На связи с 09:00 до 23:00
Веторил: инструкция по применению ветеринарного препарата
Здесь вы можете ознакомиться с подробным описанием препарата Веторил. Инструкция подготовлена ветеринарными специалистами на основе официальной информации от Dechra Pharmaceuticals.
Здесь вы можете ознакомиться с подробным описанием препарата Веторил. Инструкция подготовлена ветеринарными специалистами на основе официальной информации от Dechra Pharmaceuticals.
Капсулы в чёрно-бежевой оболочке, каждая из которых содержит 10, 30, 60 или 120 мг трилостана — лекарственного вещества, подавляющего функцию надпочечников.
Медикаментозная терапия гиперадренокортицизма у собак (синдром Кушинга).
Трилостан представляет собой синтетический аналог стероидного гормона, который избирательно ингибирует 3-бета-гидроксистероиддегидрогеназу — фермента, участвующего в синтезе прогестерона. Поскольку прогестерон служит промежуточным звеном при производстве глюкокортикоидов и минералокортикоидов, подавление его выработки приводит к снижению уровня кортизола. Так достигается лечебный эффект.
По данным инструкции производителя, концентрация активного вещества в крови достигает пика через 1,5 часа после введения, после чего постепенно снижается в течение <12 часов.
Состав и форма выпуска
Фармакологическое действие
Показания

Препарат применяют только по назначению ветеринарного эндокринолога, который подбирает оптимальные дозировки согласно инструкции и контролирует уровень кортизола у пациента.
Стартовая доза Веторила зависит от веса собаки и может составлять от 2,2 до 6,7 мг/кг в сутки (см. таблицу 1). Начинают обычно с минимальных значений, увеличивая их при необходимости.
Через две недели после начала терапии Веторилом необходимо выполнить контрольную пробу с АКТГ или дексаметазоном (через ≈5 часов после приёма препарата). По её результатам принимают решение об уменьшении, сохранении или увеличении текущей дозировки.
При любом изменении режима дозирования следует через 10–14 дней выполнять пробу с АКТГ или дексаметазоном для оценки уровня кортизола, эффективности и безопасности терапии.
| Вес собаки | Суточная доза активного вещества |
|---|---|
| ≤4,5 кг | 10 мг |
| 4,6-10 кг | 30 мг |
| 11-20 кг | 60 мг |
| 21-40 кг | 120 мг |
| 41-60 кг | 180 мг |
| Уровень кортизола,мкг/дл | Уровень кортизола,нмоль/л | Инструкция по коррекции дозировки |
|---|---|---|
| <1,45 | <40 | Начать терапию заново с меньшей дозировкой. |
| 1,45–5,4 | 40–150 | Продолжать лечение с той же дозировкой. |
| 5,4–9,1 | 150–250 | Если состояние больного заметно улучшилось, можно оставить текущую дозировку. |
| >9,1 | >250 | Суточную дозу Веторила следует увеличить. |
Режим дозирования
Таблица 1. Рекомендованные дозировки Веторила для собак с разной массой тела
Таблица 2. Коррекция суточной дозировки в зависимости от показателей кортизола
Способ применения
Противопоказания
Передозировка
Согласно инструкции Vetoryl от производителя, препарат дают собакам 1 раз в сутки — обязательно вместе с кормом. Так он лучше абсорбируется, что обеспечивает более высокую концентрацию трилостана в крови, чем при приёме натощак.
Если в течение дня состояние животного ухудшается, можно перейти на двухкратный режим дозирования: в утренние и вечерние часы. При этом не обязательно, чтобы дозы были равными: например, утром собака может получать 60 мг Веторила, а вечером — в два раза меньше. Кроме того, может потребоваться увеличение суточной дозировки на 30–50% по сравнению с той, что указана в данной инструкции.
