continues to ventilate Check the patient. Provide High sure Sensor Calibra- with air only alternative ventilation. -
Page 125
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-5: Vent Inoperative alarm messages: summary and troubleshooting Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Vent Inoperative Technical failure. The Check the patient. Provide al- High 1000 ventilator is in the ven- ternative ventilation. -
Page 126
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-5: Vent Inoperative alarm messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Vent Inoperative Technical failure. The Check the patient. Provide al- High 1009 ventilator is in the ven- ternative ventilation. -
Page 127
Disinfection is most effective on medical devices that were previously cleaned. NOTE: For all V60/V60 Plus hardware accessories recommended by Philips, follow the cleaning and disinfection guidelines in this chapter. For multi-patient interface and circuit accessories, consult the product For single patient use accessories, no cleaning instructions for use. -
Page 128: Care And Maintenance
Care and maintenance Exterior and CAUTION: To prevent possible damage to the ventilator, use only those cleaning and disinfecting agents listed in this manual. touchscreen cleaning CAUTION: To prevent possible damage to the ventilator, do not drip or spray any liquids directly onto any surface including the front panel, touchscreen, and navigation ring.
-
Page 129: Exterior And Touchscreen Disinfection
Care and maintenance Exterior and CAUTION: To prevent possible damage to the ventilator, use only those cleaning and disinfecting agents listed in this manual. touchscreen CAUTION: To prevent possible damage to the ventilator, do not drip or spray any disinfection liquids directly onto any surface including the front panel, touchscreen, and navigation ring.
-
Page 130: Bacteria Filter, Patient Circuit, And Other Accessories
Because some environments cause a quicker collection of lint and dust than others, inspect the filters more often when needed. The air inlet filter should be replaced; the cooling fan filter should be cleaned. CAUTION: To ensure proper system performance, use a Respironics-approved air inlet filter. 10-4…
-
Page 131: Preventive Maintenance
Care and maintenance Preventive WARNING: Only authorized service personnel should replace parts within the ventilator or perform other service activities. Unauthorized personnel maintenance without proper training are at risk of electric shock. WARNING: Turn off the ventilator and disconnect it from the AC mains outlet before you perform decontamination or maintenance procedures.
-
Page 132: Replacing The Air Inlet Filter
Care and maintenance Replacing the air inlet filter Replace the air inlet filter as follows, referring to Figure 10-1. 1. Power down the ventilator and disconnect it from AC power. Remove ventilator from cart, if applicable. 2. Turn the captive D-ring fastener counter-clockwise one-quarter turn and release.
-
Page 133: Cleaning Or Replacing The Cooling Fan Filter
Care and maintenance Cleaning or replacing the cooling fan filter Clean or replace the cooling fan filter as follows, referring to Figure 10-2: 1. Insert a small, flat blade driver tip between the foam filter and the filter retaining cover (Figure 10-2). 2.
-
Page 134: Removing And Replacing The Battery
Care and maintenance Removing and replacing the battery See “Installing the battery” on page A-4. Disposal WARNING: This product consists of devices that may contain mercury, which must be recycled or disposed of in accordance with local, state, or federal laws. (Within this system, the backlight lamps in the monitor display contain mercury.) Dispose of all parts removed from the device according to your institution’s…
-
Page 135: Service And Repairs
For technical service or repair information not included in this chapter, contact Philips. A V60/V60 Plus service manual is available (order number 989805612651, part number 1049766), and can also be downloaded from www.philips.com/ hrcmanuals. The service manual includes removal and installation procedures, parts lists, and testing and troubleshooting information.
-
Page 136
Care and maintenance 10-10… -
Page 137: Technical Specifications
4 cmH target) Flow 10 to 80 L/min 5 L/min 35 L/min (High flow therapy, 3.00 software and above, and V60 Plus) IPAP 4 to 40 cmH 1 cmH ± (2 cmH O + 4% of 12 cmH target) I-Time (Inspiratory 0.30 to 3.00 sec…
-
Page 138
Rise (Rise Time) 1 to 5 (AVAPS Target Tidal 200 to 2000 mL BTPS 5 mL ± 15% 500 mL Volume) Table 11-2: Controls active in Respironics V60/V60 Plus ventilation modes CPAP AVAPS Timing Rate Rate I-Time I-Time* Baseline pressure… -
Page 139: Patient Data
Technical specifications Patient data Table 11-3: Patient data ranges, resolutions, and accuracies during ventilation Parameter Range Resolution Accuracy Patient data window Breath phase/trigger indicator Spont, Timed, Exhale Color-coded display: Spont — turquoise, Timed — orange, Ex- hale — blue 0 to 50 cmH 1 cmH ±…
-
Page 140: Alarms
Exhalation Port Selection • DEP (Philips Respironics Disposable Exhalation Port • Whisper Swivel (Philips Respironics Whisper Swivel), • PEV (Philips Respironics Plateau Exhalation Valve), • Other (Other Exhalation Port), • None (No circuit exhalation port) Screen Lock Off, On Auto-Trak+ (optional) Trigger: Normal, +1 to +7.
-
Page 141: Diagnostic Mode Functions
Technical specifications Diagnostic mode Table 11-6: Diagnostic mode functions functions Function Range Language English, Nederlands, Français, Deutsch, Italiano, Por- tuguês, Español, Dansk, Suomi, Norsk, Svenska, Chi- nese, Japanese, Türkçe Date/Time Pressure Units O, hPa Restore Default Settings Software Options Baud Rate 9,600, 19,200, 115,200 Alarm Volume Escalation Enable, Disable (default)
-
Page 142: Physical Characteristics
12 kg (26 lb) with battery V60/V60 Plus ventilator in its most usual configuration Installed weight V60/V60 Plus Ventilator with backup battery, ventila- tor stand, O tank holder, two E-cylinders (full), two (V60/V60 Plus ventilator on gauge clusters, oxygen analyzer with mount, humidifi-…
-
Page 143: Pneumatic Specifications
Pressure: 3.31 to 6.00 bar / 331 to 600 kPa / 48 to 87 psig Flow: 175 SLPM High-pressure oxygen supply Connector: DISS male, DISS female, NIST (using V60/V60 Plus manifold) Pressure: 3.10 to 6.00 bar / 310 to 600 kPa / 45 to 87 psig Flow: 175 SLPM Connector: SIS Pressure: 3.66 to 6.00 bar / 366 to 600 kPa / 53 to…
-
Page 144: Electrical Specifications
Technical specifications Electrical specifications Table 11-10: Electrical specifications Parameter Specification AC voltage 100 to 240 VAC AC frequency 50/60 Hz AC power 300 VA Battery PN 1076374: 14.4 V, 11.0 Ah, 163 Wh Maximum system current draw: 11 A Charge voltage: +16.9 V maximum Operating time: 360 minutes (6 hours) under normal conditions Accessory…
-
Page 145: Alarm-Related Specifications
Technical specifications Alarm-related specifications Table 11-12: Alarm-related specifications Parameter Specification Delay time from the onset of the < 10 ms from onset of the alarm condition to the alarm condition to the point that transmission of the signal the representation of the alarm <…
-
Page 146
Parameter Specification High flow therapy 10 to 80 L/min BTPS (3.00 software and above, and V60 Plus) NOTE: The maximum deliverable flow rate varies based on the orifice size of the nasal cannula and on the patient’s nasal passage resistance. -
Page 147
Appendix A. First-time installation WARNING: Philips-authorized personnel must install the ventilator. For information about installation, contact your Philips representative. Before putting the ventilator into service for the first time, install it as described in this chapter. Unpacking and Unpack the ventilator and inspect it for damage. Inspect the exterior cabinet of the ventilator for cracks, scratches, or blemishes. -
Page 148: First-Time Installation
Ensure that the locking lever on the back right of the stand locks into place. Figure A-1: Mounting the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator on the stand…
-
Page 149
Figure A-2 shows the installed ventilator. Use the brakes to lock and unlock the wheels as needed. Make sure the wheels are unlocked before moving the ventilator. Power cords can be stored on stand hooks Wheel lock Figure A-2: Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator on stand… -
Page 150: Installing The Battery
— Do not short-circuit the battery or allow metallic or conductive objects to contact the battery connector housing. — Use the battery with the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator only. Install the battery as follows (Figure A-3). 1. Shut down and then unplug the ventilator.
-
Page 151
First-time installation 7. Attach the option label as shown in Figure 3-5 on page 3-8. WARNING: Never attempt to disconnect or connect the battery during operation. CAUTION: Following battery installation, if a Check Vent or Vent Inoperative alarm occurs when verifying ventilator operation, discontinue use of the ventilator immediately and contact Philips. -
Page 152
First-time installation Captive fastener Bracket Battery Orient with vent hole on top and Philips logo facing out Battery cable Figure A-3: Installing the battery… -
Page 153: Installing Oxygen Inlet Connector And Ac Power Cord
First-time installation Installing oxygen The Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator destined for Japan, China, and the U.S. are typically pre-configured. V60/V60 Plus Ventilators shipped to other inlet connector and countries may require installation of the power cord and oxygen inlet AC power cord connector.
-
Page 154
Philips-supplied cord securely in place. WARNING: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator should not be positioned in a way that makes it difficult to disconnect from mains power if necessary. Disconnect from supply mains by removing the power cord from the wall outlet. The AC mains plug is used as disconnection device. -
Page 155: Installing The Oxygen Manifold Kit
First-time installation Installing the oxygen If desired, install the oxygen manifold kit as described in the accompanying instructions. manifold kit Verifying ventilator Perform the following steps to verify ventilator and audible alarm operation: operation and audible 1. Assemble and install a patient circuit. (See Chapter 5 for instructions alarm on installing a patient circuit.) 2.
-
Page 156
First-time installation A-10… -
Page 157: Communications Interface
Appendix B. Communications interface WARNING: Connect to the ventilator only items that are specified as part of or compatible with the ventilator system. Additional equipment connected to medical electrical equipment must comply with the respective IEC or ISO standards. Furthermore, all configurations shall comply with the requirements for medical electrical systems (see IEC 60601-1-1 or clause 16 of edition 3 of IEC 60601-1, respectively).
-
Page 158: Rs-232 Serial Port
• Legacy (VRPT/SNDA): Fixed text-based protocol (not to be used for developing new driver interfaces). For this protocol specification, refer to the V60 Communications interface VRPT / SNDA Developers Guide (1147828MC), available at www.philips.com/IFU. Using Philips Using Philips monitors and the IntelliBridge or VueLink Open Interfaces…
-
Page 159: Data Display
Figure B-3: Connection from ventilator to Philips patient monitor Data display The data from your Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is displayed in several windows on your Philips monitor. This data may be labeled differently on the monitor than on the ventilator. Refer to Table B-1 to interpret these labels.
-
Page 160
Communications interface Table B-1: Ventilator data displayed on Philips monitor (continued) Monitor label Ventilator label STNDBY Standby Control settings sEppv Max E Not shown C-Flex PAVsup PPV % sCPAP CPAP sEPAP EPAP sfgFl Flow (in HFT) sFIO sInsTi I-Time (Inspiratory Time) sIPAP IPAP sPmax… -
Page 161: Remote Alarm Port
To prevent possible patient injury due to nonannunciating alarms, verify the operation of any remote alarm device before use. WARNING: To ensure the functionality of the remote alarm, connect only Respironics- approved cables to the remote alarm port. CAUTION: The remote alarm port is intended to connect only to an SELV (safety extra-low voltage and ungrounded system with basic insulation to ground), in accordance with IEC 60601-1.