При превышении допустимой дозы Веторила, указанной в инструкции, могут наблюдаться признаки дефицита глюкокортикоидов и минералокортикоидов: повышенная жажда, олигурия, рвота, понос, обезвоживание, апатия и вялость. При появлении этих признаков следует обратиться за медицинской помощью. Вышеперечисленные симптомы купируют введением соответствующих гормонов.
- Индивидуальная чувствительность к лекарственному веществу.
- Тяжёлые заболевания печени и/или почек.
- Беременность (опасность развития аномалий, гибели плода).
- Не допускается использование препарата «вне инструкции».
После того как будет подобрана оптимальная схема лечения, собаку наблюдают у специалиста. Первое контрольное обследование проводится через месяц, затем — каждые 3 месяца. Оно включает в себя физикальный осмотр, подробный опрос владельца, пробу с АКТГ или дексаметазоном, анализ крови на электролиты, печёночные и почечные показатели.
Лекарственные взаимодействия
Побочные реакции
Ингибиторы АПФ. Эта группа включает в себя широкий перечень лекарственных средств. Их назначают при гипертензии, ХБП и ХПН у собак. Как и Веторил, они снижают уровень альдостерона, поэтому их совместное применение требует осторожности и контроля баланса электролитов.
Калийсберегающие диуретики. Совместное применение с Веторилом не рекомендуется из-за риска гиперкалиемии.
Митотан — противоопухолевое средство. Митотан подавляет функцию надпочечников, поэтому со дня его отмены до начала лечения Веторилом должно пройти минимум 30 дней. Кроме того, необходимо удостовериться, что уровень кортизола повышен (см. инструкцию выше).
Долгосрочные наблюдения при длительном лечении собак показали, что чаще всего у них наблюдаются слабость и желудочно-кишечные симптомы. Тяжёлые побочные реакции развиваются крайне редко, но, как правило, внезапно, и требуют срочной отмены Веторила и экстренной медицинской помощи.
- Чаще всего у собак отмечаются понос, рвота, ухудшение аппетита, апатия и вялость.
- В редких случаях — кровавый понос, коллапс, гипоадренокортикальный криз, а также некроз и/или разрыв надпочечников, потенциально приводящие к гибели животного.
- Также у ветеринарного пациента может развиться гипоадренокортицизм, причём независимо от дозы активного вещества. Иногда функция надпочечников ухудшается настолько, что её невозможно восстановить и можно только компенсировать медикаментозно.
- Так, в краткосрочном исследовании у двух из 107 собак с синдромом Кушинга во время лечения Веторилом развился гипоадренокортицизм. Третья собака перенесла разрыв надпочечника, у четвёртой сформировался некроз надпочечников, который привёл к внезапной гибели животного.
На второй неделе терапии Веторила у собаки может развиваться специфическое состояние, аналогичное синдрому отмены кортикостероидных гормонов. Оно вызвано снижением в крови уровня глюкокортикоидов и проявляется вялостью, сонливостью, отказом от пищи и потерей веса. Если такое происходит, терапию отменяют и начинают заново, но с меньшей дозировкой Веторила согласно инструкции для собак. Кроме того, важно дифференцировать это состояние от гипоадренокортикального криза. Для этого измеряют уровни кортизола и электролитов.
Остались еще вопросы? Оставьте заявку на консультацию!
Лекарственная форма
| Веторил |
Капсулы для орального применения 10 мг рег. 826-3-3.18-4082№ПВИ-3-3.18/05211 |
Форма выпуска, состав и упаковка
Капсулы для орального применения твердые, с корпусом цвета слоновой кости и колпачком черного цвета; на оболочке капсулы указана дозировка.
Вспомогательные вещества: титана диоксид (Е171), железа оксид желтый (Е172), железа оксид черный (Е172), крахмал кукурузный, лактозы моногидрат, магния стеарат, желатин, шеллак.
Расфасованы по 10 шт. в блистере из алюминиевой фольги, упакованные по 3 блистера в индивидуальные картонные коробки (30 капсул). Каждая единица потребительской упаковки снабжена инструкцией по применению.
Показания к применению препарата ВЕТОРИЛ
Для лечения гипофизарно-зависимого и адреналзависимого гиперадренокортицизма собак
Побочные эффекты
Согласно инструкции
Противопоказания к применению препарата ВЕТОРИЛ
Согласно инструкции
Условия хранения Веторил
При температуре от 0 до 25. в недоступном для детей месте.
Условия отпуска
По рецепту ветеринарного врача
Веторил отзывы
Помогите другим с выбором, оставьте отзыв об Веторил
Оставить отзыв
Package insert / product label
Generic name: trilostane capsules
Dosage form: FOR ANIMAL USE ONLY
CAUTION:
Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Vetoryl Description
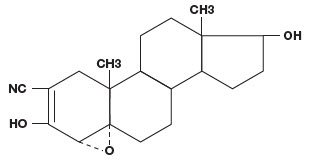
VETORYL Capsules are available in 5 sizes (5, 10, 30, 60 and 120 mg) for oral administration based on body weight. Trilostane (4α,5α-epoxy-17β-hydroxy-3-oxoandrostane-2α-carbonitrile) is an orally active synthetic steroid analogue that selectively inhibits 3 β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the adrenal cortex, thereby inhibiting the conversion of pregnenolone to progesterone. This inhibition blocks production of glucocorticoids and to a lesser extent, mineralocorticoids and sex hormones while steroid precursor levels increase. The structural formula is:
INDICATIONS:
VETORYL Capsules are indicated for the treatment of pituitary-dependent and adrenal-dependent hyperadrenocorticism in dogs.
Vetoryl Dosage and Administration
Always provide the Client Information Sheet with prescription (see INFORMATION FOR DOG OWNERS).
1. Starting dose
The starting dose for the treatment of hyperadrenocorticism in dogs is 1-3 mg/lb (2.2-6.7 mg/kg) once a day. Start with the lowest possible dose based on body weight and available combinations of capsule sizes. VETORYL Capsules should be administered with food.
2. Action at 10-14 day evaluation (Table 1)
After approximately 10-14 days at this dose, re-examine the dog and conduct a 4-6 hour post-dosing ACTH stimulation test and serum biochemical tests (with particular attention to electrolytes, and renal and hepatic function). If physical examination is acceptable, take action according to Table 1.
Owners should be instructed to stop therapy and contact their veterinarian immediately in the event of adverse reactions such as vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, poor/reduced appetite, weakness, collapse or any other unusual developments. If these clinical signs are observed, conduct an ACTH stimulation test and serum biochemical tests (with particular attention to electrolytes, and renal and hepatic function).
| Post-ACTH serum cortisol | Action | |
|---|---|---|
| µg/dL | nmol/L | |
|
||
| < 1.45 | < 40 | Stop treatment. Re-start at a decreased dose |
| 1.45 to 5.4 | 40 to 150 | Continue on same dose |
| > 5.4 to 9.1 | > 150 to 250 | EITHER: Continue on current dose if clinical signs are well controlled OR: Increase dose if clinical signs of hyperadrenocorticism are still evident* |
| > 9.1 | > 250 | Increase initial dose |
3. Individual dose adjustments and close monitoring are essential
Re-examine and conduct an ACTH stimulation test and serum biochemical tests (with particular attention to electrolytes, and renal and hepatic function) 10-14 days after every dose alteration. Care must be taken during dose increases to monitor the dog’s clinical signs.
Once daily administration is recommended. However, if clinical signs are not controlled for the full day, twice daily dosing may be needed. To switch from a once daily dose to a twice daily dose, the total daily dose should be divided into 2 portions given 12 hours apart. It is not necessary for the portions to be equal. If applicable, the larger dose should be administered in the morning and the smaller dose in the evening. For example, a dog receiving 90 mg would receive 60 mg in the morning, and 30 mg in evening.