-
Page 162
For ¼” jack. Remote alarm cable kit, Use on Normally Opened nurse call systems (system expects to 1003742 alarm state = closed see closed contacts when ventilator alarms). For ¼” jack. Remote alarm cable kit Philips Respironics (LifeCare) 1003743… -
Page 163
Respironics-approved accessories with the ventilator. For the most current list of approved accessories plus comprehensive ordering information for compatible parts available from Philips, contact your Philips representative or refer to the V60/V60 Plus ordering and accessories guide (downloadable from philips.com/V60). -
Page 164: Parts And Accessories
Respironics AF531 Respironics PerforMax, adult only Total HFT interfaces For use with V60 Plus ventilators and V60 ventilators that have 3.00 software (or higher) and the HFT option installed. Description Respironics AC611 high flow nasal cannula Respironics AC611 high flow nasal cannula, FEP Connect…
-
Page 165: Patient Breathing Circuits
Description Quantity Part number Order number Humidifiers Respiratory humidifier, Fisher & Paykel MR850 Refer to the V60 ordering and Respiratory humidifier, WILAmed AIRcon Gen2, 230V accessories guide (Not available in North America) Chambers Humidifier chamber, adult, Fisher & Paykel MR290…
-
Page 166: Bacteria Filters
Description Quantity Part number Order number Cooling fan filter 1054280 453561507301 Air inlet filter 1054279 453561505991 Other parts Compatible with all V60/V60 Plus Ventilators: Description Part number Order number Test lung, hard-sided (low-compliance) 1021671 989805611871 Backup battery 1076374 989805626941…
-
Page 167: Regulatory Compliance
EMC information provided in this document. declaration WARNING: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator may cause radio interference or may disrupt the operation of nearby equipment. It may be necessary to take mitigation measures, such as re-orienting or relocating the ventilator or shielding the location.
-
Page 168: Electromagnetic Emissions
Guidance and manufacturer’s declaration — electromagnetic emissions The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The user of the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator should assure that it is used in such an envi- ronment. Emissions test…
-
Page 169: Electromagnetic Immunity
Guidance and manufacturer’s declaration — electromagnetic immunity The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The user of the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator should assure that it is used in such an environment. IEC 60601-1-2…
-
Page 170
Guidance and manufacturer’s declaration — electromagnetic immunity The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or the user of the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator should assure that it is used in such an environment. -
Page 171
Regulatory compliance Recommended separation distances between portable and mobile RF communications equipment and the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator Separation distance according to frequency of transmitter (m) 150 kHz to 80 MHz 150 kHz to 80 MHz 80 MHz to 800 MHz 800 MHz to 2.7 GHz… -
Page 172: Rf Immunity
Regulatory compliance RF immunity Test specifications for RFID immunity The frequencies specified are not yet part of formal regulatory standard IEC 60601-1-2 4.0ED. They are based on 1) a working draft of IEC60601-1-2 4.1ED:2018 Table 11 Medical electrical equipment – Part 1-2: General requirements for basic safety and essen- tial performance –…
-
Page 173: Cables That May Affect Iec 60601-1-2 Compliance
Regulatory compliance So, in addition to selection of RFID systems and medical electrical equipment and systems, EMC management includes maintaining adequate separation distances between them. For medical electrical equipment and systems that meet this standard, the minimum necessary separation distances are shown in Annex J of the AIMS standard 7351731, as well as the guidance required by standards such as IEC 60601-1-2.
-
Page 174: Classification
Regulatory compliance Classification Protection Against Electric Class I Shock Degree of Protection Against Type B Electric Shock Degree of protection against IP21 ingress of particulate matter Protected against solid objects ≥ 12.5 mm in diameter. and water given by the enclo- Protected against vertically falling water drops when en- sure closure is tilted up to 15°…
-
Page 175: Applied Parts
Regulatory compliance Applied parts The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator system includes these applied parts: • Masks • Tracheal and endotracheal tubes • Nebulizer T-adapter • Ventilator Breathing System — Type B (inspiratory or expiratory pathways through which gas flows at respiratory pressures and…
-
Page 176
Regulatory compliance D-10… -
Page 177: Diagnostic Mode
Appendix E. Diagnostic mode In the diagnostic mode you select the language of software display, set the date and time, select pressure units, enable software options, and calibrate the touchscreen. NOTE: The diagnostic mode is primarily for use by authorized service personnel to download software and perform other diagnostic procedures.
-
Page 178
Diagnostic mode 3. Within less than 5 seconds, release and press the Accept button again. The Diagnostics Menu (Figure E-1) is displayed. Figure E-1: Diagnostics Menu 4. Select the desired function. -
Page 179: System Settings
Diagnostic mode System settings From the System Settings screen (Figure E-2) you can perform the functions below. Figure E-2: System Settings screen…
-
Page 180: Language
Diagnostic mode Language The Language function lets you set the language of software display. 1. From the System Settings screen, select Language to display the Set Language screen (Figure E-3). Figure E-3: Set Language screen 1…
-
Page 181
Diagnostic mode 2. The active language is shown in white type. Select the new language. 3. A second Set Language screen is displayed (Figure E-4). Select Ventilator Shutdown to apply the change. The change is effective after you restart the ventilator. Figure E-4: Set Language screen 2… -
Page 182: Date/Time
Diagnostic mode Date/Time The Date/Time function lets you verify date and time settings. 1. From the System Settings screen, select Date/Time to display the Set Date and Time screen (Figure E-5). Figure E-5: Set Date and Time screen 2. Adjust the date and time with the + and — buttons; then Apply.
-
Page 183: Pressure Units
Diagnostic mode Pressure Units The Pressure Units function lets you select the unit of measure for pressure display. 1. From the System Settings screen, select Pressure Units to display the Set Pressure Units screen (Figure E-6). Figure E-6: Set Pressure Units screen 2.
-
Page 184: Restore Default Settings
Diagnostic mode Restore Default Settings The Restore Default Settings function lets you return ventilator settings to factory defaults. The factory defaults are listed in Chapter 11. 1. From the System Settings screen, select Restore Default Settings to display the Restore Default Settings screen (Figure E-7). Figure E-7: Restore Default Settings screen 2.
-
Page 185: Software Options
Diagnostic mode Software Options With the Software Options function, you enable a software option using a unique code specific to the option and the ventilator serial number. Options can also be enabled through the Respi-Link remote service program. NOTE: Before installing an option, verify that the ventilator serial number matches the serial number shown in the Vent Info window (“Vent Info (ventilator information)”…
-
Page 186: Baud Rate
Diagnostic mode Baud Rate The Baud Rate function lets you set the baud rate for serial communications. 1. From the System Settings screen, select Baud Rate to display the Set Baud Rate for Serial Communications screen (Figure E-9). Figure E-9: Set Baud Rate for Serial Communications screen 2.
-
Page 187: Alarm Volume Escalation
Enabled, you will see a selectable Disable button. Press the button to change the setting. 3. The new setting is applied after the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is shut down and powered on again. 1. Available in Revision 2.30 software and above.
-
Page 188: Service
Diagnostic mode Service NOTE: All ventilator mode and alarm settings, alarm messages and significant events are automatically logged and retained, even when power is lost. The Service screen lets you view the event log. Other service functions are for use by authorized service personnel. Significant Event Log The Significant Event Log contains data about clinically relevant ventilator occurrences, including alarms and setting changes.
-
Page 189
Diagnostic mode 3. The Significant Event Log opens (Figure E-12). Use the buttons on right side to navigate through the log. Figure E-12: Significant Event Log screen E-13… -
Page 190: Touchscreen Calibration
Diagnostic mode Touchscreen Calibrate the touchscreen X and Y coordinates as follows: calibration 1. From the Diagnostics Menu, select Touch Screen Calibration. The Touch Screen Calibration screen is displayed (Figure E-13). NOTE: If the Touch Screen Calibration button does not respond, press the Accept button on the navigation ring to begin.
-
Page 191: Exiting The Diagnostic Mode
Diagnostic mode 3. When prompted, touch the screen to exit calibration. If the calibration is not successful, have the ventilator serviced. Exiting the diagnostic Exit the diagnostic mode by turning off ventilator power with the ON/Shutdown key. mode E-15…
-
Page 192
Diagnostic mode E-16… -
Page 193: Glossary
Auto-Trak+ An optional feature that allows adjustments to trigger and cycle thresholds beyond Auto-Trak Sensitivity settings. Auto-Trak Sensitivity A Respironics innovation in triggering and cycling that utilizes several different methods to provide enhanced sensitivity in the presence of leaks and changing breathing patterns.
-
Page 194
Glossary CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure. A ventilation mode that provides a single, continuous level of positive pressure to the patient and a control setting in that mode. Cycle To end inspiration. dB(A) Decibel, a unit of acoustic power. DISS Diameter index safety standard, a standard for high-pressure gas inlet fittings. -
Page 195
Glossary hPa Hectopascal, a unit of pressure measurement. 1 hPa is equal to 1 mbar, which is approximately equal to 1 cmH ID Inner diameter. IEC International Electrotechnical Commission. I:E ratio Ratio of inspiratory to expiratory time. Inop Inoperative. Inspiration:exhalation ratio See I:E ratio. Inspiratory positive airway pressure See IPAP. -
Page 196
Glossary Max P AVAPS Maximum IPAP Pressure. A control setting in AVAPS. Max P Maximum Pressure. See PPV Maximum Pressure Limit. Max R Maximum resistance (flow assist). A control setting in PPV. Max V Maximum Volume. See PPV Maximum Volume Limit. Min P AVAPS Minimum IPAP Pressure. -
Page 197
Glossary psi Pounds per square inch. psig Pounds per square inch gauge (above atmospheric pressure). Proportional pressure ventilation see PPV. Pt. Leak The leak resulting from leaks around the mask or from unintentional leaks in the circuit. A monitored parameter shown when the intentional leak is known. -
Page 198
Glossary Time Trigger Initiation of inspiration by the ventilator according to the Respiratory Rate setting. Timed indicator Denotes machine-triggered (mandatory) breathing. Inspiratory duty cycle. Inspiratory time divided by total cycle time, averaged over 8 breaths, a monitored parameter. Tot.Leak Estimated total leak, both intentional and unintentional. A monitored parameter shown when the mask leak and type of exhalation port are not known. -
Page 199
Index AVAPS: Target V Not Achieved. Insufficient Max Pressure message 9-7 AC power Average volume-assured pressure support mode. See AVAPS how to connect to 5-2 mode specifications 11-8 AC power cord, how to install A-7–A-8 Accessories part numbers C-1–?? Backup alarm 3-9 Air inlet filter. -
Page 200
Index Check Vent: Internal Temperature High Daq alarm 9-15 how to change date and time E-6 Check Vent: Internal Temperature High Mtr alarm 9-15 how to change language E-4–E-5 Check Vent: Machine Pressure Sensor Auto-Zero Failed how to change pressure unit E-7 alarm 9-15 how to enable or disable Alarm Volume Escalation E-11 Check Vent: Machine Pressure Sensor Calibration Data Error… -
Page 201
Modes, ventilation. See Ventilation modes IntelliBridge Monitored parameters using with Philips monitors B-2–B-5 definitions 8-2 Intended use, Respironics V60 Ventilator 3-1 ranges, resolutions, and accuracies 11-3 Interface. See Patient interface or Communications inter- Mounting the ventilator A-2–A-3 face IPAP (inspiratory positive airway pressure) setting, definition… -
Page 202
3-4 how to select 6-12–6-15 location of Ethernet connector 3-8 how to test 6-16–6-17 Respiratory rate. See Rate part numbers C-2 Respironics V60 Ventilator Power cord front view 3-6 how to install A-8 physical description 3-4–3-8 location 3-8 potential side effects 3-2… -
Page 203
Index Startup alarm 9-17 time specifications 11-10 Vent Inoperative 1007 Machine and Proximal Pressure Sen- ventilator startup 3-13 sors Failed alarm 9-17 Symbols 2-1–2-8 Vent Inoperative 1008 Machine and Proximal Pressure Sen- System Settings functions, in diagnostic mode E-3 sors Failed alarm 9-17 Vent Inoperative 1009 Pressure Regulation High alarm 9-18 Vent Inoperative 100A Data Acquisition PCBA ADC Refer- ence Failed alarm 9-18… -
Page 204: Index
Index Index-6…
-
Page 206
Respironics California, LLC 2271 Cosmos Court Carlsbad, CA 92011 USA Respironics Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG Gewerbestrasse 17 82211 Herrsching Germany Australian sponsor Philips Electronics Australia Ltd 65 Epping Road North Ryde, NSW Australia 2113 You can find the most current electronic copy of this user manual at: www.philips.com/IFU…
This manual is also suitable for:
V60 plus
-
Page 1
Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator User Manual… -
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Table of contents Warnings, cautions, and notes ……. 1-1 Definitions ……….1-1 General.
-
Page 4
Leak adaptation ……..4-5 Auto-Trak+ (optional) . -
Page 5
Standby ……….6-20 Help function . -
Page 6
Repacking and shipping ……..10-9 Technical specifications ……..11-1 Control settings . -
Page 7
Electromagnetic compatibility declaration ….. . D-1 Electromagnetic emissions ……D-2 Electromagnetic immunity . -
Page 8
viii… -
Page 9: Warnings, Cautions, And Notes
Chapter 1. Warnings, cautions, and notes Before using the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator on a patient, familiarize yourself with this user manual, particularly the safety considerations listed. Be aware, however, that this manual is a reference only. It is not intended to supersede your institution’s protocol regarding the safe use of assisted…
-
Page 10
Do not leave the ventilator unattended when stationed on an incline. WARNING: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator may cause radio interference or may disrupt the operation of nearby equipment. It may be necessary to take mitigation measures, such as re-orienting or relocating the ventilator or shielding the location. -
Page 11
EMC emissions or decrease the EMC immunity performance of the equipment. WARNING: Do not use the ventilator in an MRI environment. The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is MR Unsafe. Keep it outside the MRI scan room (Zone IV). It represents a projectile hazard. -
Page 12: Preparing For Ventilation
To reduce the risk of fire, do not use a high-pressure oxygen hose that is worn or contaminated with combustible materials like grease or oil. WARNING: The Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is designed to use ambient air and high pressure 100% oxygen. No other gases should be used. WARNING: Do not use the ventilator with helium or helium mixtures.
-
Page 13
For example, positioning the ventilator next to a curtain that blocks the flow of cooling air can cause the equipment to overheat. Use the V60/V60 Plus in an upright position that does not block the air inlet. -
Page 14
Philips-supplied cord securely in place. WARNING: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator should not be positioned in a way that makes it difficult to disconnect from mains power if necessary. Disconnect from supply mains by removing the power cord from the wall outlet. The AC mains plug is used as disconnection device. -
Page 15: Operation
SIS adapters such as the O transport manifold. NOTE: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is a single-limb device with substantial intentional and unintentional leak in the ventilator breathing system. Under those conditions, CO cannot be measured accurately. Therefore, we do not recommend the use of CO monitoring.
-
Page 16: Alarms And Messages
— Do not short-circuit the battery or allow metallic or conductive objects to contact the battery connector housing. — Use the battery with the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator only. WARNING: Modification of the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator and associated equipment is not permitted and may compromise ventilator operation and patient safety.
-
Page 17: First-Time Installation
(or as stipulated by your institution). CAUTION: To ensure proper system performance, use a Respironics-approved air inlet filter. CAUTION: Because some environments cause a quicker collection of lint and dust than others, inspect the filters more often when needed.
-
Page 18: Diagnostic Mode
To prevent possible patient injury due to nonannunciating alarms, verify the operation of any remote alarm device before use. WARNING: To ensure the functionality of the remote alarm, connect only Respironics- approved cables to the remote alarm port. CAUTION: The remote alarm port is intended to connect only to an SELV (safety extra-low voltage and ungrounded system with basic insulation to ground), in accordance with IEC 60601-1.
-
Page 19: Symbols
Chapter 2. Symbols Refer to these tables to interpret symbols used on the ventilator labels, backup battery labels, and packaging and on the ventilator screen. To interpret symbols pertaining to accessories, refer to their instructions for use. Table 2-1: Symbols used on ventilator labels, battery, and packaging Symbol Description Warning: Risk of explosion.
-
Page 20
Symbols Table 2-1: Symbols used on ventilator labels, battery, and packaging Symbol Description Stacking limit by number This end up Type B applied part, which is equipment that provides a particular degree of protection against electric shock, particularly in regard to allowable leakage current and of the protective earth connection Requires alternating current (AC) Degree of fluid ingress protection provided by the enclosure (drip-proof) -
Page 21
Symbols Table 2-1: Symbols used on ventilator labels, battery, and packaging Symbol Description Manufacturer. Symbol accompanied by manufacturer’s name and address. EC representative Serial number Order number Lot or batch number Model number Use by date RS-232 serial input/output USB port Oxygen (Yellow) Warning Ethernet connection… -
Page 22
Noninvasive ventilation (patient with mask) Invasive ventilation (intubated patient) The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is MR Unsafe and presents a projectile haz- ard. Keep the ventilator outside MRI scan room (Zone IV). Do not block the cooling fan Inlet (at the rear of the ventilator). -
Page 23
Symbols Table 2-1: Symbols used on ventilator labels, battery, and packaging Symbol Description Recycle (Taiwan) 廢 電 池 請 回 收 RoHS (China). Administrative Measure on the Control of Pollution Caused by Electronic Information Products. Contains RoHS substances with 50 years environmentally friendly use period (EFUP). uR UL recognition symbol Direct current (DC). -
Page 24
Table 2-1: Symbols used on ventilator labels, battery, and packaging Symbol Description Auto-Trak+ software option High flow therapy Note: 3.00 software and above. HFT is optional for model V60 and included with model V60 Plus. Table 2-2: Symbols used on graphical user interface Symbol Description… -
Page 25
Symbols Table 2-2: Symbols used on graphical user interface (continued) Symbol Description Cancel button. Cancels set values. +2:00 minutes button. Adds two minutes to 100% O delivery. Ventilator is powered by AC power and the battery is installed. Ventilator is powered by AC power and the battery is not installed. Ventilator is powered by the battery. -
Page 26
Flow, liters per minute. BTPS compensated. Volume, milliliters User-set Ramp Time. Ramp graphic fills in as Ramp Time progresses. Ramp Time is OFF (no ramp time set). Intentional leak. The number corresponds to the leak symbol printed on Philips Respironics masks. -
Page 27: General Information
Philips-recommended patient circuits, interfaces (masks), humidifiers, and other accessories. Indications for use The Respironics V60/V60 Plus is an assist ventilator and is indicated for use to augment patient breathing. The ventilator is indicated for spontaneously breathing individuals who require mechanical ventilation: patients with respiratory failure, chronic respiratory insufficiency, or obstructive sleep apnea in a hospital or other institutional settings under the direction of a physician.
-
Page 28: Contraindications
General information Contraindications The Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is contraindicated for patients with any of the following conditions: • Lack of spontaneous respiratory drive • Inability to maintain a patent airway or adequately clear secretions • At risk for aspiration of gastric contents •…
-
Page 29: General Description
Flow and O percentage settings are selected by the clinician. HFT is available for 3.00 software and above, as well as for the V60 Plus. Auto-Trak Sensitivity allows the ventilator to automatically compensate for intentional and unintentional leaks by maintaining a stable baseline and adjusting trigger and cycle thresholds for optimum patient-to-ventilator synchrony.
-
Page 30: Physical Description
RS-232 port. Physical description Patient circuits, masks/patient interfaces, and accessories Figure 3-2 shows the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator with its patient circuit and accessories. Appendix C provides ordering information for parts and accessories.
-
Page 31
General information Bacteria filter Mask Oxygen monitor Humidifier Patient circuit Oxygen cylinder Figure 3-2: Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator with accessories… -
Page 32: Ventilator Unit
General information Ventilator unit Figure 3-3 through Figure 3-5 show the controls, indicators, and other important parts of the ventilator unit. Key panel Figure 3-3: Front view Number Description Graphical user interface. Color LCD (liquid crystal display) with touchscreen. Navigation ring. Lets you adjust values and navigate the graphical user interface by rotating the finger on its touchpad.
-
Page 33
General information Number Description Battery (charged) LED. Flashes when battery is charging. On continuously when battery is charged. Off when ventilator is running on battery, when a battery er- ror or failure is detected, or when the ventilator is off and AC power is not con- nected. -
Page 34
General information 5 4 3 2 Figure 3-5: Rear view Number Description Backup battery (compartment under side panel). Remote alarm/nurse call connector Reserved for future use Power cord retainer Power cord RS-232 serial connector (female DB-25). Connects to hospital information systems and other serial devices. -
Page 35: About The Backup Battery
General information About the backup WARNING: To reduce the risk of power failure to the ventilator, pay close attention to the battery’s charge level. The battery’s operation time is approximate and battery is affected by ventilator settings, discharge and recharge cycles, battery age, and ambient temperature.
-
Page 36
General information CAUTION: Avoid allowing the ventilator battery to become completely discharged. Otherwise, the battery may become over-discharged and require long recharge times of up to 16 hours or more. The over- discharged condition may permanently damage the battery so that it is unable to recharge. -
Page 37: About The Graphical User Interface
General information About the graphical Through the graphical user interface (Figure 3-7) you make ventilator settings and view ventilator and patient data. During ventilation, the upper screen user interface displays alarms and patient data. The middle screen displays real-time waveforms and alarm and informational messages. The lower screen lets you access modes and other ventilator settings, display help information, and see the power status.
-
Page 38: Navigating The Graphical User Interface
General information Navigating the graphical user interface Select a function by touching the desired tab or button on the touchscreen. Use this as the primary method to control the ventilator. You can use the navigation ring as an alternative to the following touchscreen functions: Touchscreen equivalent Navigation ring equivalent…
-
Page 39: Starting Up The Ventilator
General information Starting up the NOTE: Upon power-on the ventilator automatically runs a test of the backup audible alarm followed by the primary audible alarm. You should hear ventilator a high-pitched tone, followed by a beep. If you do not hear all of these sounds, discontinue use of the ventilator and have it serviced.
-
Page 40
General information 3-14… -
Page 41
Chapter 4. Principles of operation System operational The Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is a microprocessor-controlled pneumatic system that delivers a mixture of air and oxygen. It is powered by overview AC with battery backup to protect against power failure or unstable power and to facilitate intrahospital transport. -
Page 42: Principles Of Operation
CO removal. Breath delivery Control variable Breaths delivered by the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator are pressure characteristics controlled. In the AVAPS mode, the ventilator’s applied pressure is automatically adjusted over a period of time to maintain a target tidal volume.
-
Page 43: Pressure Rise Time
Auto-Trak Sensitivity An important characteristic of the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is its ability to recognize and compensate for intentional and unintentional leaks in the system, and to automatically adjust its triggering and cycling algorithms to maintain optimum performance in the presence of leaks.
-
Page 44
Principles of operation Shape signal method of cycling and triggering. The shape signal or “shadow trigger” method uses a mathematical model derived from the flow signal. A new flow signal (shape signal) is generated by offsetting the signal from the actual flow and delaying it (Figure 4-2). -
Page 45: Leak Adaptation
Principles of operation Leak adaptation Noninvasive ventilation in particular may involve considerable leakage around the mask or through the mouth. Some leakage is known or intentional: it is a characteristic of the mask/patient interface design. So that it can accurately adjust its baseline flow, the ventilator has you enter the intentional leakage value specific to the mask/patient interface (“Selecting the mask and exhalation port”…
-
Page 46: Auto-Trak+ (Optional)
Volume adjustment Figure 4-5: Tidal volume adjustment Auto-Trak+ (optional) The Auto-Trak+ option for the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator lets you further adjust the level of Auto-Trak Sensitivity, a feature that recognizes and compensates for intentional and unintentional leaks. This algorithm has multiple breath trigger and cycle thresholds.