4. Long term monitoring
Once an optimum dose of VETORYL Capsules has been reached, re-examine the dog at 30 days, 90 days and every 3 months thereafter. At a minimum, this monitoring should include:
- A thorough history and physical examination.
- An ACTH stimulation test (conducted 4-6 hours after VETORYL Capsule administration) — a post-ACTH stimulation test resulting in a cortisol of < 1.45 µg/dL (< 40 nmol/L), with or without electrolyte abnormalities, may precede the development of clinical signs of hypoadrenocorticism.
- Serum biochemical tests (with particular attention to electrolytes, and renal and hepatic function).
Good control is indicated by favorable clinical signs as well as post-ACTH serum cortisol of 1.45-9.1 µg/dL (40-250 nmol/L).
If the ACTH stimulation test is < 1.45 µg/dL (< 40 nmol/L) and/or if electrolyte imbalances characteristic of hypoadrenocorticism (hyperkalemia and hyponatremia) are found, VETORYL Capsules should be temporarily discontinued until recurrence of clinical signs consistent with hyperadrenocorticism and ACTH stimulation test results return to normal (1.45-9.1 µg/dL or 40-250 nmol/L). VETORYL Capsules may then be re-introduced at a lower dose.
Contraindications
The use of VETORYL Capsules is contraindicated in dogs that have demonstrated hypersensitivity to trilostane.
Do not use VETORYL Capsules in animals with primary hepatic disease or renal insufficiency (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS).
Do not use in pregnant dogs. Studies conducted with trilostane in laboratory animals have shown teratogenic effects and early pregnancy loss.
Warnings
Hypoadrenocorticism can develop at any dose of VETORYL Capsules. In some cases, it may take months for adrenal function to return and some dogs never regain adequate adrenal function.
All dogs should undergo a thorough history and physical examination before initiation of therapy with VETORYL Capsules. Other conditions, such as primary hepatic and/or renal disease should be considered when the patient is exhibiting signs of illness in addition to signs of hyperadrenocorticism (e.g. vomiting, diarrhea, poor/reduced appetite, weight loss, and lethargy). Appropriate laboratory tests to establish hematological and serum biochemical baseline data prior to, and periodically during, administration of VETORYL Capsules should be considered.
Owners should be advised to discontinue therapy immediately and contact their veterinarian if signs of potential drug toxicity are observed (see INFORMATION FOR DOG OWNERS, DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, PRECAUTIONS, ADVERSE REACTIONS, ANIMAL SAFETY and POST-APPROVAL EXPERIENCE).
In case of overdosage, symptomatic treatment of hypoadrenocorticism with corticosteroids, mineralocorticoids and intravenous fluids may be required.
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors should be used with caution with VETORYL Capsules, as both drugs have aldosterone-lowering effects which may be additive, impairing the patient’s ability to maintain normal electrolytes, blood volume and renal perfusion. Potassium sparing diuretics (e.g. spironolactone) should not be used with VETORYL Capsules as both drugs have the potential to inhibit aldosterone, increasing the likelihood of hyperkalemia.
HUMAN WARNINGS:
Keep out of reach of children. Not for human use.
Wash hands after use. Do not empty capsule contents and do not attempt to divide the capsules. Do not handle the capsules if pregnant or if trying to conceive. Trilostane is associated with teratogenic effects and early pregnancy loss in laboratory animals. In the event of accidental ingestion/overdose, seek medical advice immediately and take the labeled container with you.
Precautions
Mitotane (o,p’-DDD) treatment will reduce adrenal function. Experience in foreign markets suggests that when mitotane therapy is stopped, an interval of at least one month should elapse before the introduction of VETORYL Capsules. It is important to wait for both the recurrence of clinical signs consistent with hyperadrenocorticism, and a post-ACTH cortisol level of > 9.1 µg/dL (> 250 nmol/L) before treatment with VETORYL Capsules is initiated. Close monitoring of adrenal function is advised, as dogs previously treated with mitotane may be more responsive to the effects of VETORYL Capsules.