-
Page 47: Ventilation Modes
Patient alarms are not available during high flow therapy. This therapy is not considered a breath delivery mode. HFT requires 3.00 software and above. Ventilation modes The Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator operates in the following ventilation modes: • CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) mode •…
-
Page 48: Cpap Mode
Principles of operation CPAP mode In the CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) mode, the ventilator functions as a demand flow system, with the patient triggering all breaths and determining their timing and size. The patient triggers and cycles based on the ventilator’s Auto-Trak Sensitivity algorithms.
-
Page 49: Pcv Mode
Principles of operation PCV mode The PCV (pressure-controlled ventilation) mode delivers pressure-controlled breaths, either triggered by the ventilator (Timed) or the patient (Spont). The control settings active in the PCV mode are shown in Figure 4-8. The IPAP setting defines the applied inspiratory pressure for all breaths. If the patient fails to trigger a breath through Auto-Trak within the interval determined by the rate setting, the ventilator triggers a mandatory breath.
-
Page 50: S/T Mode
Principles of operation S/T mode The S/T (spontaneous/timed) mode guarantees breath delivery at the user-set rate. It delivers pressure-controlled, time-cycled mandatory and pressure- supported spontaneous breaths, all at the IPAP pressure level. If the patient fails to trigger a breath within the interval determined by the Rate setting, the ventilator triggers a mandatory breath with the set I-Time.
-
Page 51: Avaps Mode
Principles of operation AVAPS mode NOTE: When you adjust AVAPS minimum and maximum pressures, remember that IPAP is adjusted to meet the target value. If the calculated target pressure is outside of the minimum and maximum pressure range, the target volume will not be achieved. Unlike most pressure modes, the AVAPS (average volume-assured pressure support) mode delivers a target tidal volume.
-
Page 52
Principles of operation Max P Mandatory (Timed) Rise breath Min P EPAP I-Time Patient-triggered (Spont) 1/Rate spontaneous breath Time Figure 4-13: AVAPS waveforms 4-12… -
Page 53: Ppv Mode (Optional)
Principles of operation PPV mode (optional) The PPV (proportional pressure ventilation) mode provides patient-triggered breaths that deliver pressure in proportion to patient effort. Additionally a user- settable backup rate activates machine-triggered, pressure-limited, and time- cycled breaths in the case of apnea. In the PPV mode, patient effort determines the pressure, flow, and tidal volume delivered by the ventilator.
-
Page 54
Principles of operation setting. If the patient fails to trigger a breath within the interval determined by the Rate control, the ventilator triggers a Timed (backup) breath with the set I-Time, Rise, and IPAP settings. The control settings active in the PPV mode are shown in Figure 4-14. Figure 4-14: PPV controls Figure 4-15 shows PPV mode waveforms. -
Page 55: Oxygen Mixing
Principles of operation Oxygen mixing The ventilator’s oxygen mixer regulates and proportions oxygen into the air from the blower according to the O setting. The delivered oxygen accuracy is ±5% of the set value up to the maximum oxygen flow available. The ventilator can deliver up to 240 L/min of air/oxygen mix to assist in managing uncontrolled leaks during noninvasive ventilation.
-
Page 56
Principles of operation 4-16… -
Page 57: Setting Up The Ventilator For Use
The Analytical Industries 2000M monitor includes user-settable high and low oxygen % alarms and is approved for use with the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator. Refer to the monitor instructions for use for detailed instructions on the proper setup and operation of the oxygen monitor.
-
Page 58: Connecting To Ac Power
WARNING: Do not use extension cords, adapters, or power cords with the ventilator that are not approved by Respironics. WARNING: To prevent unintentional disconnection of the power cord, always use the correct, Philips-supplied power cord and lock it into place with the power cord retainer before you switch the ventilator on.
-
Page 59: Installing The Patient Circuit
To prevent patient or ventilator contamination, always use a main flow bacteria filter on the patient gas outlet port. Filters not approved by Respironics may degrade system performance. WARNING: During ventilation, patient exhalate is released into room air. Use of a patient circuit with a filter on its exhalation port is recommended.
-
Page 60
Setting up the ventilator for use Assemble the patient circuit, including the main flow (inspiratory) bacteria filter, proximal pressure line, oxygen sensor tee, and if desired, humidifier and nebulizer. Figure 5-2 and Figure 5-3 show circuit configurations for noninvasive and invasive ventilation. Follow the manufacturers’ instructions for use for the individual parts. -
Page 61
Setting up the ventilator for use NOTE: This circuit setup is recommended for noninvasive ventilation. Proximal pressure port Ventilator outlet Oxygen sensor tee Bacteria filter Proximal pressure line Figure 5-2: Noninvasive patient circuit, without humidification… -
Page 62: Connecting External Devices
The Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator can communicate with a Philips patient monitor using the IntelliBridge Open Interface. See “Using Philips monitors and the IntelliBridge or VueLink Open Interfaces” on page B-2. The ventilator also supports the VueLink Open Interface.
-
Page 63: Before Placing A Patient On The Ventilator
Setting up the ventilator for use Before placing a WARNING: To ensure the ventilator’s safe operation, always verify ventilator operation as described in “Verify ventilator operation” on page 5-7 before patient on the using the ventilator on a patient. If the ventilator fails any tests, remove it ventilator from clinical use immediately.
-
Page 64: Running Alarm Tests
Setting up the ventilator for use d. VERIFY that the blue “Running on Internal Battery” message is displayed. 6. Install a fully-charged battery and reconnect the ventilator to AC power. 7. Repeat step 5 to verify that the ventilator switches over to battery power.
-
Page 65: Low Tidal Volume
Setting up the ventilator for use Low Tidal Volume 1. Raise the Lo V alarm setting above the displayed, measured V 2. VERIFY that the alarm is activated. Low Tidal Volume 3. Turn the Lo V alarm setting OFF. 4. VERIFY that the alarm resets. Patient Disconnect 1.
-
Page 66: Using The Ventilator For Intra-Hospital Transport
WARNING: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator requires a pressurized oxygen supply that provides a minimum flow of 175 SLPM. Do not use any devices such as valves, hoses, Grab n’ Go regulators or other brands of combined cylinder/ regulators that limit supply of oxygen flow below 175 SLPM.
-
Page 67: Storing The Ventilator Between Patient Use
Setting up the ventilator for use 95 100 Leak of 10 L/min Leak of 20 L/min Leak of 30 L/min Leak of 40 L/min Leak of 50 L/min a. V = 500 mL, Rate = 40 BPM, EPAP = 6 cmH O, IPAP = 18 cmH 95 100 Leak of 20 L/min…
-
Page 68: Mri Safety Information
Setting up the ventilator for use MRI safety WARNING: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is MR Unsafe. Keep it outside the MRI scan room (Zone IV). It represents a projectile hazard. information 5-12…
-
Page 69: Operation
Chapter 6. Operation WARNING: To ensure the ventilator’s safe operation, always verify ventilator operation as described in “Verify ventilator operation” on page 5-7 before using the ventilator on a patient. If the ventilator fails any tests, remove it from clinical use immediately. Do not use the ventilator until necessary repairs are completed and all tests have passed.
-
Page 70: Changing The Mode
Operation Changing the mode The active ventilation mode is displayed in the bottom, left-hand corner of the screen. Change the mode as follows. For details on modes, see “Ventilation modes” on page 4-7. 1. Open the Modes window. 2. Select the desired mode. Active mode 3.
-
Page 71: Changing Control Settings
Operation Changing control Table 6-3 on page 6-23 is an alphabetical list of the control settings with their ranges. Table 11-2 on page 11-2 shows the control settings applicable to the settings different modes. For more information on control settings as they apply in the different ventilation modes, see “Ventilation modes”…
-
Page 72: Changing Individual Ventilator Settings
Operation Changing individual ventilator settings You can make ventilator settings from the Settings window. 1. Open the Settings window. 2. Select the desired setting. As an example we will show the IPAP adjustment. 3. The setting window opens. Adjust the setting. Select Accept to apply. Adjustment Setting range scale arrow button…
-
Page 73: Using The Ramp Time Function
Operation Using the Ramp Time The Ramp Time function helps your patient adapt to ventilation by gradually increasing inspiratory and expiratory pressure (IPAP and EPAP/CPAP) from function subtherapeutic to user-set pressures over a user-set interval. Table 6-3 on page 6-23 describes this function’s principles of operation. Follow these instructions to use the Ramp Time function: 1.
-
Page 74: Using The 100% O2 Function
Operation Using the 100% O NOTE: The 100% O feature is available in Revision 2.30 software and above. function The 100% O function delivers 100% oxygen to the patient. It is available during Screen Lock status. Follow these instructions to use the 100% O function: 1.
-
Page 75: Using Ppv
Operation Using PPV Follow these instructions to set up the ventilator in the PPV mode, referring to Figure 6-3. For principles of operation, see “PPV mode (optional)” on page 4-13. 1. Open the PPV Settings window. 2. Set EPAP, O , alarm limits, and backup settings to appropriate values.
-
Page 76
Operation Max V Inspiration terminated Max V Sudden increase in flow Time Figure 6-1: PPV waveform – Max V limit When the Max P (PPV maximum pressure limit) is reached, pressure is limited but the breath is not terminated, and a message is displayed. After the limit is reached in three consecutive breaths, the audible alarm sounds. -
Page 77: Guidelines For Using Ppv
Operation Guidelines for using PPV NOTE: The guidelines below are based on recommendations by clinicians. They do not replace the clinical judgment of a physician and should not, on their own, be used for clinical decision making. Determining Max R and Max E settings It is recommended you set Max R (flow assist) and Max E (volume assist) to initial values and then titrate them based on the patient’s disease process: •…
-
Page 78
Operation 2. Adjust Max E: a. Evaluate the patient. Check whether any of these conditions is true: • The patient says they are getting too much air, pressure, or volume • The patient is using accessory muscles to actively stop inspiration •… -
Page 79
Operation Start Max R Make initial settings: titration EPAP: 4 cmH : Current setting or per prescription Max P: 25 cmH Does the patient say the air Max V: 1000 to 1500 mL is coming too fast ? PPV %: 80 to 100% Max E: 5 cmH Max R: 2 cmH O/L/s… -
Page 80: Changing Alarm Settings
Operation Changing alarm WARNING: To prevent possible patient injury, avoid setting alarm limits to extreme values, which can render the alarm system useless. settings Some ventilator alarm settings are operator adjustable. You can adjust these at any time. Table 6-4 on page 6-26 lists the alarm settings and their ranges. Review and adjust the alarm settings as follows: 1.
-
Page 81
Description ET/Trach ET or tracheostomy tube Leak 1 Mask with minimal intentional leak characteristics. En- ter Leak 1 for any of these Philips Respironics masks: • Contour Deluxe nasal mask • PerformaTrak mask • AF531, AF541 (EE) Leak 2 Mask with medium intentional leak characteristics. En- ter Leak 2 for this mask: •… -
Page 82
Not allowed with current mask is displayed. NOTE: In ventilation modes, ET/tracheostomy tubes and most Philips Respironics masks require the use of an exhalation port. If you selected ET/Trach or Leak 1 as a mask/patient interface, you may not select None as an exhalation port. -
Page 83
Exhalation port test Port type recommended? Philips Respironics Disposable Exhalation Port Whisper Swivel Philips Respironics Whisper Swivel Philips Respironics Plateau Exhalation Valve Other Exhalation port not supplied by Philips Respi- ronics. None No inline circuit exhalation port NOTE: If you select None, refer to the manufacturer’s instructions to make sure the mask selected contains an exhalation port. -
Page 84: Running The Exhalation Port Test
Operation Running the The exhalation port test is required and its window is automatically displayed when PEV or Other is selected. exhalation port test Procedure Run the test as follows: 1. Disconnect the patient circuit from the mask/patient interface. 2. Occlude the circuit outlet. Select Start Test. 3.
-
Page 85: Troubleshooting
Operation 5. Reconnect the patient circuit to the mask/interface. 6. Select Start Ventilation to initiate ventilation. Troubleshooting If Test Failed is displayed, check for leaks in the patient circuit, and install an exhalation device with lower leak characteristics. Repeat test. If the exhalation port test fails again, the intentional leak is unknown and Tot.Leak rather than Pt.
-
Page 86: Mask/Port
Operation Mask/Port See “Selecting the mask and exhalation port” on page 6-12. Vent Info (ventilator information) The Ventilator Information window displays software version and other information specific to your ventilator. Screen Lock Screen Lock deactivates all buttons and tabs on the touchscreen except Alarm Silence, Alarm Reset, the Alarm/Message button, and Help.
-
Page 87
Operation 2. Select the desired adjustment. As an example, the E-Cycle adjustment is shown below. 3. The setting window opens. Adjust the setting, referring to the pressure-time graphic which represents the effect on I-Time. Select Accept to apply. Proposed value When Auto-Trak+ is active (when either Trigger or E-Cycle is set to a value other than Normal), the ventilator setting window displays Auto-Trak+. -
Page 88: Standby
Operation Standby Standby lets you safely suspend ventilation to temporarily disconnect the patient from the ventilator or to set up the ventilator before connecting the patient. Alarms are disabled during standby. You can also change ventilator settings and most menu functions during standby.
-
Page 89
Operation 2. Disconnect the patient from the ventilator now. The ventilator enters standby and displays the Standby screen. 3. To resume ventilation, reconnect the patient. When the ventilator senses a patient breathing effort, ventilation automatically resumes in the previous mode. NOTE: You can also manually resume ventilation with the Restart Mode button. -
Page 90: Help Function
Operation Help function Select the help button to display additional information. Help messages are displayed: Help message 6-22…
-
Page 91: Table Of Modes And Control Settings
Operation Table of modes and control settings Table 6-3: Modes and control settings with ranges Setting Description Range Modes Modes Ventilation mode AVAPS, CPAP, S/T, PCV Optional: PPV Control settings C-Flex Enhances traditional CPAP by reducing the OFF, 1 to 3 Pressure relief pressure at the beginning of exhalation––a time when patients may be uncomfortable…
-
Page 92
Operation Table 6-3: Modes and control settings with ranges (continued) Setting Description Range I-Time (Inspira- Time to deliver the required gas. Inverse ra- 0.30 to tory Time) tio ventilation is not allowed. 3.00 secs Resulting I:E Shows where I:E ratio ratio becomes inverse Max E… -
Page 93
Operation Table 6-3: Modes and control settings with ranges (continued) Setting Description Range Min P (AVAPS The minimum pressure to be applied. 5 to 30 cmH Minimum IPAP Pressure) NOTE: When you adjust the AVAPS minimum and maximum pressures, remember that IPAP is adjusted to meet the target value. -
Page 94
Operation Table 6-3: Modes and control settings with ranges (continued) Setting Description Range Trigger Trigger Sensitivity. Auto-Trak+ employs several algorithms to determine the point at which Normal, +1 to (optional) the inspiration begins. The larger the value, the more sensitive the trigger (that is, the pa- tient can trigger inspiration with less effort). -
Page 95
Operation Table 6-4: Alarm settings (continued) Setting Description Range NOTE: In the S/T and PCV modes, the LIP alarm should be set 3-5 cmH O below the IPAP level. When set in this manner, the alarm works in conjunction with the LIP T alarm to indicate if there is a failure to trigger between the two pressure levels. -
Page 96
Operation 6-28… -
Page 97
Chapter 7. High flow therapy The high flow therapy (HFT) feature is available for 3.00 software and above, as well as V60 Plus. HFT is accessed from the Standby mode. For more information, see “Standby” on page 6-20. For principles of operation, see “High flow therapy” on page 4-6. -
Page 98: High Flow Therapy
High flow therapy High flow nasal Use either the AC611 high flow nasal cannula with FEP Connector (Figure 7-1) or the AC611 high flow nasal cannula 22 mm (Figure 7-2), which connects cannula setup directly to the patient circuit. Using the FEP Connect for high flow therapy NOTE: This section applies only if you are using the AC611 high flow nasal cannula with filter exhalation port (FEP) connector (“FEP Connect”)
-
Page 99: Changing From Ventilation To High Flow Therapy (Hft)
High flow therapy Proximal pressure port Proximal pressure line Tubing clips Changing from ventilation to high flow therapy (HFT) Follow the instructions in this chapter. Immediately after starting HFT disconnect the proximal pressure line from the ventilator. Changing from high flow therapy (HFT) to ventilation Follow the instructions in this chapter.
-
Page 100: Connecting Directly To A 22 Mm Circuit
22 mm connector DEP/FEP Figure 7-2: High flow nasal cannula, 22 mm connection Changing from an NIV Follow these instructions to use the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator for high flow therapy (HFT). mode to high flow therapy 1. Select Standby. The Entering Standby window opens.
-
Page 101: Viewing And Pausing The Hft Graph
High flow therapy 5. From the Active Mode window, you can adjust Flow and O 6. Press Start HFT. 7. The High Flow Therapy Active message is displayed during HFT. 8. Apply the HFT interface to the patient. 9. Note the low priority alarm stating that patient alarms are disabled during HFT.
-
Page 102: Changing From High Flow Therapy To An Niv Mode
High flow therapy Changing from high 1. Verify that the high flow nasal cannula is removed from the patient and disconnected from patient circuit. flow therapy to an NIV mode 2. Select Standby to open the Standby window. 3. Press the Enter Standby button. 4.
-
Page 103
High flow therapy Table 7-1: HFT Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Cannot Reach Target Displays when HFT (high Check the patient. Check Flow flow therapy) is active. In- that the high flow nasal (66) dicates that flow target is… -
Page 104
High flow therapy… -
Page 105: Patient Monitoring
Chapter 8. Patient monitoring The ventilator displays numeric patient data in the patient data window and real-time graphics in the waveform window (Figure 8-1). Numeric patient data is updated every breath.Table 8-1 on page 8-2 lists the ventilator’s monitored parameters. Breath phase/trigger indicator…
-
Page 106: Table Of Monitored Parameters
Patient monitoring Table of monitored parameters Table 8-1: Monitored parameters Parameter Definition Patient data window Breath phase/trigger indicator Spont (spontaneous): Inspiratory phase, patient-triggered breath (color: turquoise) Timed: Inspiratory phase, ventilator-triggered breath (color: orange) Exhale: Expiratory phase (color: blue) Peak inspiratory pressure. The highest patient pressure during the previous breath cycle. Pt.
-
Page 107: Freezing And Unfreezing Waveforms
Patient monitoring Freezing and Freeze waveforms for extended viewing by selecting the pause button to the left of the waveform window. unfreezing waveforms The cursor makes one complete sweep across the waveform and then displays the pause in progress symbol. The graphic display is then frozen, and the cursor is visible in the middle of the display (Figure 8-2).
-
Page 108
Patient monitoring… -
Page 109
Chapter 9. Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Alarms and messages on the ventilator alert you to situations that require your attention. The ventilator can also actuate remote alarms. Figure 9-1 on page 2 shows the visual alarm characteristics. Table 9-3 on page 9-7 summarizes the different types of alarm and tells you how to respond to each. -
Page 110: Alarms, Messages, And Troubleshooting
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Alarm status bar (nonalarm status) No active alarms Alarm Reset Alarm button button (active) (active) Up arrows indicate that you can hide message in Alarms/ Messages list Alarm status bar Alarm Silence (active alarm status) button (active) Autoreset alarm (strikeout line through message) Waveforms…
-
Page 111
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-1: Alarm summary Alarm LED on front Alarm message in Remote Status panel Alarm status bar Alarms list Audio Action required alarm No alarms None None Autoreset Red (high- Background color alarm priority) or yellow same as that of (low-priority) active alarm. -
Page 112: Setting Alarm Loudness
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Figure 9-2: Vent Inoperative screen Setting alarm You can set the alarm loudness from the Menu window (see “Loudness” on page 6-17). loudness…
-
Page 113: Silencing Alarms
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Silencing alarms Silence an alarm for 2 minutes by selecting the Alarm Silence button. The button icon is replaced by this one. A timer shows time remaining in the 2-minute alarm silence period. Select Alarm Silence again at any time to reset the counter to 2:00 minutes. During patient maneuvers, you can pre-silence audible alarms as desired.
-
Page 114: Hiding/Displaying Alarm Messages
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Hiding/displaying To hide an alarm or informational message in the Alarms or Messages list, touch the flashing alarm indicator button or informational message button alarm messages when up arrows are present. To display messages, touch the flashing alarm indicator or Informational Message button when down arrows are present.
-
Page 115: Alarms And Other Messages
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-2: Symptom-based troubleshooting (continued) Symptom Recommended Action The estimated exhaled tidal volume reading (V ) is inaccurate. Check the patient. Check for large leaks. Make sure ventilator and alarm settings are appropriate. Make sure an approved patient circuit is in use. Adjust the mask to ensure proper fit and adequate leak com- pensation.
-
Page 116
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-3: Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Cannot Reach Target Displays when HFT (high Check the patient. Check Flow flow therapy) is active. In- that the high flow nasal (53) dicates that flow target is… -
Page 117
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-3: Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Low Internal Battery Battery can provide oper- Connect ventilator to AC High ating power for only an ad- power. -
Page 118
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-3: Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Low Rate A low-priority alarm if the Check the patient. Con- Low/ measured respiratory rate firm ventilator and alarm High is less than the Lo Rate… -
Page 119
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-3: Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Patient Circuit Oc- Displays when HFT (high Check the patient. Check High cluded flow therapy) is active. -
Page 120
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-3: Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able PPV Maximum Vol- Estimated delivered pa- Check the patient. Con- Infor- tient tidal volume is great- firm ventilator and alarm mation/ er than the PPV maximum… -
Page 121
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-3: Alarm and other messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Using Default Set- Displayed after power on Check the patient. Check Infor- tings if setting values are cor- and adjust settings as re- mation… -
Page 122
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-4: Check Vent alarm messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Check Vent: Aux Backup alarm problem Check the patient. Provide High Supply Failed alternative ventilation. -
Page 123
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-4: Check Vent alarm messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Check Vent: CPU Technical failure Check the patient. Provide High PCBA ADC Failed alternative ventilation. -
Page 124
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-4: Check Vent alarm messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Check Vent: O Pres- Continues to ventilate Check the patient. Provide High sure Sensor Calibra- with air only alternative ventilation. -
Page 125
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-5: Vent Inoperative alarm messages: summary and troubleshooting Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Vent Inoperative Technical failure. The Check the patient. Provide al- High 1000 ventilator is in the ven- ternative ventilation. -
Page 126
Alarms, messages, and troubleshooting Table 9-5: Vent Inoperative alarm messages: summary and troubleshooting (continued) Priority Manually Autores Silence Message Description Corrective Action type (ID) resettable ettable able Vent Inoperative Technical failure. The Check the patient. Provide al- High 1009 ventilator is in the ven- ternative ventilation. -
Page 127
Disinfection is most effective on medical devices that were previously cleaned. NOTE: For all V60/V60 Plus hardware accessories recommended by Philips, follow the cleaning and disinfection guidelines in this chapter. For multi-patient interface and circuit accessories, consult the product For single patient use accessories, no cleaning instructions for use. -
Page 128: Care And Maintenance
Care and maintenance Exterior and CAUTION: To prevent possible damage to the ventilator, use only those cleaning and disinfecting agents listed in this manual. touchscreen cleaning CAUTION: To prevent possible damage to the ventilator, do not drip or spray any liquids directly onto any surface including the front panel, touchscreen, and navigation ring.