The use of VETORYL Capsules will not affect the adrenal tumor itself. Adrenalectomy should be considered as an option for cases that are good surgical candidates. The safe use of this drug has not been evaluated in lactating dogs and males intended for breeding.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions reported are poor/reduced appetite, vomiting, lethargy/dullness, diarrhea, and weakness. Occasionally, more serious reactions, including severe depression, hemorrhagic diarrhea, collapse, hypoadrenocortical crisis or adrenal necrosis/rupture may occur, and may result in death.
In a US field study with 107 dogs, adrenal necrosis/rupture (two dogs) and hypoadrenocorticism (two dogs) were the most severe adverse reactions in the study. One dog died suddenly of adrenal necrosis, approximately one week after starting trilostane therapy. One dog developed an adrenal rupture, believed to be secondary to adrenal necrosis, approximately six weeks after starting trilostane therapy. This dog responded to trilostane discontinuation and supportive care.
Two dogs developed hypoadrenocorticism during the study. These two dogs had clinical signs consistent with hypoadrenocorticism (lethargy, anorexia, collapse) and post-ACTH cortisol levels ≤ 0.3 μg/dL. Both dogs responded to trilostane discontinuation and supportive care, and one dog required continued treatment for hypoadrenocorticism (glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids) after the acute presentation.
Additional adverse reactions were observed in 93 dogs. The most common of these included diarrhea (31 dogs), lethargy (30 dogs), inappetence/anorexia (27 dogs), vomiting (28 dogs), musculoskeletal signs (lameness, worsening of degenerative joint disease) (25 dogs), urinary tract infection (UTI)/hematuria (17 dogs), shaking/shivering (10 dogs), otitis externa (8 dogs), respiratory signs (coughing, congestion) (7 dogs), and skin/coat abnormality (seborrhea, pruritus) (8 dogs).
Five dogs died or were euthanized during the study (one dog secondary to adrenal necrosis, discussed above, two dogs due to progression of pre-existing congestive heart failure, one dog due to progressive central nervous system signs, and one dog due to cognitive decline leading to inappropriate elimination). In addition to the two dogs with adrenal necrosis/rupture and the two dogs with hypoadrenocorticism, an additional four dogs were removed from the study as a result of possible trilostane-related adverse reactions, including collapse, lethargy, inappetence, and trembling.
Complete blood counts conducted pre- and post-treatment revealed a statistically significant (p <0.005) reduction in red cell variables (HCT, HGB, and RBC), but the mean values remained within the normal range. Additionally, approximately 10% of the dogs had elevated BUN values (≥ 40 mg/dL) in the absence of concurrent creatinine elevations. In general, these dogs were clinically normal at the time of the elevated BUN.
In a long term follow-up study of dogs in the US effectiveness study, the adverse reactions were similar to the short term study. Vomiting, diarrhea and general gastrointestinal signs were most commonly observed. Lethargy, inappetence/anorexia, heart murmur or cardiopulmonary signs, inappropriate urination/incontinence, urinary tract infections or genitourinary disease, and neurological signs were reported. Included in the US follow-up study were 14 deaths, three of which were possibly related to trilostane. Eleven dogs died or were euthanized during the study for a variety of conditions considered to be unrelated to or to have an unknown relationship with administration of trilostane.
In two UK field studies with 75 dogs, the most common adverse reactions seen were vomiting, lethargy, diarrhea/loose stools, and anorexia. Other adverse reactions included: nocturia, corneal ulcer, cough, persistent estrus, vaginal discharge and vulvar swelling in a spayed female, hypoadrenocorticism, electrolyte imbalance (elevated potassium with or without decreased sodium), collapse and seizure, shaking, muscle tremors, constipation, scratching, weight gain, and weight loss. One dog died of congestive heart failure and another died of pulmonary thromboembolism. Three dogs were euthanized during the study. Two dogs had renal failure and another had worsening arthritis and deterioration of appetite.