-
Page 129: Exterior And Touchscreen Disinfection
Care and maintenance Exterior and CAUTION: To prevent possible damage to the ventilator, use only those cleaning and disinfecting agents listed in this manual. touchscreen CAUTION: To prevent possible damage to the ventilator, do not drip or spray any disinfection liquids directly onto any surface including the front panel, touchscreen, and navigation ring.
-
Page 130: Bacteria Filter, Patient Circuit, And Other Accessories
Because some environments cause a quicker collection of lint and dust than others, inspect the filters more often when needed. The air inlet filter should be replaced; the cooling fan filter should be cleaned. CAUTION: To ensure proper system performance, use a Respironics-approved air inlet filter. 10-4…
-
Page 131: Preventive Maintenance
Care and maintenance Preventive WARNING: Only authorized service personnel should replace parts within the ventilator or perform other service activities. Unauthorized personnel maintenance without proper training are at risk of electric shock. WARNING: Turn off the ventilator and disconnect it from the AC mains outlet before you perform decontamination or maintenance procedures.
-
Page 132: Replacing The Air Inlet Filter
Care and maintenance Replacing the air inlet filter Replace the air inlet filter as follows, referring to Figure 10-1. 1. Power down the ventilator and disconnect it from AC power. Remove ventilator from cart, if applicable. 2. Turn the captive D-ring fastener counter-clockwise one-quarter turn and release.
-
Page 133: Cleaning Or Replacing The Cooling Fan Filter
Care and maintenance Cleaning or replacing the cooling fan filter Clean or replace the cooling fan filter as follows, referring to Figure 10-2: 1. Insert a small, flat blade driver tip between the foam filter and the filter retaining cover (Figure 10-2). 2.
-
Page 134: Removing And Replacing The Battery
Care and maintenance Removing and replacing the battery See “Installing the battery” on page A-4. Disposal WARNING: This product consists of devices that may contain mercury, which must be recycled or disposed of in accordance with local, state, or federal laws. (Within this system, the backlight lamps in the monitor display contain mercury.) Dispose of all parts removed from the device according to your institution’s…
-
Page 135: Service And Repairs
For technical service or repair information not included in this chapter, contact Philips. A V60/V60 Plus service manual is available (order number 989805612651, part number 1049766), and can also be downloaded from www.philips.com/ hrcmanuals. The service manual includes removal and installation procedures, parts lists, and testing and troubleshooting information.
-
Page 136
Care and maintenance 10-10… -
Page 137: Technical Specifications
4 cmH target) Flow 10 to 80 L/min 5 L/min 35 L/min (High flow therapy, 3.00 software and above, and V60 Plus) IPAP 4 to 40 cmH 1 cmH ± (2 cmH O + 4% of 12 cmH target) I-Time (Inspiratory 0.30 to 3.00 sec…
-
Page 138
Rise (Rise Time) 1 to 5 (AVAPS Target Tidal 200 to 2000 mL BTPS 5 mL ± 15% 500 mL Volume) Table 11-2: Controls active in Respironics V60/V60 Plus ventilation modes CPAP AVAPS Timing Rate Rate I-Time I-Time* Baseline pressure… -
Page 139: Patient Data
Technical specifications Patient data Table 11-3: Patient data ranges, resolutions, and accuracies during ventilation Parameter Range Resolution Accuracy Patient data window Breath phase/trigger indicator Spont, Timed, Exhale Color-coded display: Spont — turquoise, Timed — orange, Ex- hale — blue 0 to 50 cmH 1 cmH ±…
-
Page 140: Alarms
Exhalation Port Selection • DEP (Philips Respironics Disposable Exhalation Port • Whisper Swivel (Philips Respironics Whisper Swivel), • PEV (Philips Respironics Plateau Exhalation Valve), • Other (Other Exhalation Port), • None (No circuit exhalation port) Screen Lock Off, On Auto-Trak+ (optional) Trigger: Normal, +1 to +7.
-
Page 141: Diagnostic Mode Functions
Technical specifications Diagnostic mode Table 11-6: Diagnostic mode functions functions Function Range Language English, Nederlands, Français, Deutsch, Italiano, Por- tuguês, Español, Dansk, Suomi, Norsk, Svenska, Chi- nese, Japanese, Türkçe Date/Time Pressure Units O, hPa Restore Default Settings Software Options Baud Rate 9,600, 19,200, 115,200 Alarm Volume Escalation Enable, Disable (default)
-
Page 142: Physical Characteristics
12 kg (26 lb) with battery V60/V60 Plus ventilator in its most usual configuration Installed weight V60/V60 Plus Ventilator with backup battery, ventila- tor stand, O tank holder, two E-cylinders (full), two (V60/V60 Plus ventilator on gauge clusters, oxygen analyzer with mount, humidifi-…
-
Page 143: Pneumatic Specifications
Pressure: 3.31 to 6.00 bar / 331 to 600 kPa / 48 to 87 psig Flow: 175 SLPM High-pressure oxygen supply Connector: DISS male, DISS female, NIST (using V60/V60 Plus manifold) Pressure: 3.10 to 6.00 bar / 310 to 600 kPa / 45 to 87 psig Flow: 175 SLPM Connector: SIS Pressure: 3.66 to 6.00 bar / 366 to 600 kPa / 53 to…
-
Page 144: Electrical Specifications
Technical specifications Electrical specifications Table 11-10: Electrical specifications Parameter Specification AC voltage 100 to 240 VAC AC frequency 50/60 Hz AC power 300 VA Battery PN 1076374: 14.4 V, 11.0 Ah, 163 Wh Maximum system current draw: 11 A Charge voltage: +16.9 V maximum Operating time: 360 minutes (6 hours) under normal conditions Accessory…
-
Page 145: Alarm-Related Specifications
Technical specifications Alarm-related specifications Table 11-12: Alarm-related specifications Parameter Specification Delay time from the onset of the < 10 ms from onset of the alarm condition to the alarm condition to the point that transmission of the signal the representation of the alarm <…
-
Page 146
Parameter Specification High flow therapy 10 to 80 L/min BTPS (3.00 software and above, and V60 Plus) NOTE: The maximum deliverable flow rate varies based on the orifice size of the nasal cannula and on the patient’s nasal passage resistance. -
Page 147
Appendix A. First-time installation WARNING: Philips-authorized personnel must install the ventilator. For information about installation, contact your Philips representative. Before putting the ventilator into service for the first time, install it as described in this chapter. Unpacking and Unpack the ventilator and inspect it for damage. Inspect the exterior cabinet of the ventilator for cracks, scratches, or blemishes. -
Page 148: First-Time Installation
Ensure that the locking lever on the back right of the stand locks into place. Figure A-1: Mounting the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator on the stand…
-
Page 149
Figure A-2 shows the installed ventilator. Use the brakes to lock and unlock the wheels as needed. Make sure the wheels are unlocked before moving the ventilator. Power cords can be stored on stand hooks Wheel lock Figure A-2: Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator on stand… -
Page 150: Installing The Battery
— Do not short-circuit the battery or allow metallic or conductive objects to contact the battery connector housing. — Use the battery with the Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator only. Install the battery as follows (Figure A-3). 1. Shut down and then unplug the ventilator.
-
Page 151
First-time installation 7. Attach the option label as shown in Figure 3-5 on page 3-8. WARNING: Never attempt to disconnect or connect the battery during operation. CAUTION: Following battery installation, if a Check Vent or Vent Inoperative alarm occurs when verifying ventilator operation, discontinue use of the ventilator immediately and contact Philips. -
Page 152
First-time installation Captive fastener Bracket Battery Orient with vent hole on top and Philips logo facing out Battery cable Figure A-3: Installing the battery… -
Page 153: Installing Oxygen Inlet Connector And Ac Power Cord
First-time installation Installing oxygen The Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator destined for Japan, China, and the U.S. are typically pre-configured. V60/V60 Plus Ventilators shipped to other inlet connector and countries may require installation of the power cord and oxygen inlet AC power cord connector.
-
Page 154
Philips-supplied cord securely in place. WARNING: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator should not be positioned in a way that makes it difficult to disconnect from mains power if necessary. Disconnect from supply mains by removing the power cord from the wall outlet. The AC mains plug is used as disconnection device. -
Page 155: Installing The Oxygen Manifold Kit
First-time installation Installing the oxygen If desired, install the oxygen manifold kit as described in the accompanying instructions. manifold kit Verifying ventilator Perform the following steps to verify ventilator and audible alarm operation: operation and audible 1. Assemble and install a patient circuit. (See Chapter 5 for instructions alarm on installing a patient circuit.) 2.
-
Page 156
First-time installation A-10… -
Page 157: Communications Interface
Appendix B. Communications interface WARNING: Connect to the ventilator only items that are specified as part of or compatible with the ventilator system. Additional equipment connected to medical electrical equipment must comply with the respective IEC or ISO standards. Furthermore, all configurations shall comply with the requirements for medical electrical systems (see IEC 60601-1-1 or clause 16 of edition 3 of IEC 60601-1, respectively).
-
Page 158: Rs-232 Serial Port
• Legacy (VRPT/SNDA): Fixed text-based protocol (not to be used for developing new driver interfaces). For this protocol specification, refer to the V60 Communications interface VRPT / SNDA Developers Guide (1147828MC), available at www.philips.com/IFU. Using Philips Using Philips monitors and the IntelliBridge or VueLink Open Interfaces…
-
Page 159: Data Display
Figure B-3: Connection from ventilator to Philips patient monitor Data display The data from your Respironics V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is displayed in several windows on your Philips monitor. This data may be labeled differently on the monitor than on the ventilator. Refer to Table B-1 to interpret these labels.
-
Page 160
Communications interface Table B-1: Ventilator data displayed on Philips monitor (continued) Monitor label Ventilator label STNDBY Standby Control settings sEppv Max E Not shown C-Flex PAVsup PPV % sCPAP CPAP sEPAP EPAP sfgFl Flow (in HFT) sFIO sInsTi I-Time (Inspiratory Time) sIPAP IPAP sPmax… -
Page 161: Remote Alarm Port
To prevent possible patient injury due to nonannunciating alarms, verify the operation of any remote alarm device before use. WARNING: To ensure the functionality of the remote alarm, connect only Respironics- approved cables to the remote alarm port. CAUTION: The remote alarm port is intended to connect only to an SELV (safety extra-low voltage and ungrounded system with basic insulation to ground), in accordance with IEC 60601-1.
-
Page 162
For ¼” jack. Remote alarm cable kit, Use on Normally Opened nurse call systems (system expects to 1003742 alarm state = closed see closed contacts when ventilator alarms). For ¼” jack. Remote alarm cable kit Philips Respironics (LifeCare) 1003743… -
Page 163
Respironics-approved accessories with the ventilator. For the most current list of approved accessories plus comprehensive ordering information for compatible parts available from Philips, contact your Philips representative or refer to the V60/V60 Plus ordering and accessories guide (downloadable from philips.com/V60). -
Page 164: Parts And Accessories
Respironics AF531 Respironics PerforMax, adult only Total HFT interfaces For use with V60 Plus ventilators and V60 ventilators that have 3.00 software (or higher) and the HFT option installed. Description Respironics AC611 high flow nasal cannula Respironics AC611 high flow nasal cannula, FEP Connect…
-
Page 165: Patient Breathing Circuits
Description Quantity Part number Order number Humidifiers Respiratory humidifier, Fisher & Paykel MR850 Refer to the V60 ordering and Respiratory humidifier, WILAmed AIRcon Gen2, 230V accessories guide (Not available in North America) Chambers Humidifier chamber, adult, Fisher & Paykel MR290…
-
Page 166: Bacteria Filters
Description Quantity Part number Order number Cooling fan filter 1054280 453561507301 Air inlet filter 1054279 453561505991 Other parts Compatible with all V60/V60 Plus Ventilators: Description Part number Order number Test lung, hard-sided (low-compliance) 1021671 989805611871 Backup battery 1076374 989805626941…
-
Page 167: Regulatory Compliance
EMC information provided in this document. declaration WARNING: The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator may cause radio interference or may disrupt the operation of nearby equipment. It may be necessary to take mitigation measures, such as re-orienting or relocating the ventilator or shielding the location.