In a long term follow-up of dogs included in the UK field studies, the following adverse reactions were seen: hypoadrenocortical episode (including syncope, tremor, weakness, and vomiting), hypoadrenocortical crisis or renal failure (including azotemia, vomiting, dehydration, and collapse), chronic intermittent vaginal discharge, hemorrhagic diarrhea, occasional vomiting, and distal limb edema. Signs of hypoadrenocorticism were usually reversible after withdrawal of the drug, but may be permanent. One dog discontinued VETORYL Capsules and continued to have hypoadrenocorticism when evaluated a year later. Included in the follow-up were reports of deaths, at least 5 of which were possibly related to use of VETORYL Capsules. These included dogs that died or were euthanized because of renal failure, hypoadrenocortical crisis, hemorrhagic diarrhea, and hemorrhagic gastroenteritis.
Foreign Market Experience: The following events were reported voluntarily during post-approval use of VETORYL Capsules in foreign markets. The most serious adverse events were death, adrenal necrosis, hypoadrenocorticism (electrolyte alterations, weakness, collapse, anorexia, lethargy, vomiting, diarrhea, and azotemia), and corticosteroid withdrawal syndrome (weakness, lethargy, anorexia, and weight loss). Additional adverse events included: renal failure, diabetes mellitus, pancreatitis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, skin reactions (rash, erythematous skin eruptions), hind limb paresis, seizures, neurological signs from growth of macroadenomas, oral ulceration, and muscle tremors.
POST-APPROVAL EXPERIENCE:
As of June 2013, the following adverse events are based on post-approval adverse drug experience reporting. Not all adverse reactions are reported to FDA CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using this data. The following adverse events are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency: anorexia, lethargy/depression, vomiting, diarrhea, elevated liver enzymes, elevated potassium with or without decreased sodium, elevated BUN, decreased Na/K ratio, hypoadrenocorticism, weakness, elevated creatinine, shaking, renal insufficiency. In some cases, death has been reported as an outcome of the adverse events listed above.
For a cumulative listing of adverse reactions for trilostane reported to the CVM see:
http://www.fda.gov/ADEreports
This listing includes Adverse Events reported to CVM for products, such as VETORYL Capsules, that contain the active ingredient trilostane. Listings by active ingredient may represent more than one brand name.
To report suspected adverse events and/or obtain a copy of the SDS or for technical assistance, call Dechra Veterinary Products at (866) 933-2472.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or online at:
http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae
INFORMATION FOR DOG OWNERS:
Owners should be aware that the most common adverse reactions may include: an unexpected decrease in appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, or lethargy and should receive the Client Information Sheet with the prescription. Owners should be informed that control of hyperadrenocorticism should result in resolution of polyphagia, polyuria and polydipsia. Serious adverse reactions associated with this drug can occur without warning and in some cases result in death (see ADVERSE REACTIONS and POST-APPROVAL EXPERIENCE).
Owners should be advised to discontinue VETORYL Capsules and contact their veterinarian immediately if signs of intolerance such as vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, poor/reduced appetite, weakness, or collapse are observed. Owners should be advised of the importance of periodic follow-up for all dogs during administration of VETORYL Capsules.
Vetoryl — Clinical Pharmacology
Trilostane absorption is enhanced by administration with food. In healthy dogs, maximal plasma levels of trilostane occur within 1.5 hours, returning to baseline levels within twelve hours, although large inter-dog variation occurs. There is no accumulation of trilostane or its metabolites over time.
EFFECTIVENESS:
Eighty-three dogs with hyperadrenocorticism were enrolled in a multi-center US field study. Additionally, 30 dogs with hyperadrenocorticism were enrolled in two UK field studies. Results from these studies demonstrated that treatment with VETORYL Capsules resulted in an improvement in clinical signs (decreased thirst, decreased frequency of urination, decreased panting, and improvement of appetite and activity). Improvement in post-ACTH cortisol levels occurred in most cases within 14 days of starting VETORYL Capsules therapy.
In these three studies, there were a total of 10 dogs diagnosed with hyperadrenocorticism due to an adrenal tumor or due to concurrent pituitary and adrenal tumors. Evaluation of these cases failed to demonstrate a difference in clinical, endocrine, or biochemical response when compared to cases of pituitary-dependent hyperadrenocorticism.
ANIMAL SAFETY:
In a laboratory study, VETORYL Capsules were administered to 8 healthy 6 month old Beagles per group at 0× (empty capsules), 1×, 3×, and 5× the maximum starting dose of 6.7 mg/kg twice daily for 90 days. Three animals in the 3× group (receiving 20.1 mg/kg twice daily) and five animals in the 5× group (receiving 33.5 mg/kg twice daily) died between Days 23 and 46. They showed one or more of the following clinical signs: decreased appetite, decreased activity, weight loss, dehydration, soft stool, slight muscle tremors, diarrhea, lateral recumbency, and staggering gait. Bloodwork showed hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and azotemia, consistent with hypoadrenocortical crisis. Post-mortem findings included epithelial necrosis or cystic dilation of duodenal mucosal crypts, gastric mucosal or thymic hemorrhage, atrial thrombosis, pyelitis and cystitis, and inflammation of the lungs.
ACTH stimulated cortisol release was reduced in all dogs treated with VETORYL Capsules. The dogs in the 3× and 5× groups had decreased activity. The 5× dogs had less weight gain than the other groups. The 3× and 5× dogs had lower sodium, albumin, total protein, and cholesterol compared to the control dogs. The 5× dogs had lower mean corpuscular volume than the controls. There was a dose dependent increase in amylase. Post-mortem findings included dose dependent adrenal cortical hypertrophy.
Storage and Handling
Store at controlled room temperature 25°C (77°F) with excursions between 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) permitted.
How is Vetoryl supplied
VETORYL Capsules are available in 5, 10, 30, 60 and 120 mg strengths, packaged in aluminum foil blister cards of 10 capsules, with 3 cards per carton.
| VETORYL Capsules 5 mg | NDC 17033-105-30 |
| VETORYL Capsules 10 mg | NDC 17033-110-30 |
| VETORYL Capsules 30 mg | NDC 17033-130-30 |
| VETORYL Capsules 60 mg | NDC 17033-160-30 |
| VETORYL Capsules 120 mg | NDC 17033-112-30 |
| TAKE TIME |  |
OBSERVE LABEL DIRECTIONS |
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-291
Manufactured for:
Dechra Veterinary Products
7015 College Boulevard, Suite 525
Overland Park, KS 66211 USA
Method of use covered by US Patent No. 9,283,235.
VETORYL is a trademark of Dechra Limited
© 2022, Dechra Limited
F2010 Rev. February 2022
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL — 5 mg Capsule Blister Pack Package
5
mg
VETORYL® CAPSULES
(trilostane)
Adrenocortical suppressant
For oral use in dogs only
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use by or on the
order of a licensed veterinarian.
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-291
30 Capsules
Dechra

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL — 30 mg Capsule Blister Pack Package
30
mg
VETORYL® CAPSULES
(trilostane)
Adrenocortical suppressant
For oral use in dogs only
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use by or on the
order of a licensed veterinarian.
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-291
30 Capsules
Dechra

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL — 60 mg Capsule Blister Pack Package
60
mg
VETORYL® CAPSULES
(trilostane)
Adrenocortical suppressant
For oral use in dogs only
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use by or on the
order of a licensed veterinarian.