-
Page 168: Electromagnetic Emissions
Guidance and manufacturer’s declaration — electromagnetic emissions The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The user of the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator should assure that it is used in such an envi- ronment. Emissions test…
-
Page 169: Electromagnetic Immunity
Guidance and manufacturer’s declaration — electromagnetic immunity The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The user of the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator should assure that it is used in such an environment. IEC 60601-1-2…
-
Page 170
Guidance and manufacturer’s declaration — electromagnetic immunity The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or the user of the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator should assure that it is used in such an environment. -
Page 171
Regulatory compliance Recommended separation distances between portable and mobile RF communications equipment and the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator Separation distance according to frequency of transmitter (m) 150 kHz to 80 MHz 150 kHz to 80 MHz 80 MHz to 800 MHz 800 MHz to 2.7 GHz… -
Page 172: Rf Immunity
Regulatory compliance RF immunity Test specifications for RFID immunity The frequencies specified are not yet part of formal regulatory standard IEC 60601-1-2 4.0ED. They are based on 1) a working draft of IEC60601-1-2 4.1ED:2018 Table 11 Medical electrical equipment – Part 1-2: General requirements for basic safety and essen- tial performance –…
-
Page 173: Cables That May Affect Iec 60601-1-2 Compliance
Regulatory compliance So, in addition to selection of RFID systems and medical electrical equipment and systems, EMC management includes maintaining adequate separation distances between them. For medical electrical equipment and systems that meet this standard, the minimum necessary separation distances are shown in Annex J of the AIMS standard 7351731, as well as the guidance required by standards such as IEC 60601-1-2.
-
Page 174: Classification
Regulatory compliance Classification Protection Against Electric Class I Shock Degree of Protection Against Type B Electric Shock Degree of protection against IP21 ingress of particulate matter Protected against solid objects ≥ 12.5 mm in diameter. and water given by the enclo- Protected against vertically falling water drops when en- sure closure is tilted up to 15°…
-
Page 175: Applied Parts
Regulatory compliance Applied parts The V60/V60 Plus Ventilator system includes these applied parts: • Masks • Tracheal and endotracheal tubes • Nebulizer T-adapter • Ventilator Breathing System — Type B (inspiratory or expiratory pathways through which gas flows at respiratory pressures and…
-
Page 176
Regulatory compliance D-10… -
Page 177: Diagnostic Mode
Appendix E. Diagnostic mode In the diagnostic mode you select the language of software display, set the date and time, select pressure units, enable software options, and calibrate the touchscreen. NOTE: The diagnostic mode is primarily for use by authorized service personnel to download software and perform other diagnostic procedures.
-
Page 178
Diagnostic mode 3. Within less than 5 seconds, release and press the Accept button again. The Diagnostics Menu (Figure E-1) is displayed. Figure E-1: Diagnostics Menu 4. Select the desired function. -
Page 179: System Settings
Diagnostic mode System settings From the System Settings screen (Figure E-2) you can perform the functions below. Figure E-2: System Settings screen…
-
Page 180: Language
Diagnostic mode Language The Language function lets you set the language of software display. 1. From the System Settings screen, select Language to display the Set Language screen (Figure E-3). Figure E-3: Set Language screen 1…
-
Page 181
Diagnostic mode 2. The active language is shown in white type. Select the new language. 3. A second Set Language screen is displayed (Figure E-4). Select Ventilator Shutdown to apply the change. The change is effective after you restart the ventilator. Figure E-4: Set Language screen 2… -
Page 182: Date/Time
Diagnostic mode Date/Time The Date/Time function lets you verify date and time settings. 1. From the System Settings screen, select Date/Time to display the Set Date and Time screen (Figure E-5). Figure E-5: Set Date and Time screen 2. Adjust the date and time with the + and — buttons; then Apply.
-
Page 183: Pressure Units
Diagnostic mode Pressure Units The Pressure Units function lets you select the unit of measure for pressure display. 1. From the System Settings screen, select Pressure Units to display the Set Pressure Units screen (Figure E-6). Figure E-6: Set Pressure Units screen 2.
-
Page 184: Restore Default Settings
Diagnostic mode Restore Default Settings The Restore Default Settings function lets you return ventilator settings to factory defaults. The factory defaults are listed in Chapter 11. 1. From the System Settings screen, select Restore Default Settings to display the Restore Default Settings screen (Figure E-7). Figure E-7: Restore Default Settings screen 2.
-
Page 185: Software Options
Diagnostic mode Software Options With the Software Options function, you enable a software option using a unique code specific to the option and the ventilator serial number. Options can also be enabled through the Respi-Link remote service program. NOTE: Before installing an option, verify that the ventilator serial number matches the serial number shown in the Vent Info window (“Vent Info (ventilator information)”…
-
Page 186: Baud Rate
Diagnostic mode Baud Rate The Baud Rate function lets you set the baud rate for serial communications. 1. From the System Settings screen, select Baud Rate to display the Set Baud Rate for Serial Communications screen (Figure E-9). Figure E-9: Set Baud Rate for Serial Communications screen 2.
-
Page 187: Alarm Volume Escalation
Enabled, you will see a selectable Disable button. Press the button to change the setting. 3. The new setting is applied after the V60/V60 Plus Ventilator is shut down and powered on again. 1. Available in Revision 2.30 software and above.
-
Page 188: Service
Diagnostic mode Service NOTE: All ventilator mode and alarm settings, alarm messages and significant events are automatically logged and retained, even when power is lost. The Service screen lets you view the event log. Other service functions are for use by authorized service personnel. Significant Event Log The Significant Event Log contains data about clinically relevant ventilator occurrences, including alarms and setting changes.
-
Page 189
Diagnostic mode 3. The Significant Event Log opens (Figure E-12). Use the buttons on right side to navigate through the log. Figure E-12: Significant Event Log screen E-13… -
Page 190: Touchscreen Calibration
Diagnostic mode Touchscreen Calibrate the touchscreen X and Y coordinates as follows: calibration 1. From the Diagnostics Menu, select Touch Screen Calibration. The Touch Screen Calibration screen is displayed (Figure E-13). NOTE: If the Touch Screen Calibration button does not respond, press the Accept button on the navigation ring to begin.
-
Page 191: Exiting The Diagnostic Mode
Diagnostic mode 3. When prompted, touch the screen to exit calibration. If the calibration is not successful, have the ventilator serviced. Exiting the diagnostic Exit the diagnostic mode by turning off ventilator power with the ON/Shutdown key. mode E-15…
-
Page 192
Diagnostic mode E-16… -
Page 193: Glossary
Auto-Trak+ An optional feature that allows adjustments to trigger and cycle thresholds beyond Auto-Trak Sensitivity settings. Auto-Trak Sensitivity A Respironics innovation in triggering and cycling that utilizes several different methods to provide enhanced sensitivity in the presence of leaks and changing breathing patterns.
-
Page 194
Glossary CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure. A ventilation mode that provides a single, continuous level of positive pressure to the patient and a control setting in that mode. Cycle To end inspiration. dB(A) Decibel, a unit of acoustic power. DISS Diameter index safety standard, a standard for high-pressure gas inlet fittings. -
Page 195
Glossary hPa Hectopascal, a unit of pressure measurement. 1 hPa is equal to 1 mbar, which is approximately equal to 1 cmH ID Inner diameter. IEC International Electrotechnical Commission. I:E ratio Ratio of inspiratory to expiratory time. Inop Inoperative. Inspiration:exhalation ratio See I:E ratio. Inspiratory positive airway pressure See IPAP. -
Page 196
Glossary Max P AVAPS Maximum IPAP Pressure. A control setting in AVAPS. Max P Maximum Pressure. See PPV Maximum Pressure Limit. Max R Maximum resistance (flow assist). A control setting in PPV. Max V Maximum Volume. See PPV Maximum Volume Limit. Min P AVAPS Minimum IPAP Pressure. -
Page 197
Glossary psi Pounds per square inch. psig Pounds per square inch gauge (above atmospheric pressure). Proportional pressure ventilation see PPV. Pt. Leak The leak resulting from leaks around the mask or from unintentional leaks in the circuit. A monitored parameter shown when the intentional leak is known. -
Page 198
Glossary Time Trigger Initiation of inspiration by the ventilator according to the Respiratory Rate setting. Timed indicator Denotes machine-triggered (mandatory) breathing. Inspiratory duty cycle. Inspiratory time divided by total cycle time, averaged over 8 breaths, a monitored parameter. Tot.Leak Estimated total leak, both intentional and unintentional. A monitored parameter shown when the mask leak and type of exhalation port are not known. -
Page 199
Index AVAPS: Target V Not Achieved. Insufficient Max Pressure message 9-7 AC power Average volume-assured pressure support mode. See AVAPS how to connect to 5-2 mode specifications 11-8 AC power cord, how to install A-7–A-8 Accessories part numbers C-1–?? Backup alarm 3-9 Air inlet filter. -
Page 200
Index Check Vent: Internal Temperature High Daq alarm 9-15 how to change date and time E-6 Check Vent: Internal Temperature High Mtr alarm 9-15 how to change language E-4–E-5 Check Vent: Machine Pressure Sensor Auto-Zero Failed how to change pressure unit E-7 alarm 9-15 how to enable or disable Alarm Volume Escalation E-11 Check Vent: Machine Pressure Sensor Calibration Data Error… -
Page 201
Modes, ventilation. See Ventilation modes IntelliBridge Monitored parameters using with Philips monitors B-2–B-5 definitions 8-2 Intended use, Respironics V60 Ventilator 3-1 ranges, resolutions, and accuracies 11-3 Interface. See Patient interface or Communications inter- Mounting the ventilator A-2–A-3 face IPAP (inspiratory positive airway pressure) setting, definition… -
Page 202
3-4 how to select 6-12–6-15 location of Ethernet connector 3-8 how to test 6-16–6-17 Respiratory rate. See Rate part numbers C-2 Respironics V60 Ventilator Power cord front view 3-6 how to install A-8 physical description 3-4–3-8 location 3-8 potential side effects 3-2… -
Page 203
Index Startup alarm 9-17 time specifications 11-10 Vent Inoperative 1007 Machine and Proximal Pressure Sen- ventilator startup 3-13 sors Failed alarm 9-17 Symbols 2-1–2-8 Vent Inoperative 1008 Machine and Proximal Pressure Sen- System Settings functions, in diagnostic mode E-3 sors Failed alarm 9-17 Vent Inoperative 1009 Pressure Regulation High alarm 9-18 Vent Inoperative 100A Data Acquisition PCBA ADC Refer- ence Failed alarm 9-18… -
Page 204: Index
Index Index-6…
-
Page 206
Respironics California, LLC 2271 Cosmos Court Carlsbad, CA 92011 USA Respironics Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG Gewerbestrasse 17 82211 Herrsching Germany Australian sponsor Philips Electronics Australia Ltd 65 Epping Road North Ryde, NSW Australia 2113 You can find the most current electronic copy of this user manual at: www.philips.com/IFU…
перейти к содержанию
Аппарат ИВЛ PHILIPS V60/V60 Plus

Предупреждение о резистивном компоненте цепи
| Внесите эти изменения в руководство пользователя V60/V60 Plus. Замените это предупреждение (в главах «Предупреждения, предостережения и примечания», «Подготовка аппарата ИВЛ к использованию» и «Детали и принадлежности»): | |
| ПРЕДУПРЕЖДЕНИЕ: | Избегайте добавления резистивных компонентов контура на стороне пациента проксимальной линии давления. Такие компоненты могут отключить сигнал тревоги отключения. |
| с этим предупреждением: | |
| ПРЕДУПРЕЖДЕНИЕ: | Избегайте добавления резистивных компонентов схемы где-либо в цепи пациента. Такие компоненты могут отключить сигнал тревоги отключения. |
| Замените это примечание (в главах «Подготовка аппарата ИВЛ к работе» и «Запчасти и принадлежности»): | |
| ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ: | Резистивные компоненты могут включать, помимо прочего, HME, проксимальные датчики потока, фильтр на соединении с пациентом или контур узкого диаметра, прикрепленный к маске. |
| с этим примечанием: | |
| ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ: | Резистивные компоненты могут включать, помимо прочего, HME, неутвержденные увлажнители, датчики проксимального потока, фильтр на соединении с пациентом или контур узкого диаметра, прикрепленный к маске. |
| Замените это примечание (в главах «Предупреждения, предостережения и примечания» и «Детали и принадлежности»): | |
| ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ: | Чтобы обеспечить правильную работу аппарата ИВЛ и точность данных о пациенте, мы рекомендуем использовать с аппаратом ИВЛ только аксессуары, одобренные Philips. |
| с этим примечанием: | |
| ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ: | Чтобы обеспечить правильную работу аппарата ИВЛ и точность данных о пациенте, мы рекомендуем вам использовать только аксессуары, одобренные Philips, которые перечислены в приложении «Детали и аксессуары» к руководству пользователя. |
www.philips.com/healthcare
health@philips.com
 Респироникс Калифорния, ООО
Респироникс Калифорния, ООО
2271 Космический Суд
Карлсбад, Калифорния 92011 США

Австралийский спонсор
Филипс Электроникс Австралия Лтд.