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-291
30 Capsules
Dechra

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL — 10 mg Capsule Blister Pack Package
10
mg
VETORYL® CAPSULES
(trilostane)
Adrenocortical suppressant
For oral use in dogs only
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use by or on the
order of a licensed veterinarian.
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-291
30 Capsules
Dechra
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL — 120 mg Capsule Blister Pack Package
120
mg
VETORYL® CAPSULES
(trilostane)
Adrenocortical suppressant
For oral use in dogs only
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use by or on the
order of a licensed veterinarian.
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-291
30 Capsules
Dechra

Веторил применяется для терапии пожилых собак, заболевших синдромом Кушинга (болезнь подтверждают спецтестом на адренокортикотропный гормон (АКТГ)). Лекарственное средство позволяет продлить физическую активность, а также значительно улучшить качество жизни вашего любимца. Несмотря на то, что синдром Кушинга не излечим, применение Веторила (10 мг, 30 мг, 60 мг) способно вернуть вашему питомцу радость жизни.
Гиперадренокортицизм (ГАК), или синдром Иценко-Кушинга является одной из самых распространенных гормональных патологий. Встречаются как спонтанная, так и ятрогенная формы заболевания. Синдром вызывается избытком глюкокортикостероидов (в первую очередь, кортизола) у питомца. В норме он используется организмом для адекватного ответа на стресс, помогает регулированию уровня сахара в крови и модифицирует иммунный ответ на воспалительные процессы.
Избыток кортизола в организме собаки приводит к развитию вышеназванного синдрома, который приводит к облысению, а также ухудшению качества его жизни.
Веторил позволяет:
- блокировать излишнюю выработку кортикостероидов;
- уменьшить полиурию и сократить количество кровоподтеков;
- продлить срок активной жизни собаки.
Веторил: инструкция по применению
Капсулы препарата Веторил выдаются собаке перорально вместе с порцией пищи 1 раз в 24 часа. По итогам клинических исследований препарата эффективная доза Веторил составляет 6 мг на 1 кг веса вашего питомца. Дозировка подбирается специалистом индивидуально, она зависит от реакции организма собаки на процесс лечения (отслеживается путем мониторинга состояния животного). Рекомендованные стартовые варианты дозировок препарата:
| Масса тела (кг) | Начальная доза (мг) | Дозировки (мг/кг) |
| ≧ 3 и < 10 | 30 | 3-10 |
| ≧ 10 и < 20 | 60 | 3-6 |
| ≧ 20 и < 40 | 120 | 3-6 |
| ≧ 40 | 120-240 | 3-6 |
Согласно проведенным исследованиям, стандартная дозировка для подавляющего большинства собак составляет от 2 до 10 мг на 1 кг в день. Если симптоматика заболевания не идет на спад в течение 24-часовых интервалов между приемами лекарства, нужно применить вариант с увеличением суточной дозировки препарата Веторил, либо разделить на два суточных приема. Предостережение: капсулы с активным веществом Веторил нельзя вскрывать или делить на части.
В некоторых случаях могут применяться дозы большие, чем условная норма в 10 мг на 1 кг массы в день. В таком случае следует вести дополнительный мониторинг состояния животного относительно уровня кортизола и иных кортикостероидов в организме. Маленьким породам возможно назначение меньших доз. Выбор вариантов ограничен дозировкой Веторила в капсулах, также доза препарата за один прием не может быть ниже 10 мг.
Веторил: внешний вид и фасовка
На оболочке капсул Веторил присутствует печать с надписью VETORYL и информация о дозировке действующего вещества в вариантах 10 мг, 30 мг, 60 мг и 120 мг. Препарат необходимо хранить при соблюдении температурного режима в пределах от +15 до +30 градусов. Срок годности составляет 3 года.
У нас Вы можете приобрести Веторил с инструкцией для поддерживающей терапии своего питомца. Все товары в каталоге расположены удобным для Вас образом, поэтому вы найдете все интересующие вас ветеринарные препарата.