65 Эппинг Роуд
Норт-Райд, Новый Южный Уэльс, Австралия 2113
 © 2022 Koninklijke Philips NV
© 2022 Koninklijke Philips NV
Все права защищены. Воспроизведение или передача полностью или частично, в любой форме и любыми средствами, электронными, механическими или иными, запрещены без предварительного письменного согласия владельца авторских прав.
Напечатано в США
1154563MC Ред. A * 2022-11

Документы / Ресурсы
Рекомендации

Продвижение технологий цифрового здравоохранения | Филипс
Аппарат ИВЛ Philips Respironics V60 — современный представитель широкой линейки аппаратов для проведения искусственной вентиляции легких от Philips.
Описание аппарата ИВЛ Philips Respironics V60
Прибор обладает различными автоматическими алгоритмами для своевременной адаптации рабочего процесса под индивидуальные потребности как пациентов, так и специалистов. К ним относятся Auto Track и более расширенная версия Auto Track Plus. А осуществление непрерывного давления в легочных путях с характерным понижением во время вдоха достигается с помощью инструмента C Flex. Помимо этого доступны 3 различных профиля с учетом коррекции других параметров. Все это необходимо для качественного улучшения самочувствия пациента на протяжении всего процесса терапии.
Основные преимущества аппарата ИВЛ Philips Respironics V60
— яркий цветной экран с наглядной демонстрацией всех необходимых параметров и диагональю в 12,1 дюймов,
— сенсорный тип управления облегчает эксплуатацию и делает ее более комфортной,
— встроенная система тревожных оповещений в случае критических изменений показателей или технических неполадок,
— интуитивно понятный интерфейс со множеством настраиваемых параметров и режимов ИВЛ инвазивным и неинвазивным методом (AVAPS, CPAP, PPV, PCV, S/T и т.д.),
— пневматический тип вентиляционного привода,
— встроенный тип аккумулятора обеспечивает рабочий процесс в автономном режиме в течение 6 часов,
— поддерживаемый дыхательный объем от 200 до 2000 мл,
— оптимизация вентиляции неинвазивным методом с помощью функции Auto Track,
— грамотное распределение времени с помощью заданных настроек,
— поддержка нескольких разновидностей лечения в зависимости от степени тяжести заболевания,
— технология AVAPS для гарантированной сохранности параметров давления,
— высокий уровень мобильности,
— оптимизированный способ интеграции в центральную систему медицинского учреждения,
— поддержка систематического обновления системы с помощью Respi Link,
— стильный эргономичный дизайн и компактные размеры.
Philips Respironics V60 использует многолетний опыт производителей, сочетает в себе альтернативное решение многих поставленных задач.
Авто-адаптируемая технология синхронизации аппарата с дыханием пациента и улучшения результатов лечения. Усовершенствованная технология обработки сигнала позволяет точно подобрать настройки для взрослых и детей.
Улучшенная неинвазивная вентиляция легких с Auto-Trak
Наличие авто-адаптируемой системы компенсации утечек, синхронизации с вдохом и экспираторным циклом позволяет обеспечить оптимальную синхронизацию аппарат-пациент в условиях постоянно изменяющихся утечек. Это значительно облегчает процесс наблюдения и ручную настройку аппарата у постели пациента.
Заданные настройки маски позволяют экономить время
Аппарат Respironics V60 поддерживает успешную неинвазивную вентиляцию легких и повышает скорость лечения благодаря заданным настройкам больничных масок. После выбора параметров маски V60 автоматически калибрует показатели потока воздуха для улучшения мониторирования и терапии.
CPAP с функцией C-Flex для повышения комфорта пациента
CPAP (постоянное положительное давление в дыхательных путях) с функцией C-flex обеспечивает три уровня снижения давления на выдохе. Данная функция позволяет улучшить качество сна и обеспечивает комфорт пациенту, повышая положительной эффект терапии.
Несколько режимов лечения для широкого спектра пациентов
Philips Respironics V60 отвечает потребностям различных групп пациентов, включая детей. Аппарат оснащен различными режимами вентиляции, чтобы удовлетворять любым возникающим требованиям.
Большой цветной сенсорный экран для простоты эксплуатации
Philips Respironics V60 оснащен цветным сенсорным экраном высокого разрешения. Высокий уровень визуализации данных облегчает работу и упрощает интерпретацию графиков.
Вентиляция в режиме PCV улучшает контроль
Вентиляция с контролем по давлению может использоваться в случаях, когда к дыханию пациента требуется повышенное внимание.
AVAPS
Режим вентиляции AVAPS (поддержка давлением с гарантированным объемом) поддерживает заданный дыхательный объем в режиме ограничения по подавлению, что обеспечивает дополнительную уверенность в вентиляции.
Функция режима ожидания облегчает взаимодействие врача и пациента
Уделяйте больше внимания пациенту, не отвлекаясь на ложные сигналы тревоги, благодаря режиму ожидания.
Вентиляции с положительным давлением (PPV) при изменчивом характере дыхания
В режиме PPV давление, расход и дыхательный объем, поддерживаемые аппаратом ИВЛ, определяются усилиями пациента. Аппарат ИВЛ оценивает усилия пациента, позволяя ему самостоятельно начинать и завершать дыхание, а также регистрирует изменения расхода и давления на протяжении дыхательного цикла.
Гибкость при транспортировке
Встроенная батарея на 6 часов работы для транспортировки аппарата внутри больницы.
Auto-Trak Plus для индивидуальной схемы лечения
Алгоритм Auto-Trak Plus доступен в режимах S/T, PC, AVAPS и PPV и предназначен для подгруппы пациентов, которым может потребоваться индивидуальная титрация критериев активации цикла. Алгоритм синхронизации Auto-Trak Plus позволяет задавать более тонкие настройки общего алгоритма для синхронизации дыхания пациента с аппаратом ИВЛ, что необходимо для больных с очень слабыми дыхательными попытками.
Улучшенный обмен данными
Возможности обмена данными обеспечивают совместимость с больничными системами.
Respi-Link для эффективного обновления
Используя возможность удаленного подключения, можно выполнять эффективную диагностику системы и легко устанавливать обновления через Интернет.
Технические характеристики ИВЛ аппарата Филипс Respironics V60
| Общее | |
| Диапазон давления кислорода на входе | 276-600 кПА (40-87 фунтов на кв. дюйм) |
| Соответствие | Дети (≥ 20 кг) и взрослые |
| Масса с дополнительной батареей | 10,9 кг (24 фунта) |
| Масса без дополнительной батареи | 10,0 кг (22 фунта) |
| Размеры | 33,7 см В × 39,4 см Ш × 42,9 см Г (13,3″В × 15,5″ Ш × 16,5″ Г) |
| Настройки | |
| C-Flex | Откл., 1-3 |
| Напряжение переменного тока | 100-240 VAC |
| IPAP | 4-40 cm H2O |
| CPAP | 4-25 cm H2O |
| Частота переменного тока | 50-60 Гц |
| Мощность переменного тока | 300 V·A |
| Макс. P (максимальный предел давления PPV) | 5-40 cm H2O |
| EPAP | 4-25 cm H2O |
| Время работы от батареи | 6 часов в нормальных условиях |
| Максимальное давление (максимальное IPAP при AVAPS) | 6-40 cm H2O |
| Время вдоха | 0,30-3,00 с. |
| Минимальное давление (максимальное IPAP при AVAPS) | 5-30 cm H2O |
| Процент кислорода | 21-100 % |
| Время подготовки к работе | Откл., 5 — 45 мин. |
| Частота дыхания | 4-60 уд/мин. |
| Время повышения | 1-5 |
| Запуск и цикл | Автоматическая адаптация (Auto-Trak) или Auto-Trak Plus (дополнительно). Запуск: норма, +1…+7. Цикл: -2, -1, норма, +1…+6 |
| Целевой дыхательный объем AVAPS | 200-2000 мл BTPS |
| Макс. E | 0-100 см H2O/л |
| Макс. R | 0-50 см H2O/л/с |
| Вентиляция с пропорциональным давлением, % | 0-100 % |
| Макс. V (максимальный предел объема PPV) | 200-3500 мл |
| Данные пациента | |
| Фаза дыхания / индикатор триггера | Спонтанное, по времени, выдох |
| PIP | 0-50 cm H2O |
| Пациент/общая утечка | 0-200 л/мин BTPS |
| Триггер пациента | 0-100 % |
| Частота дыхания | 0-90 уд/мин. |
| Ti/Ttot | 0-91% |
| Минутный объем | 0-99,0 л/мин BTPS |
| Дыхательный объем | 0-3000 мл BTPS |
| Окно графика | |
| График давления | 0-50 cm H2O |
| График потока | 240-2401 /мин btps |
| График объема | 0-3 500 мл btps |
| Настраиваемый диапазон тревоги | |
| Lo Rate (тревога при низкой частоте дыхания) | 1-89 уд/мин |
| Hi Rate (тревога при высокой частоте дыхания) | 5-90 уд/мин |
| Hi Vr (тревога при высоком дыхательном объеме) | 200-3500 мл |
| Lo Vr (тревога при низком дыхательном объеме) | ОТКЛ — 1 500 мл |
| HIP (тревога при высоком давлении на вдохе) | 5-50 cm H2O |
| LIP T (тревога при малом времени задержки давления на вдохе) | 5-60 с. |
| LIP (тревога при низком давлении на вдохе) | ОТКЛ, 1-40 cm H2O |
| Lo VE (тревога при низкой минутной вентиляции) | ОТКЛ, 0,1-991 /мин |
